Exclusive: if discovery is confirmed it will have global implications as 90% of people breathe dirty air.
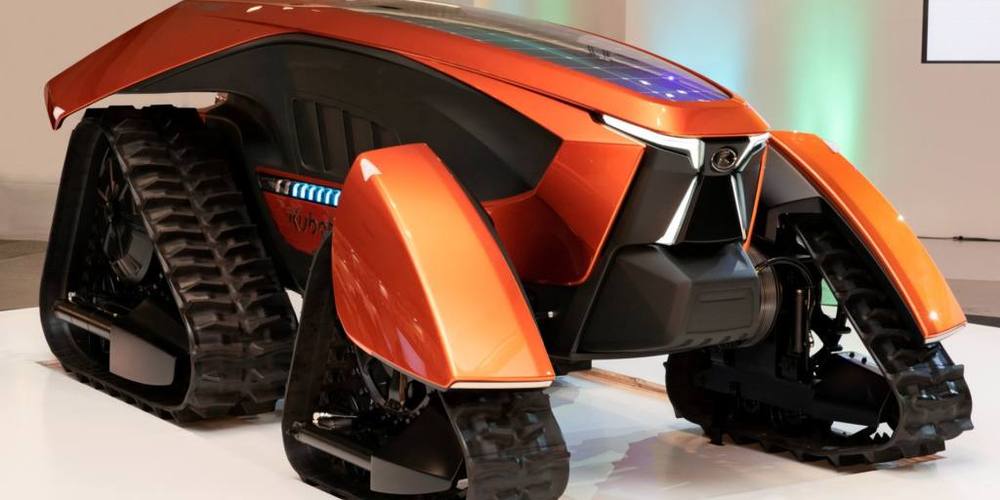



Autonomous tractors for farming.
OSAKA — Kubota has partnered with U.S. chipmaker Nvidia to develop highly sophisticated self-driving farm tractors, the Japanese machinery maker said Tuesday.
The tractors will be equipped with Nvidia graphics processing units and artificial intelligence, coupled with cameras to instantly process collected data.
The farming technology is expected to provide a labor-saving solution that will help address the shortage of workers in Japan’s agricultural industry.



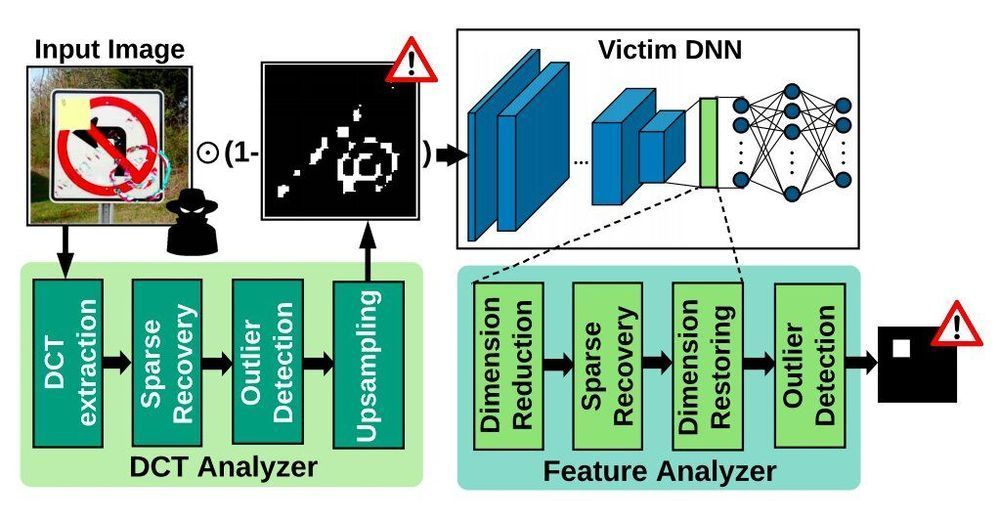
With artificial intelligence (AI) tools and machine learning algorithms now making their way into a wide variety of settings, assessing their security and ensuring that they are protected against cyberattacks is of utmost importance. As most AI algorithms and models are trained on large online datasets and third-party databases, they are vulnerable to a variety of attacks, including neural Trojan attacks.
A neural Trojan attack occurs when an attacker inserts what is known as a hidden Trojan trigger or backdoor inside an AI model during its training. This trigger allows the attacker to hijack the model’s prediction at a later stage, causing it to classify data incorrectly. Detecting these attacks and mitigating their impact can be very challenging, as a targeted model typically performs well and in alignment with a developer’s expectations until the Trojan backdoor is activated.
Researchers at University of California, San Diego have recently created CLEANN, an end-to-end framework designed to protect embedded artificial neural networks from Trojan attacks. This framework, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv and set to be presented at the 2020 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, was found to perform better than previously developed Trojan shields and detection methods.

