Success against sickle-cell would be “the first genetic cure of a common genetic disease” and could free tens of thousands of Americans from agonizing pain.
An artificial intelligence solution (AI) can accurately identify precancerous changes that could require medical attention in images from a woman’s cervix. Researchers from the National Institutes of Health and Global Good developed the computer algorithm, which is called automated visual evaluation.
Researchers created the algorithm by using more than 60,000 cervical images from a National Cancer Institute (NCI) archive of photos collected during a cervical cancer screening study that was carried out in Costa Rica in the 1990s.
More than 9,400 women participated in that population study, with follow up that lasted up to 18 years. Because of the prospective nature of the study, the researchers said that they gained nearly complete information on which cervical changes became pre-cancers and which did not.
No matter how abundant or renewable, solar power has a thorn in its side. There is still no cheap and efficient long-term storage for the energy that it generates.
The solar industry has been snagged on this branch for a while, but in the past year alone, a series of four papers has ushered in an intriguing new solution.
Scientists in Sweden have developed a specialised fluid, called a solar thermal fuel, that can store energy from the sun for well over a decade.
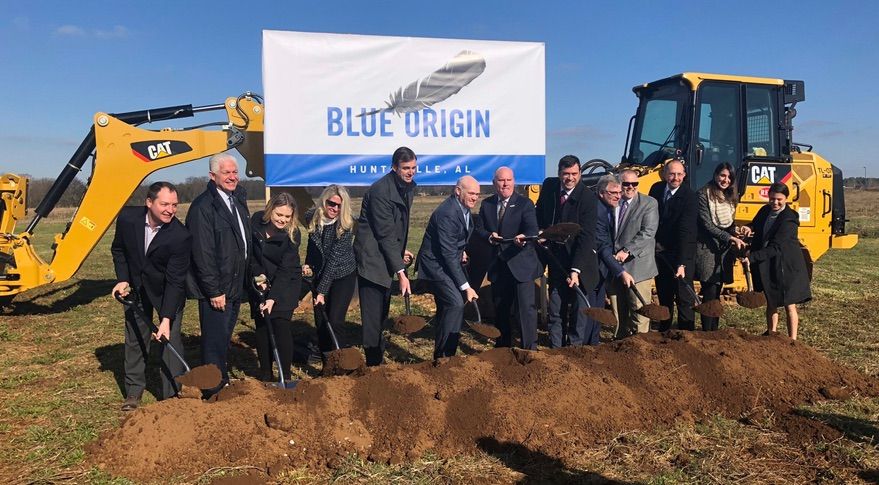
WASHINGTON — As Blue Origin breaks ground on a new factory for producing rocket engines, the company says development of its BE-4 engine will be completed later this year.
Blue Origin held a groundbreaking ceremony in Huntsville, Alabama, Jan. 25 to formally mark the start of construction of a factory that will be used for building BE-4 engines. The company announced plans to build the factory there in June 2017, contingent on the selection of the engine by United Launch Alliance for its Vulcan rocket. ULA picked the BE-4 in September 2018.
The factory, scheduled for completion in March 2020, will build dozens of BE-4 engines a year for both Vulcan as well as Blue Origin’s own New Glenn vehicle. Both rockets are scheduled to make first launches in 2021. Vulcan will use two BE-4 engines in its first stage while New Glenn’s reusable first stage will be powered by seven BE-4 engines.
The Big Bang didn’t just result in our familiar universe, according to a mind-bending new theory — it also generated a second “anti-universe” that extended backwards in time, like a mirror image of our own.
A new story in Physics World explores the new theory, which was proposed by a trio of Canadian physicists who say that it could explain the existence of dark matter.
The new theory, which is laid out in a recent paper in the journal Physical Review of Letters, aims to preserve a rule of physics called CPT symmetry. In the anti-universe before the Big Bang, it suggests, time ran backwards and the cosmos were made of antimatter instead of matter.
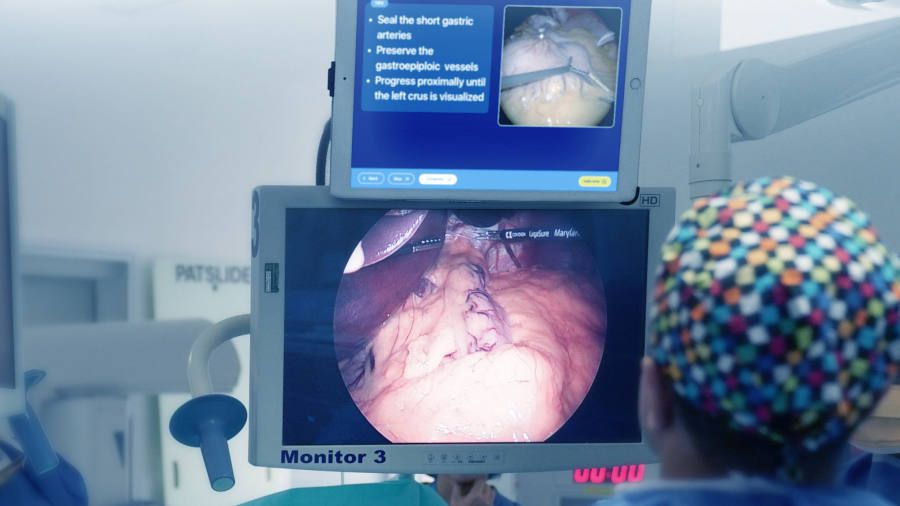
Prof Pugh is using motion-tracking sensors to test how trainee surgeons use the instruments, for example in a simulated hernia repair. Their performance is measured, videoed and compared with best practice at each stage, so they can understand where they need to improve.
“Like Olympic athletes, they can practise repeatedly until they understand the routine and where they need to improve. That is the goal in training surgeons.” The next step is to use sensors in real operations.
Being able to measure pressure will help create better surgical robots, says Richard Trimlett, a cardiothoracic surgeon and head of mechanical support at the Royal Brompton and Harefield Trust, London.
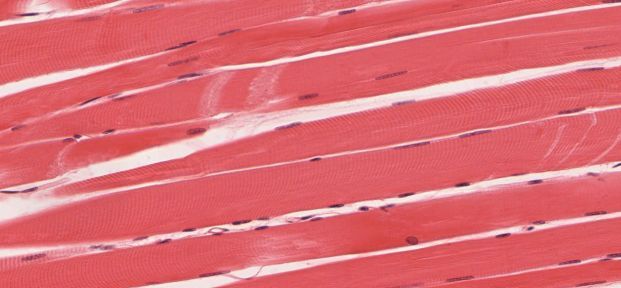
The old adage “use it or lose it” tells us: if you stop using your muscles, they’ll shrink. Until recently, scientists thought this meant that nuclei—the cell control centers that build and maintain muscle fibers—are also lost to sloth.
But according to a review published in Frontiers in Physiology, modern lab techniques now allow us to see that nuclei gained during training persist even when muscle cells shrink due to disuse or start to break down. These residual ‘myonuclei’ allow more and faster growth when muscles are retrained—suggesting that we can “bank” muscle growth potential in our teens to prevent frailty in old age. It also suggests that athletes who cheat and grow their muscles with steroids may go undetected.