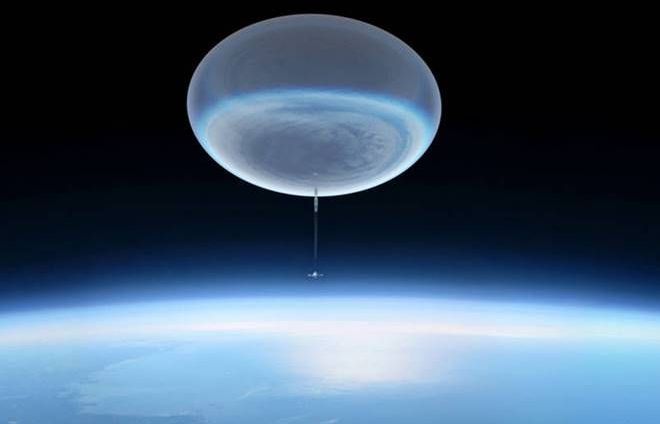
The ASTHROS mission will be carried on a big balloon that will be about 150 meters wide — or roughly the size of a football stadium — and will be inflated with helium. A carrier below the balloon will hold the instruments and the telescope. During its flight, it will allow scientists to control the direction of the telescope with precision and download the data in real-time using satellite links.
The ASTHROS team expects that stratospheric winds will help the balloon complete two to three loops around the South Pole in approximately 21 to 28 days. Once complete, the parachute will return the carrier to the ground and the telescope will be recovered and refurbished for future missions.
Get live Stock Prices from BSE, NSE, US Market and latest NAV, portfolio of Mutual Funds, calculate your tax by Income Tax Calculator, know market’s Top Gainers, Top Losers & Best Equity Funds. Like us on Facebook and follow us on Twitter.