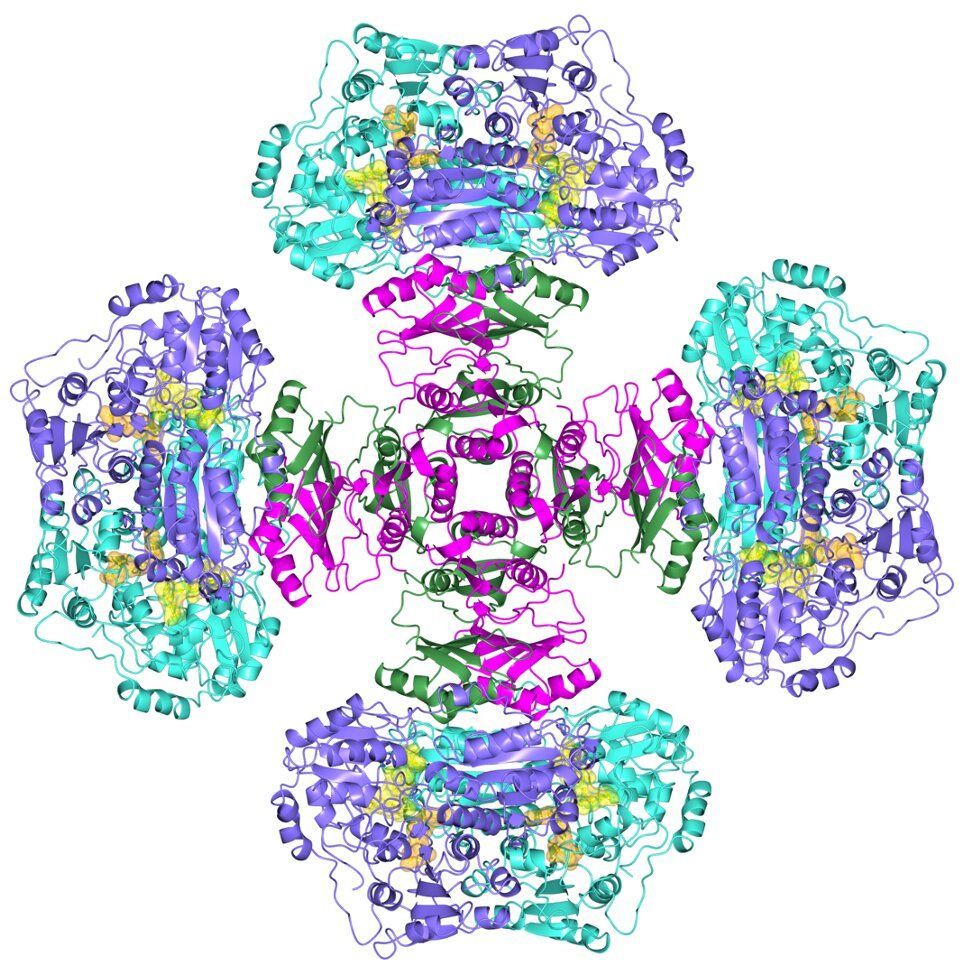
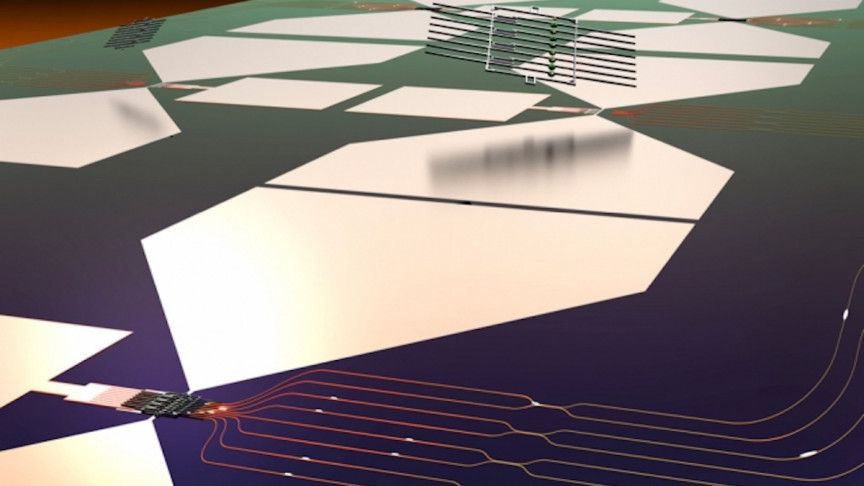
In a new study, a group of researchers led by Prof. Lior Klein, from the physics department and the Institute of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials at Bar-Ilan University, has shown that relatively simple structures can support an exponential number of magnetic states—much greater than previously thought. They have additionally demonstrated switching between the states by generating spin currents. Their results may pave the way to multi-level magnetic memory with an extremely large number of states per cell; it could also have application in the development of neuromorphic computing, and more. Their research appears as a featured article on the cover of a June issue of Applied Physics Letters.
Spintronics is a thriving branch of nano-electronics which uses the spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment in addition to the electron charge used in traditional electronics. The main practical contributions of spintronics are in magnetic sensing and non-volatile magnetic data storage, and researchers are pursuing breakthroughs in developing magnetic-based processing and novel types of magnetic memory.
Spintronics devices commonly consist of magnetic elements manipulated by spin-polarized currents between stable magnetic states. When spintronic devices are used for storing data, the number of stable states sets an upper limit on memory capacity. While current commercial magnetic memory cells have two stable magnetic states corresponding to two memory states, there are clear advantages to increasing this number, as it will potentially allow increasing memory density and enable the design of novel types of memory.