Alexey Turchin and Maxim Chernyakov, researchers belonging to the transhumanism movement, wrote a paper outlining the main ways technology might someday make resurrection possible.
From cryonics to time travel, here are some of the (highly speculative) methods that might someday be used to bring people back to life.


Einstein’s theory of special relativity gave us the speed limit of the Universe — that of light in a vacuum. But the absolute top speed of sound, through any medium, has been somewhat trickier to constrain.
It’s impossible to measure the speed of sound in every single material in existence, but scientists have now managed to pin down an upper limit based on fundamental constants, the universal parameters by which we understand the physics of the Universe.
That speed limit, according to the new calculations, is 36 kilometres per second (22 miles per second). That’s about twice the speed of sound travelling through diamond.
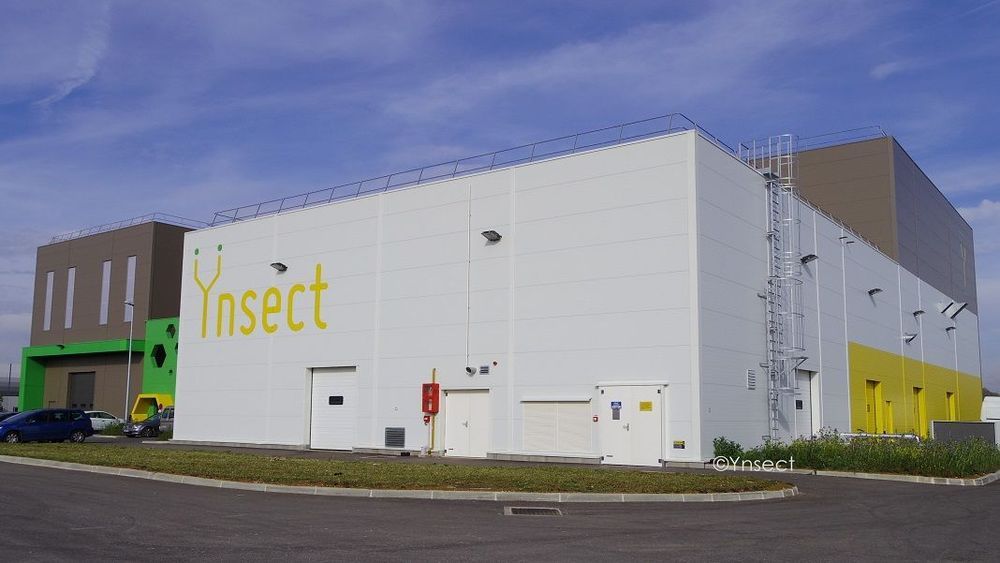

It looks like our food for the future will be bugs. A factory in France will grow bugs as a food source.
in Series C funding in early 2019, and at the time already had $70 million worth of aggregated orders to fill. Now they’re building a bug-farming plant to churn out tiny critters in record numbers.
You’ve probably heard of vertical farms in the context of plants; most existing vertical farms use LED lights and a precise mixture of nutrients and water to grow leafy greens or other produce indoors. They maximize the surface area used for growing by stacking several layers of plants on top of one another; the method may not make for as much space as outdoor fields have, but can yield a lot more than you might think.
Ÿnsect’s new plant will use layered trays too, except they’ll be cultivating beetle larvae instead of plants. The ceilings of the facility are 130 feet high—that’s a lot of vertical space to grow bugs in. Those of us who are grossed out by the thought will be glad to know that the whole operation will be highly automated; robots will tend to and harvest the beetles, and AI will be employed to keep tabs on important growing conditions like temperature and humidity.