A saying from one of my favorite movies is, “Tie two birds together and even though they have four wings they cannot fly.” Can’t say the same about flying drones.
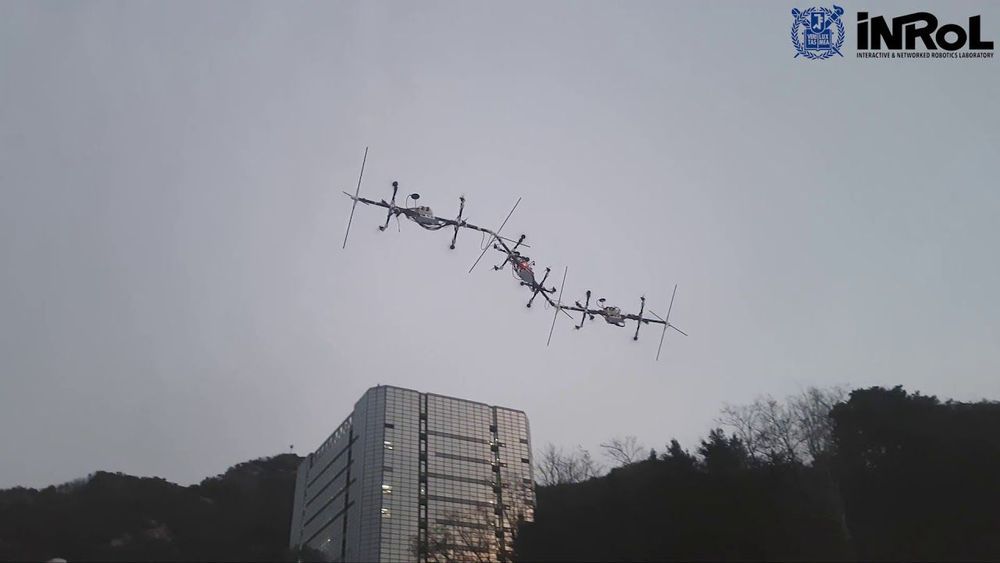
“We perform outdoor autonomous flying experiment of f-LASDRA, constructed with multiple ODAR-8 links connected via cable with each other. Each ODAR-8 can compensate for its own weight, rendering f-LASDRA scalable. Utilizing SCKF with IMU/GNSS-module on each link and inter-link kinematic-constraints, we attain estimation accuracy suitable for stable control (5cm: cf. 1-5m w/ GNSS).”
We perform outdoor autonomous flying experiment of f-LASDRA (flying Large-size Aerial Skeleton with Distributed Rotor Actuation), which is constructed with multiple ODAR-8 links (https://youtu.be/S3i9NspWtr0), connected via flexible cable with each other. Each ODAR-8 link can generate omni-directional force/torque and also compensate for its own weight, thereby, rendering the f-LASDRA scalable w.r.the number of links.