CHATTANOOGA, Tenn. — Who needs a mate? Certainly not a female Komodo dragon at a Tennessee zoo.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
New Electronic State of Matter May Lead to Quantum Teleportation
Scientists uncovered a new state of matter that could lead us to many exciting new forms of quantum computing and teleportation.


Avengers: Infinity War — Iron Man Mark 50 Suit Up
Watch avengers: infinity war on digital HD july 31 and blu-ray august 14!
I own nothing!
Credit goes to Marvel Studios and Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures.
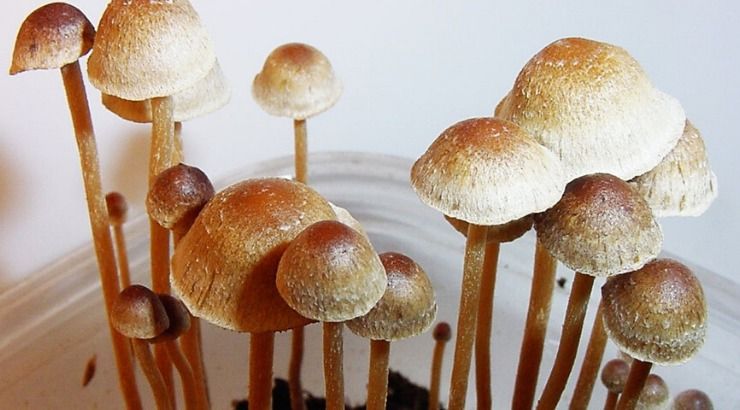


Magic Mushrooms One Step Closer to Treating Depression After Successful Clinical Trials
(TT) — Psilocybin, the active ingredient in the most commonly used psychedelic mushrooms, is coming closer to becoming a mainstream treatment for depression.
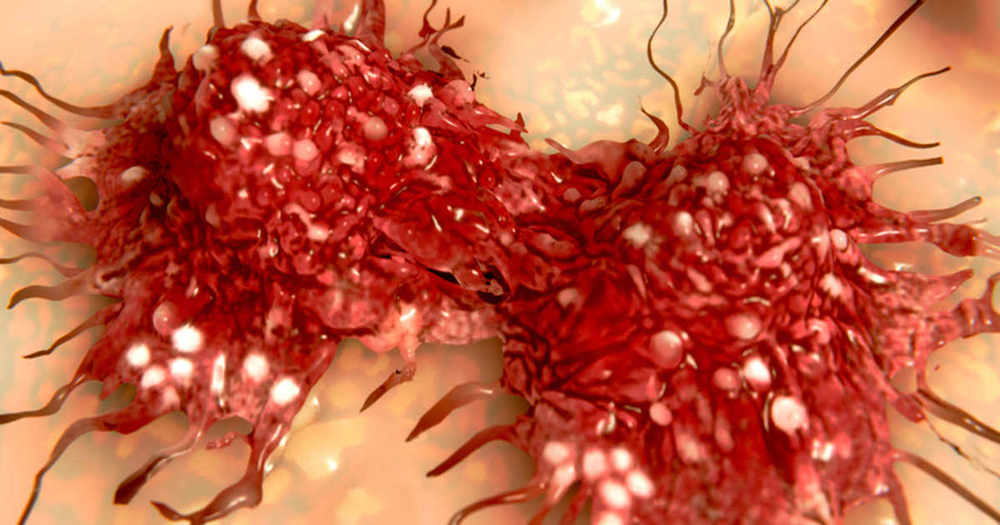
Scientists Have Proven That Negativity Makes Cancer Grow Inside The Body

Everybody feels negative emotions once in a while, but these emotions have a stronger effect on your health than you may realize. Every time you think about regrets, experience resentment or replay bad memories in your head, your body suffers just as much as your mind. That’s why harboring negative emotions can lead to devastating long-term disease.
But there is one simple solution: forgiveness. Trouble is, our culture seems to perceive forgiveness as a sign of weakness, submission, or both. This makes it harder to actually do the work to forgive people who’ve done you harm.

Unraveling turbulence: New insights into how fluids transform from order to disorder
Turbulence is everywhere—it rattles our planes and makes tiny whirlpools in our bathtubs—but it is one of the least understood phenomena in classical physics.
Turbulence occurs when an ordered fluid flow breaks into small vortices, which interact with each other and break into even smaller vortices, which interact with each other and so-on, becoming the chaotic maelstrom of disorder that makes white water rafting so much fun.
But the mechanics of that descent into chaos have puzzled scientists for centuries.

Physicists model the supernovae that result from pulsating supergiants like Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse has been the center of significant media attention lately. The red supergiant is nearing the end of its life, and when a star over 10 times the mass of the Sun dies, it goes out in spectacular fashion. With its brightness recently dipping to the lowest point in the last hundred years, many space enthusiasts are excited that Betelgeuse may soon go supernova, exploding in a dazzling display that could be visible even in daylight.
While the famous star in Orion’s shoulder will likely meet its demise within the next million years—practically couple days in cosmic time—scientists maintain that its dimming is due to the star pulsating. The phenomenon is relatively common among red supergiants, and Betelgeuse has been known for decades to be in this group.
Coincidentally, researchers at UC Santa Barbara have already made predictions about the brightness of the supernova that would result when a pulsating star like Betelgeuse explodes.