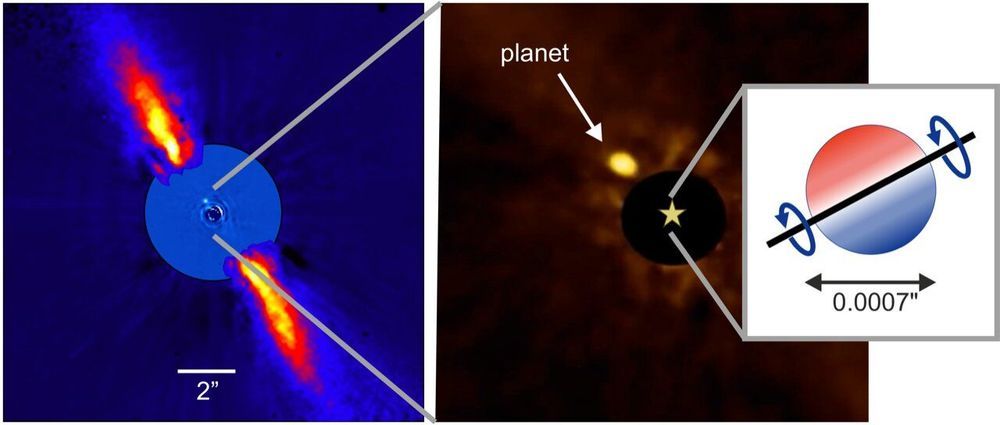
Astronomers have made the first measurement of spin-orbit alignment for a distant ‘super-Jupiter’ planet, demonstrating a technique that could enable breakthroughs in the quest to understand how exoplanetary systems form and evolved.
An international team of scientists, led by Professor Stefan Kraus from the University of Exeter, has carried out the measurements for the exoplanet Beta Pictoris b—located 63 light years from Earth.
The planet, found in the Pictor constellation, has a mass of around 11 times that of Jupiter and orbits a young star on a similar orbit as Saturn in our solar system.