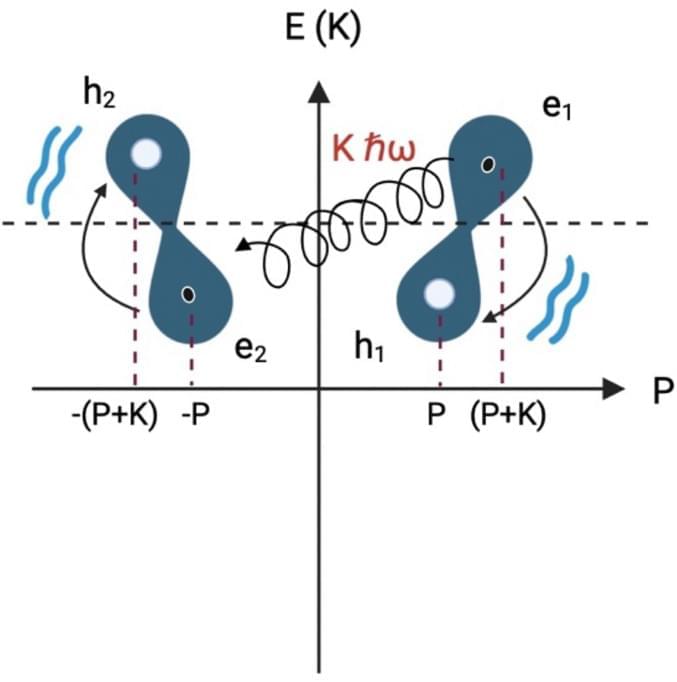
I believe that dna will be able to answer just about all our genetic coding questions so much that it will lead to even better breakthroughs in the future and use hardly any energy. I believe also that the master algorithm can eventually be derived from DNA as dna seems already a perfect master algorithm for human beings where human beings are the key to all future progress. I say this as quantum computing is still not stable but we already know that dna computers seem already a masterpiece already especially even organoids of the human brain. Really it becomes really quite simple as even the quantum realm is unstable but dna computers that are quantum would stabilize this currently unstable realm.
Riera Aroche, R., Ortiz García, Y.M., Martínez Arellano, M.A. et al. DNA as a perfect quantum computer based on the quantum physics principles. Sci Rep 14, 11,636 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-62539-5