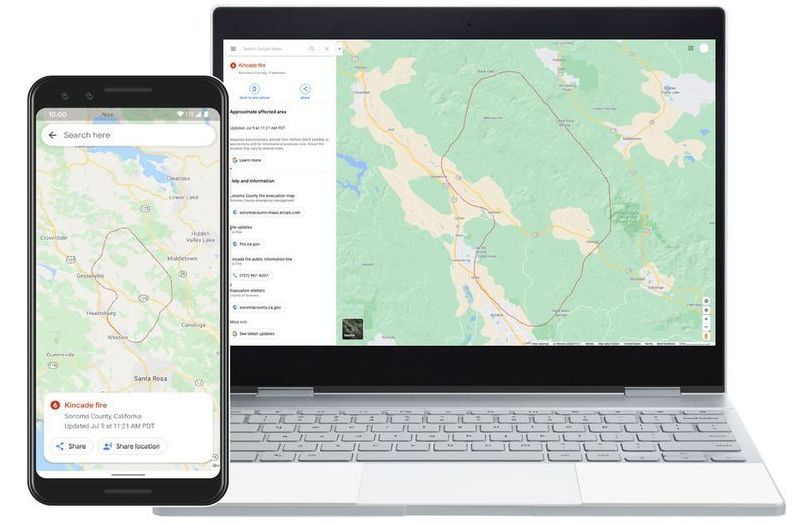
A new feature on Google search and Maps will give users near-real-time information on wildfires in the US. Data from NOAA satellites allows Google to update wildfire boundaries on its maps hourly.

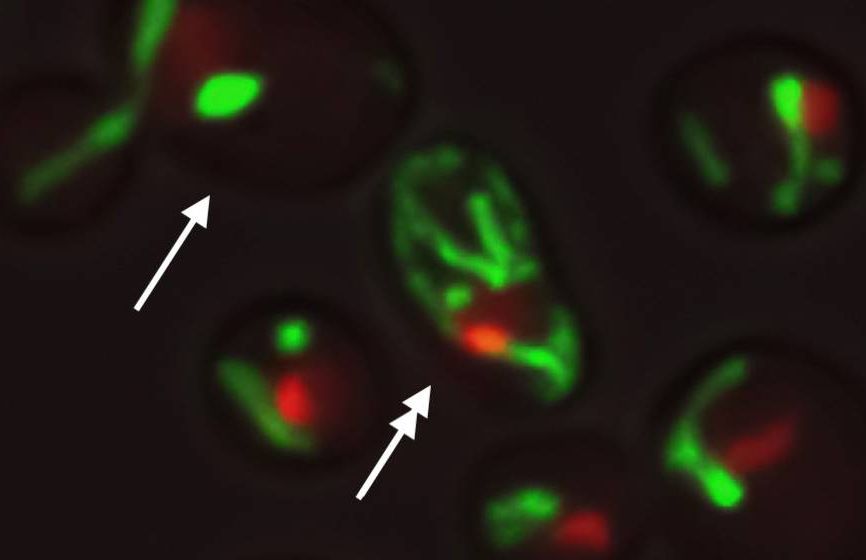
“Using microfluidics, computer modeling and other techniques, they found that about half of the cells age through a gradual decline in the stability of the nucleolus, a region of nuclear DNA where key components of protein-producing “factories” are synthesized,” a press release announcing the research explains. “In contrast, the other half age due to dysfunction of their mitochondria, the energy production units of cells.”
Researchers studying aging have discovered that cells tend to follow one of two aging pathways. The way each individual cell ages is determined early on, and scientists can predict how a cell will age based on early observations.
« The U.S. Air Force is at least researching what it might take to develop a nuclear-armed hypersonic boost-glide vehicle with a range equivalent to a traditional intercontinental ballistic missile, or ICBM. This vehicle could potentially go on top of the service’s future Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent ICBMs, which are now in development. Publicly, the hypersonic weapons programs now in progress across the U.S. military are all conventionally-armed.
Aviation Week was first to report on this potential nuclear hypersonic weapon effort on Aug. 18, 2020, based on information the Air Force Nuclear Weapons Center had included in a request for information posted online six days earlier. That document, which was marked “For Official Use Only” and has since been taken offline, outlined seven potential upgrade tracks for an ICBM with a “modular open architecture.” «
At present, all other hypersonic weapons of this type that the US military is developing are conventionally armed.

