GPT-3 can be eerily human-like—for better and for worse.


US chipmaker Intel is investigating a security breach after earlier today 20 GB of internal documents, with some marked “confidential” or “restricted secret,” were uploaded online on file-sharing site MEGA.
The data was published by Till Kottmann, a Swiss software engineer, who said he received the files from an anonymous hacker who claimed to have breached Intel earlier this year.
Kottmann received the Intel leaks because he manages a very popular Telegram channel where he regularly publishes data that accidentally leaked online from major tech companies through misconfigured Git repositories, cloud servers, and online web portals.
Taiwan’s semiconductor industry, a centerpiece of the global supply chain for smartphones and computing equipment, was the focus of a hacking campaign targeting corporate data over the last two years, Taiwan-based security firm CyCraft Technology claimed Thursday.
The hackers went after at least seven vendors in the semiconductor industry in 2018 and 2019, quietly scouring networks for source code and chip-related software, CyCraft said. Analysts say the campaign, which reportedly hit a sprawling campus of computing firms in northwest Taiwan, shows how the tech sector’s most prized data is sought out by well-resourced hacking groups.
“They’re choosing the victims very precisely,” C.K. Chen, senior researcher at CyCraft, said of the hackers. “They attack the top vendor in a market segment, and then attack their subsidiaries, their competitors, their partners and their supply chain vendors.”


Live coverage of the countdown and launch of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mission will launch SpaceX’s tenth batch of Starlink broadband satellites. Text updates will appear automatically below. Follow us on Twitter.
Spaceflight Now members can watch a live view of the pad. Join now.
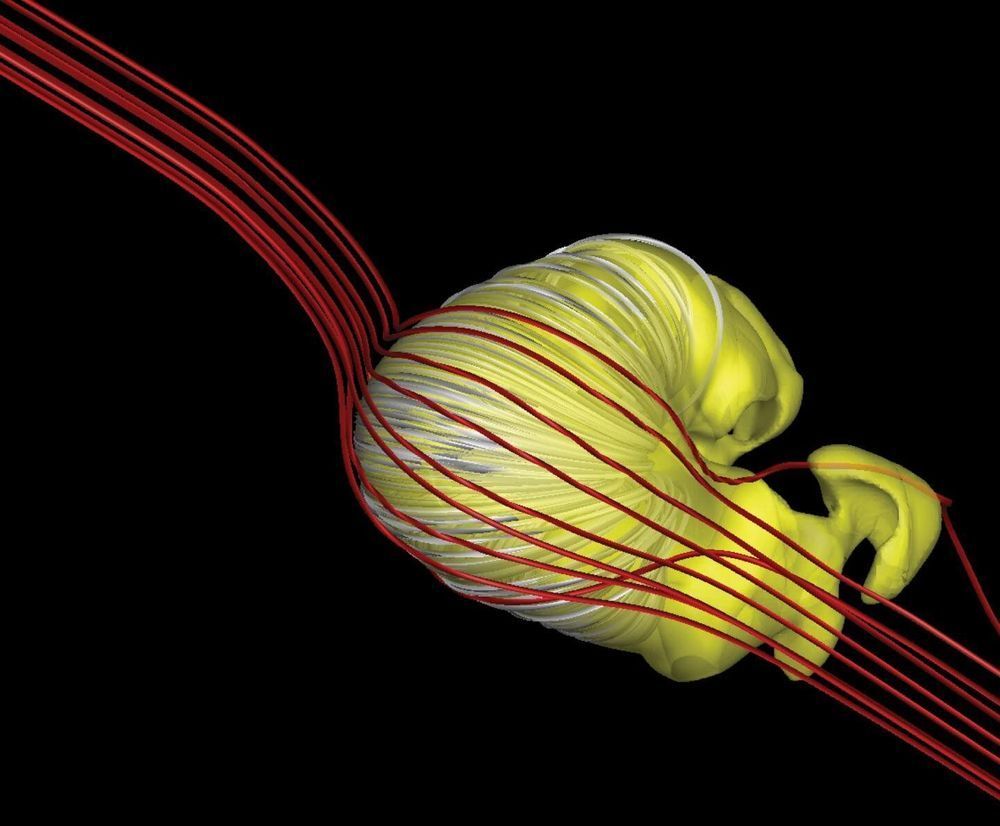
Scientists have developed a new prediction of the shape of the bubble surrounding our solar system using a model developed with data from NASA missions.
All the planets of our solar system are encased in a magnetic bubble, carved out in space by the Sun’s constantly outflowing material, the solar wind. Outside this bubble is the interstellar medium—the ionized gas and magnetic field that fills the space between stellar systems in our galaxy. One question scientists have tried to answer for years is on the shape of this bubble, which travels through space as our Sun orbits the center of our galaxy. Traditionally, scientists have thought of the heliosphere as a comet shape, with a rounded leading edge, called the nose, and a long tail trailing behind.
Research published in Nature Astronomy in March and featured on the journal’s cover for July provides an alternative shape that lacks this long tail: the deflated croissant.

