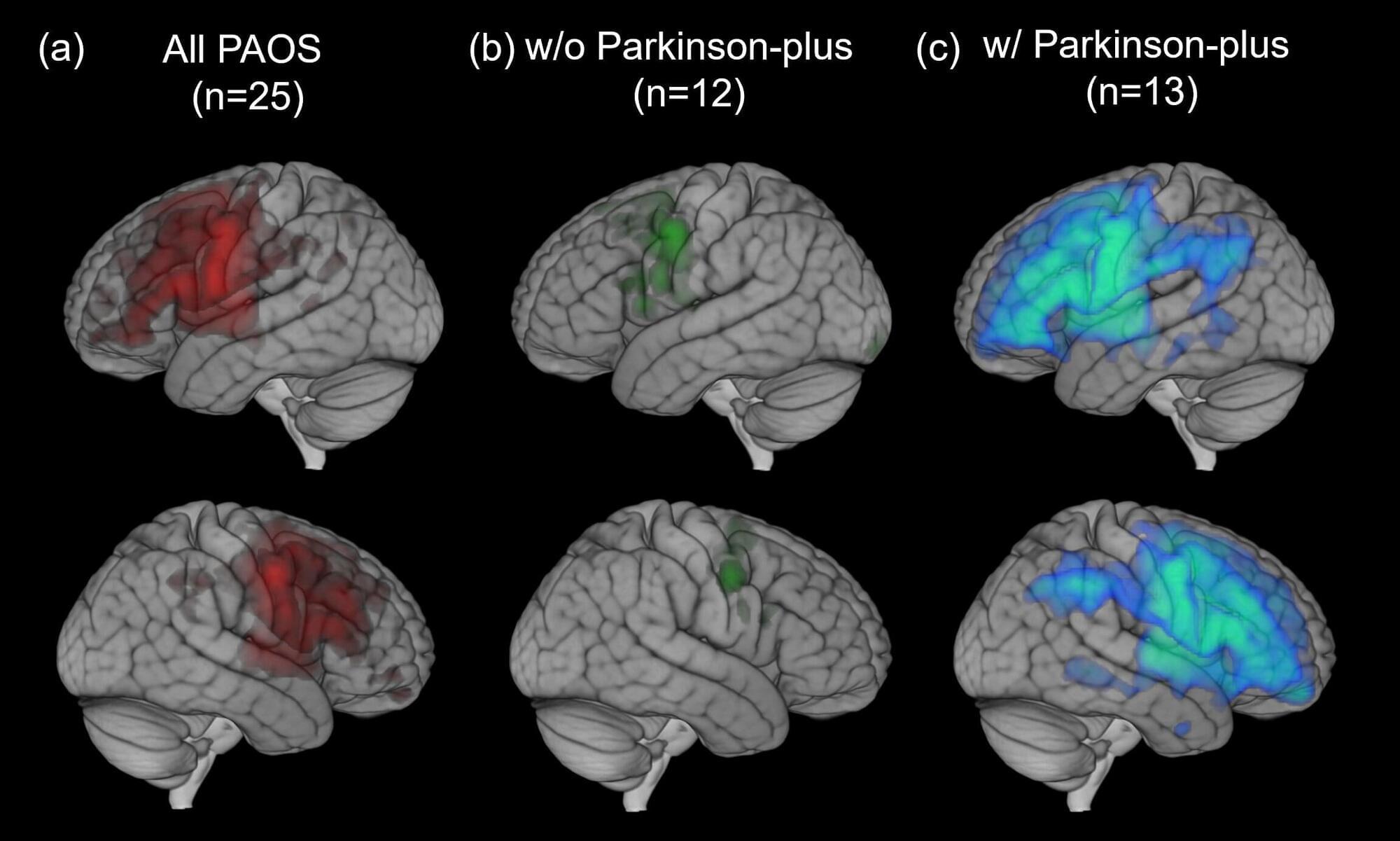
A novel PET imaging approach has revealed distinct patterns of brain inflammation in patients with progressive apraxia of speech (PAOS), a rare neurodegenerative disorder that affects speech planning. These findings provide new insight into how neuroinflammation and tau pathology may drive disease progression in PAOS, opening potential avenues for earlier diagnosis and targeted treatments.
This research was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2025 Annual Meeting and published as a supplement in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
PAOS is a neurodegenerative disorder that impairs the brain’s ability to plan and coordinate speech. It is marked by a slow speaking rate, distorted sounds, and effortful facial movements during speech. Patients with PAOS are likely to have Parkinson-plus syndrome in the later stages, meeting criteria for progressive supranuclear palsy or corticobasal syndrome, and typically have a 4-repeat tauopathy at autopsy.