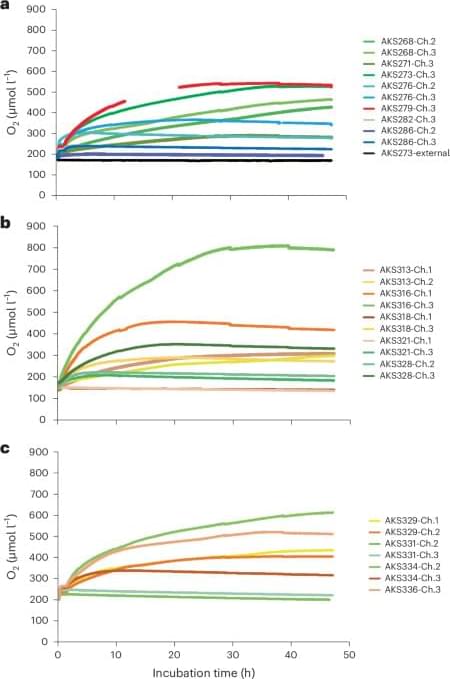
Oxygen is generated abiotically at the abyssal seafloor in the presence of polymetallic nodules, potentially by seawater electrolysis, according to in situ chamber and ex situ incubation experiments.

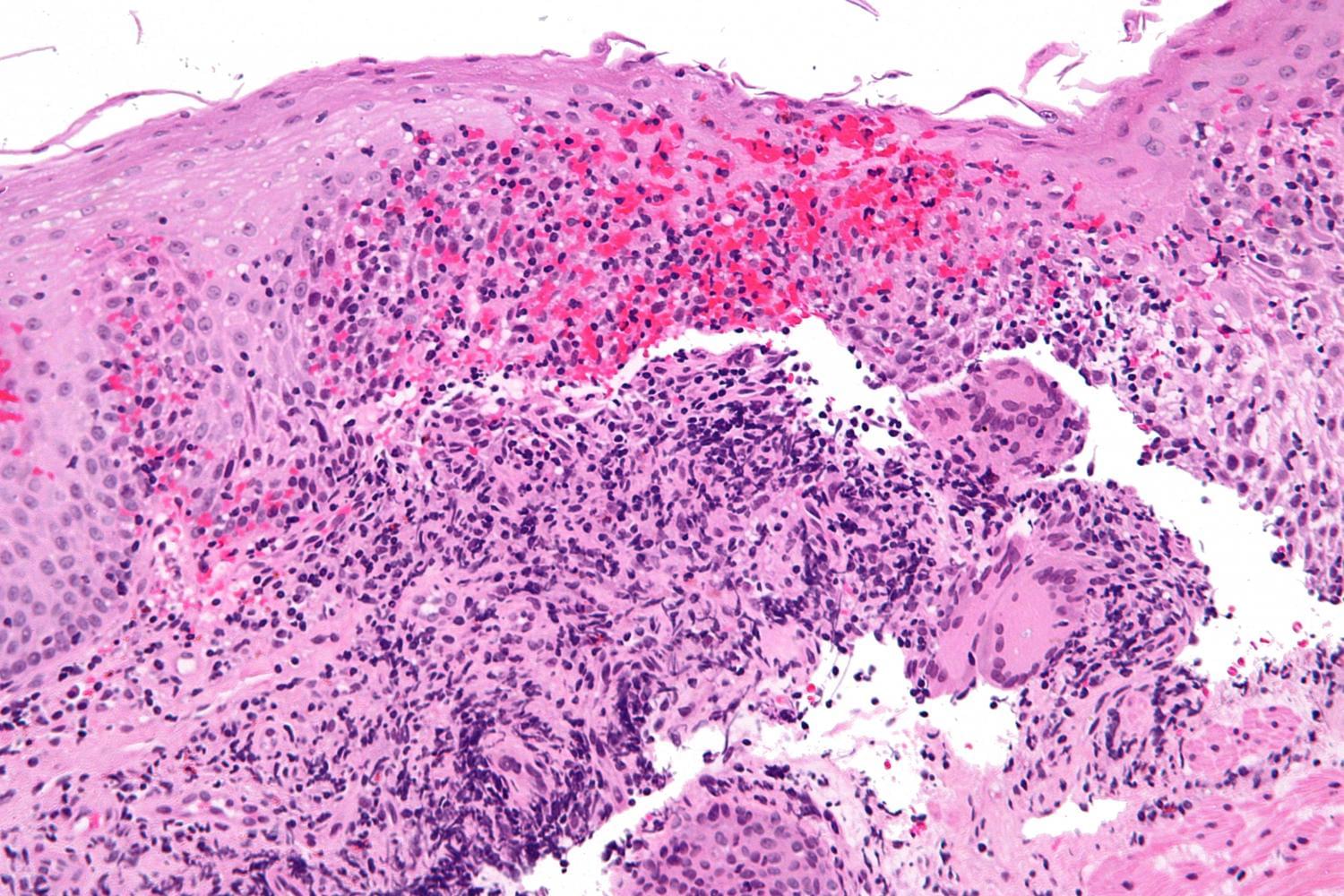
A study led by biomedical scientists at the University of California, Riverside School of Medicine shows how a genetic mutation associated with Crohn’s disease can worsen iron deficiency and anemia—one of the most common complications experienced by patients with inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD.
While IBD—a group of chronic inflammatory disorders that includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis—primarily affects the intestines, it can have effects beyond the gut. Iron deficient anemia is the most prevalent of these effects, contributing to chronic fatigue and reduced quality of life, particularly during disease flare-ups.
The study, performed on serum samples from IBD patients, reports that patients carrying a loss-of-function mutation in the gene PTPN2 (protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2) exhibit significant disruption in blood proteins that regulate iron levels. This mutation is found in 14–16% of the general population and 19–20% of the IBD population. A loss-of-function mutation is a genetic change that reduces or eliminates the normal function of a gene or its product, a protein.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/