Sanofi and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) will be awarded up to $2.1 billion by the U.S. Departments of Health and Human Services (HHS) and Defense (DoD) toward development and manufacturing of the recombinant protein-based COVID-19 vaccine being produced by the companies, they and the U.S. government said.
HHS and DoD are providing the funding as part of Operation Warp Speed—the program through which President Donald Trump’s administration has committed the nation to delivering 300 million vaccine doses protecting against SARS-CoV-2 by January 2021.
“The portfolio of vaccines being assembled for Operation Warp Speed increases the odds that we will have at least one safe, effective vaccine as soon as the end of this year,” HHS Secretary Alex Azar II stated.
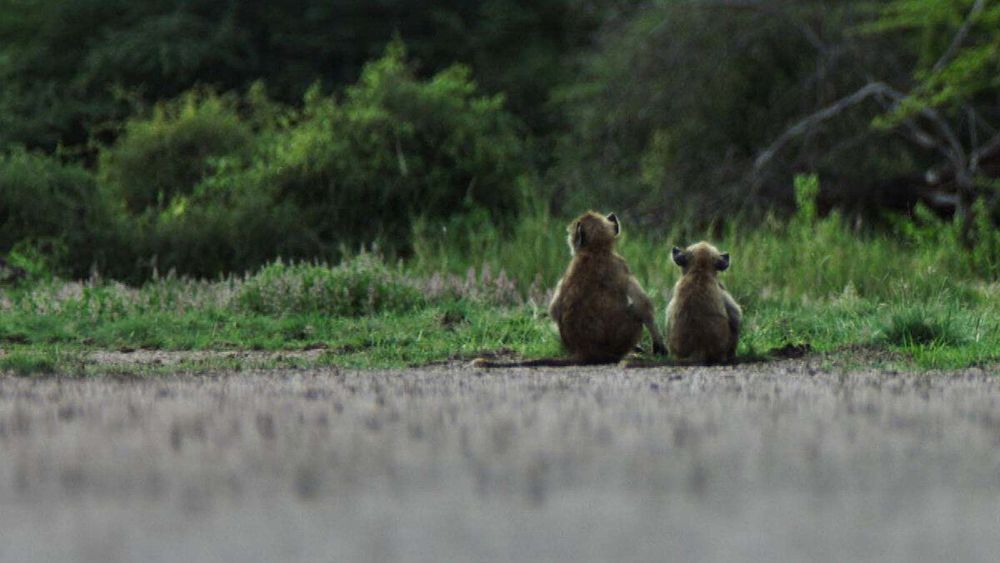

When baboons experience trauma in early life, they have higher levels of stress hormones in adulthood—a potential marker of poor health—than their peers who don’t experience trauma, even if they have strong social relationships as adults, according to a study led by a University of Michigan researcher.
The study examined the links between childhood adversity, adult social relationships and glucocorticoid concentrations. The goal was to determine whether one of the reasons that baboons who experience early trauma live shorter, less healthy lives was because they fail to develop strong social relationships in adulthood, which could be beneficial to health.
U-M biological anthropologist Stacy Rosenbaum and her co-authors found that while early life adversity didn’t strongly affect baboons’ ability to have social relationships, any positive effect of those relationships was much smaller than the large negative effects of early life trauma.
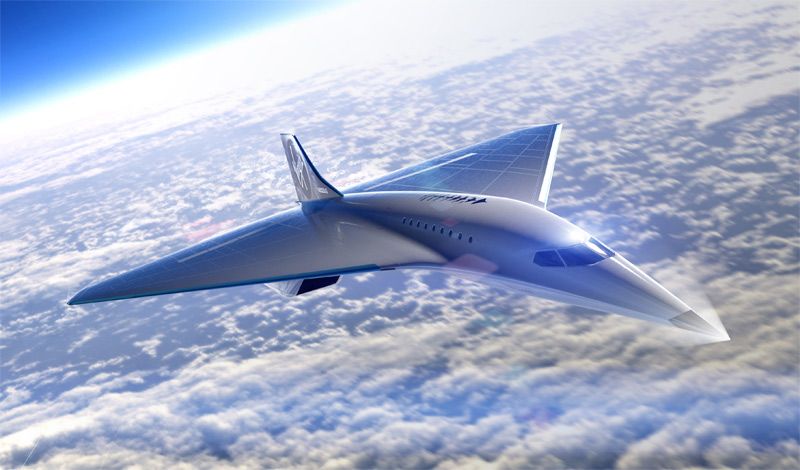

Aerospace company Virgin Galactic has announced a first stage design scope for the build of a new aircraft capable of reaching speeds of Mach 3 (3,700 km/h, or 2,300 mph).
Rolls-Royce will collaborate with The Spaceship Company (TSC) – a subsidiary of Virgin Galactic – in designing and developing the engine propulsion technology for this high-speed commercial plane. This follows the successful completion of a Mission Concept Review (MCR) that included representatives from NASA and resulted in authorisation from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). It means the companies can now work together to produce a certification framework.
Rolls-Royce has a proven track record of delivering high Mach propulsion, powering the only civil-certified commercial aircraft capable of supersonic flight – Concorde, which flew from 1969 to 2003. This new plane, if successfully developed and put into operation, would be more than 50% faster than Concorde. Journeys across the Atlantic, which typically take almost eight hours in a conventional airliner, could be completed in less than two hours.