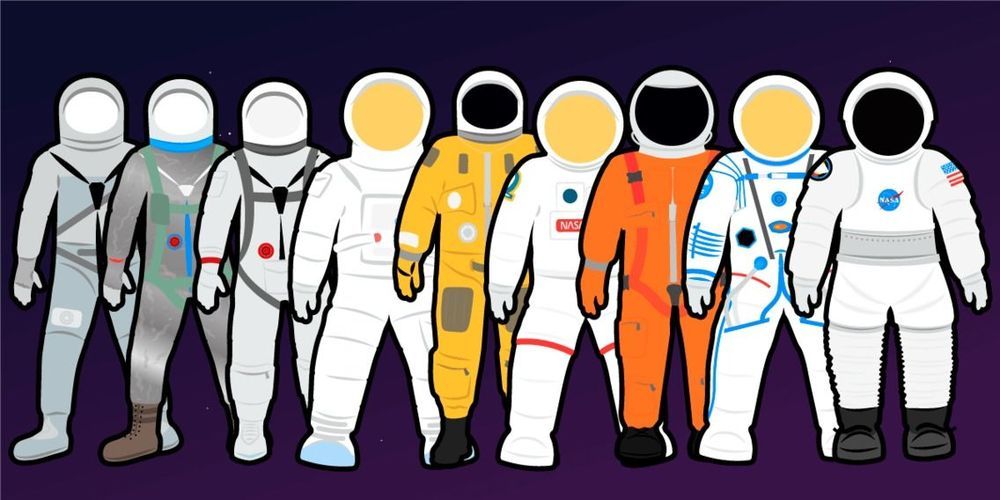
Astronaut spacesuits debuted in the 1960s but continue to evolve as NASA and companies like Boeing and SpaceX push to explore the moon and Mars.
https://paper.li/e-1437691924#/ https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-019-0375-9
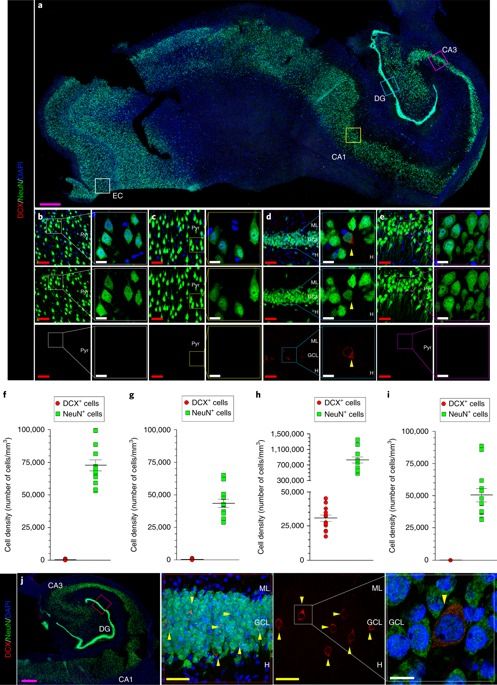
The hippocampus is one of the most affected areas in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Moreover, this structure hosts one of the most unique phenomena of the adult mammalian brain, namely, the addition of new neurons throughout life. This process, called adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN), confers an unparalleled degree of plasticity to the entire hippocampal circuitry3,4. Nonetheless, direct evidence of AHN in humans has remained elusive. Thus, determining whether new neurons are continuously incorporated into the human dentate gyrus (DG) during physiological and pathological aging is a crucial question with outstanding therapeutic potential. By combining human brain samples obtained under tightly controlled conditions and state-of-the-art tissue processing methods, we identified thousands of immature neurons in the DG of neurologically healthy human subjects up to the ninth decade of life. These neurons exhibited variable degrees of maturation along differentiation stages of AHN. In sharp contrast, the number and maturation of these neurons progressively declined as AD advanced. These results demonstrate the persistence of AHN during both physiological and pathological aging in humans and provide evidence for impaired neurogenesis as a potentially relevant mechanism underlying memory deficits in AD that might be amenable to novel therapeutic strategies.
The Post spoke to tech workers in Zhongguancun and other parts of Beijing for a snapshot of what life is really like living in China’s Silicon Valley, as these tech hubs – home to internet giants like Baidu, Meituan and ByteDance – have been dubbed.
Life in China’s tech industry is not easy, with young employees and entrepreneurs battling burnout while also worrying about career ceilings and lay-offs.
100th Missile Defense Brigade
Posted in futurism
In an electronic filing with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), SpaceX has demonstrated a higher than necessary safety for their Starlink constellation satellites in terms of collision risk with other objects in orbit in the scenario that a Starlink satellite becomes uncontrollable after launch.
The filing, in response to FCC questions, reveals SpaceX’s upcoming space-based internet project carries a collision risk 2.1 times less likely than the accepted NASA standard.
The filing occurred on 13 March 2019 in response to a series of FCC follow-up questions from previous approvals and relates to SpaceX’s upcoming deployment of the first batch of Starlink satellites into an initial operational orbit of 550 km.
Using a modified version of CRISPR, a team of geneticists has successfully triggered 13,200 genetic changes to a single human cell. That’s a new record, by a long shot. This sweeping new editing process could eventually be used to strip DNA of useless or dangerous genetic information—or create entirely new kinds of life.
New research uploaded to the preprint bioRxiv server describes the achievement, in which a Harvard University team led by George Church edited the living crap out of a single human cell to the tune of 13,200 total modifications. Incredibly, the cell survived. The previous record for bulk edits made to a single cell was set in 2017, when Church and his colleagues knocked out 62 copies of a retrovirus found in pig genomes. The new achievement is thus “three orders of magnitude greater” than the previous standard, the authors wrote in their paper.
A new review discusses how neutrophils release toxic substances into the body under inflammatory conditions, detailing one of the ways in which chronic inflammation causes long-term damage.
Casting a deadly NET
As we age, we suffer from the ever-increasing chronic inflammation known as inflammaging. This persistent, smoldering background of low-grade inflammation harms wound healing and promotes multiple age-related diseases. Senescent cells, a weakened immune system, and chronic infections are all proposed to contribute to inflammaging.