Soaring temperatures, intensified flood risks and heightened water stress will threaten 57 U.S. nuclear plants over the next 20 years, forcing operators to take additional resiliency measures, according to a new report.
“The consequences of climate change can affect every aspect of nuclear plant operations—from fuel handling and power and steam generation to maintenance, safety systems and waste processing,” said the analysis, which was published yesterday by Moody’s Investors Service.
If you eschew hyperbole and hang in for the long haul, maintaining a discipline of understatement in the midst of a flashy neon world, you may be offered a modicum of credence when you make an extraordinary announcement. No one is entitled to this courtesy twice. If the news that you trumpet to the moon does not pan out, your readers will be justified in discounting everything you say thereafter.
Here goes.
I believe major rejuvenation has been achieved in a mammal, using a relatively benign intervention that shows promise of scaling up to humans. I’m going to stake my reputation on it.
Comments shown at the moment when they appeared in the video.
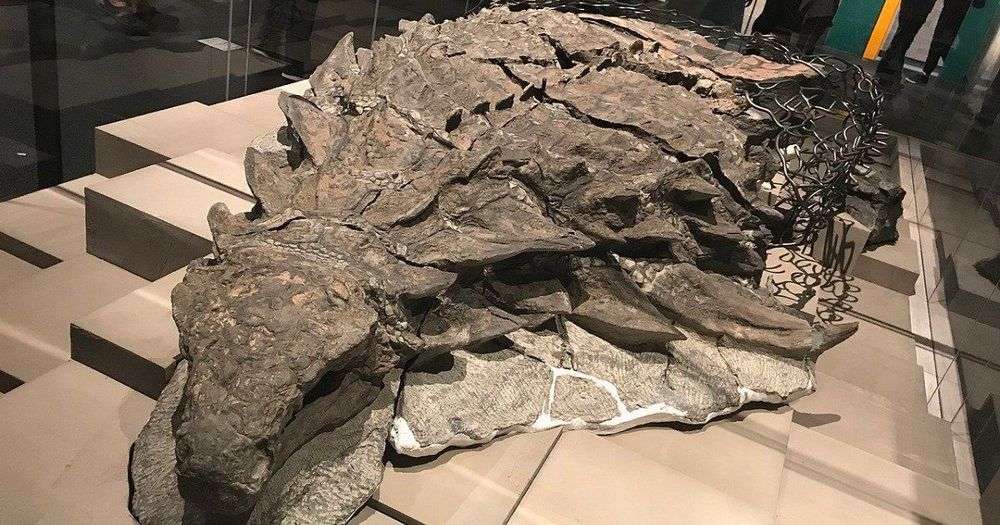

The specimen is so well preserved, entombed as it was in pure mud, that it is the best, most complete dinosaur fossil ever found — anywhere. We can even see what its last meal was!
Canada’s western provinces are famous for many things: dinosaur fossils, the Rocky Mountains, helicopter skiing in Banff, and one of the world’s best and most famous dinosaur museums, the Royal Tyrell Museum of Paleontology in Drumheller, Alberta. One of the museum’s finest fossils belongs to a plant eating dinosaur called a “nodosaur,” a creature archaeologists say was almost 20 feet long and weighed in at close to 3,000 pounds when it lived 110 million years ago during the Early Cretaceous period.
A particularly unusual feature of this dinosaur was the way in which it expired; after eating a full dinner, it simply passed away while lying in a river bed, ultimately making its way out to sea. Perhaps a rain storm washed it away, or perhaps some other climactic event; no matter how it ended up there, the consequence was that the fossil survived in almost perfect form. It was discovered in 2011 by an oil sands worker in northern Alberta.
The dinosaur has given experts many fresh insights not only into this particular species, but the time period in which it lived. Experts at the museum say the specimen is so well preserved, entombed as it was in pure mud, that it is the best, most complete dinosaur fossil ever found — anywhere.

Even before the COVID crisis added its impetus, technological trends were accelerating the creation of robots that could fan out into our lives. Mechanical parts got lighter, cheaper, and sturdier. Electronics packed more computing power into smaller packages. Breakthroughs let engineers put powerful data-crunching tools into robot bodies. Better digital communications let them keep some robot “brains” in a computer elsewhere—or connect a simple robot to hundreds of others, letting them share a collective intelligence, like a beehive’s.
Machines now perform all sorts of tasks: They clean big stores, patrol borders, and help autistic children. But will they make life better for humans?

The plan in the next big war will probably be to let waves of AI fighters wipe out all the enemies targets, Anti aircraft systems, enemy fighters, enemy air fields etc…, however many waves that takes. And, then human pilots come in behind that.
An artificial intelligence algorithm defeated a human F-16 fighter pilot in a virtual dogfight sponsored by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency Thursday.
The MIT-Harvard Medical School Healthcare Innovation Bootcamp brings the rigorous, collaborative, action-learning experience of our in-person Healthcare Innovation Bootcamps online. Over 10 weeks, you’ll have the opportunity to work with a global team of innovators selected by MIT Bootcamps to build the foundations of a new healthcare venture. You will learn principles… See More.
The MIT — Harvard Medical School Healthcare Innovation Bootcamp will be different than most online courses you can take. A combination of live teaching sessions and workshops (which are recorded for your flexibility), office hours, building the foundations of a venture with your global team, and receiving regular team-based coaching, the Bootcamp is a hands-on, immersive, and rigorous learning experience. In 10 weeks, you’ll learn to identify an innovation opportunity, develop a superior solution, and select a business model for the venture you build with your global team. Expect to spend 10–15 hours per week on live sessions, individual, and team work.