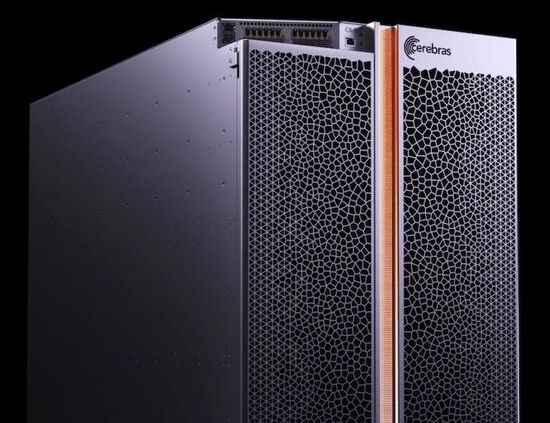
To the Moon and back, twice.
It is mainly about greater reliability.

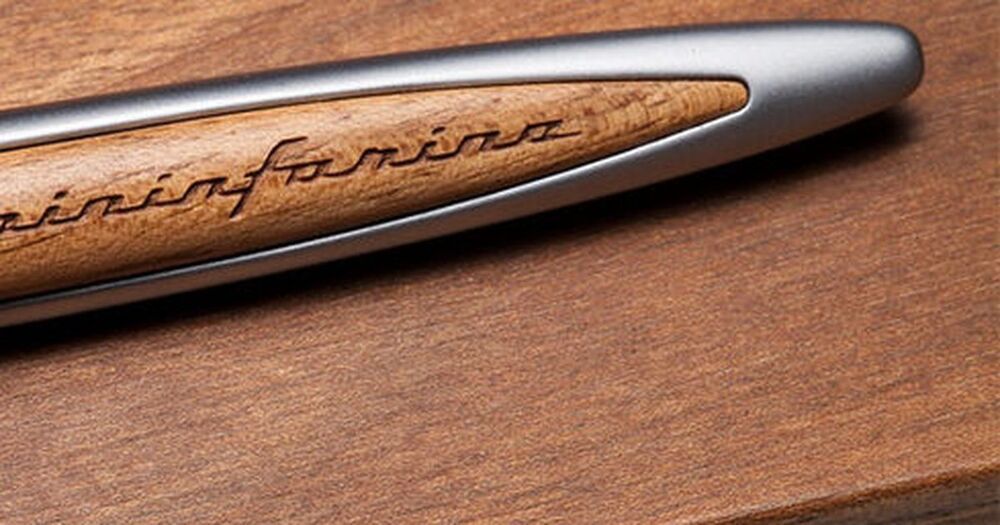
To the Moon and back, twice.
It is mainly about greater reliability.
Professor of theoretical epidemiology Sunetra Gupta has criticised the planned return to a Covid tier system in December.
Speaking with talkRADIO’s Julia Hartley-Brewer, the Great Barrington Declaration co-author said it “still leaves the doors open to the enormous harms of lockdown”.
She added: “Lockdowns are a luxury of the affluent…the UK cannot afford it.”
It comes ahead of Boris Johnson setting out plans for a strengthened three-tier system of restrictions to replace England national lockdown and to pave the way for a limited relaxation at Christmas.

‘Sound beaming’ 3D technology from Noveto Systems tracks ear and sends it audio using ultrasonic waves, creating personal listening pockets.


Multilayer plastic materials are ubiquitous in food and medical supply packaging, particularly since layering polymers can give those films specific properties, like heat resistance or oxygen and moisture control. But despite their utility, those ever-present plastics are impossible to recycle using conventional methods.
About 100 million tons of multilayer thermoplastics — each composed of as many as 12 layers of varying polymers — are produced globally every year. Forty percent of that total is waste from the manufacturing process itself, and because there has been no way to separate the polymers, almost all of that plastic ends up in landfills or incinerators.
Now, University of Wisconsin-Madison engineers have pioneered a method for reclaiming the polymers in these materials using solvents, a technique they’ve dubbed Solvent-Targeted Recovery and Precipitation (STRAP) processing. Their proof-of-concept is detailed today (November 20, 2020) in the journal Science Advances.
Builder eBob —
A new generation of machines is automating a tech-averse industry.