Progress is rarely linear, and AI is no exception.
As academics, independent developers, and the biggest tech companies in the world drive us closer to artificial general intelligence — a still hypothetical form of intelligence that matches human capabilities — they’ve hit some roadblocks. Many emerging models are prone to hallucinating, misinformation, and simple errors.
Google CEO Sundar Pichai referred to this phase of AI as AJI, or “artificial jagged intelligence,” on a recent episode of Lex Fridman’s podcast.
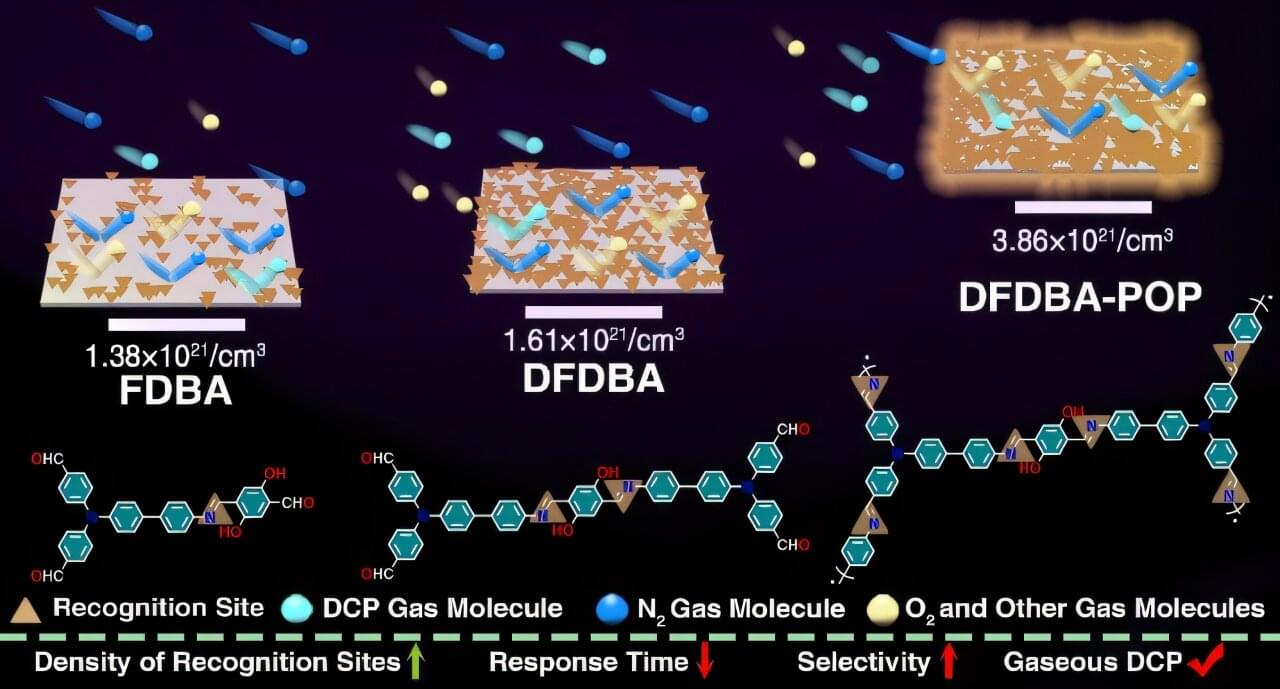
Sarin (isopropyl methyl fluorophosphonate) is an organophosphorus nerve agent regulated by the Convention on the Banning of Chemical Weapons. It can enter the body through the respiratory system, skin, or eyes, paralyzing the central nervous system by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, which can lead to death. Therefore, rapid and sensitive detection of trace sarin is vital for safety and environmental protection.
Due to its high toxicity, sarin’s use is strictly controlled, leading researchers to use diethyl chlorophosphate (DCP) as a safer simulant. The common fluorescence detection method takes advantage of DCP’s strong electrophilicity, using recognition sites like hydroxyl oxime and imine for fluorescence quenching to identify the target.
However, this method is affected by photobleaching, acid, and other environmental factors, limiting its application.
New research from Caltech’s Center for Autonomous Systems and Technologies finds robots that morph before landing are more robust



Advances in Quantum technologies offer a step improvement in phase noise performance compared to conventional oscillators. University of Birmingham (UoB) is developing a new class of ultra low phase noise optical lattice clock Quantum oscillator that can provide several orders of magnitude improvement in radar sensitivity against clutter.
To facilitate this enabling research, the Advanced Radar Network (ADRAN) facility funded by the EPSRC Quantum Technologies Hub is being set-up to enable comparative performance assessment of a radar systems with quantum oscillators as compared to conventional alternatives.
This may be shared as something else, but these guys just used quantum tech to “unstealth stealth”. I think that’s a pretty cool thing to accomplish.
Information about quantum enabled radar research in the Microwave Integrated Systems Laboratory (MISL) at the University of Birmingham.
