Microsoft warns of active SharePoint exploits affecting on-prem users; 54 victims confirmed in major attack.


Dopamine is one of the most extensively studied chemical messengers in the human brain, and yet scientists are still figuring out how it works to accomplish so much.
For years, the classic view has been that, when released, dopamine slowly diffuses through the brain like a chemical megaphone, broadcasting information far and wide to numerous target cells.
Recently, however, that perspective has changed. Newer research suggests that dopamine is also capable of short, sharp whispers, precisely directed within milliseconds to neighboring cells.

A new risk prediction tool developed by the American Heart Association (AHA) estimated cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk in a diverse patient cohort more accurately than current models, according to a recent study published in Nature Medicine.
The tool, called the Predicting Risk of Cardiovascular Disease EVENTs (PREVENT) equations which was developed in 2023, could help health care providers more accurately identify patients who have higher CVD risk and enhance preventive care efforts, according to Sadiya Khan, the Magerstadt Professor of Cardiovascular Epidemiology and co-first author of the study.
“Evaluating the new PREVENT equations in a diverse sample of patients is critical to provide primary care providers and cardiologists with further assurance that they can utilize these equations to accurately predict patients’ CVD risk, particularly in vulnerable populations,” said Khan, who is also an associate professor of Medical Social Sciences in the Division of Determinants of Health and of Preventive Medicine in the Division of Epidemiology.
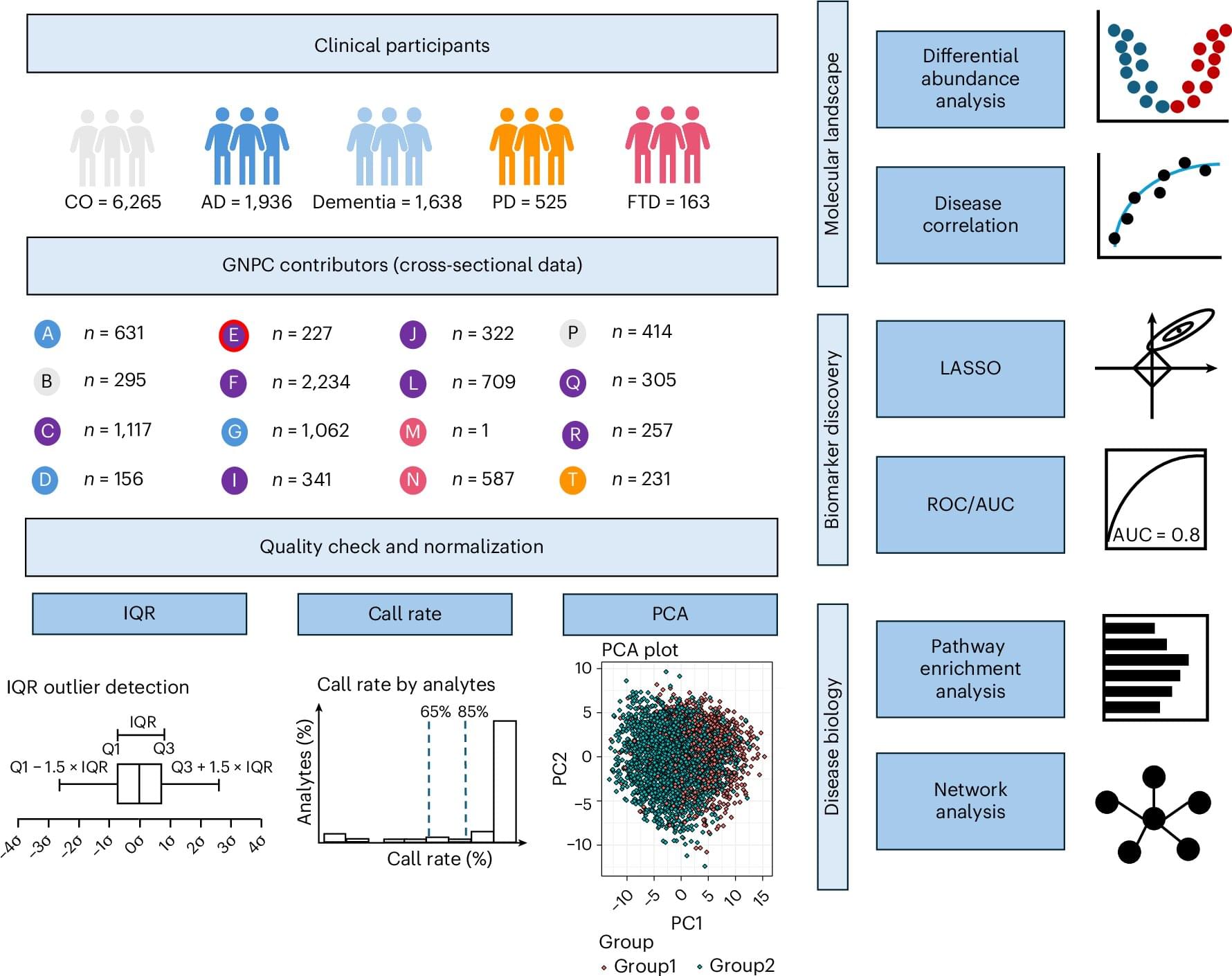
Scientists know that many proteins and pathways are involved in the development and progression of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and that these proteins can be detected in the plasma of people with the conditions.
But it hasn’t been clear exactly which proteins are distinct to one disease vs. shared among two or more of them, adding to the difficulty both of diagnosing these complex diseases from blood samples and of developing effective treatments.
A new study by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis researchers, published in Nature Medicine, provides some answers. Led by Carlos Cruchaga, the Barbara Burton & Reuben Morriss III Professor in the Department of Psychiatry and director of the NeuroGenomics and Informatics Center at WashU Medicine, the researchers analyzed protein activity in more than 10,500 blood plasma samples from patients with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease or FTD.
Further analysis for immune-specific processes revealed APOE ε4 enrichment in various infection-related pathways, including herpes, influenza A, hepatitis, measles, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Significant enrichment was also observed for B-cell, T-cell, and inflammatory signaling cascades. Next, immune cell subtype enrichment analysis revealed the most APOE ε4 enrichment in intermediate and non-classical monocytes among innate immune cells.
Among adaptive immune cells, memory cluster of differentiation 8 (CD8) T cells, regulatory T (Treg) cells, and memory CD4 T cells were the most enriched. Besides, γδ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells showed APOE ε4 enrichment. In the liver, a cell-type-specific enrichment analysis revealed the most APOE ε4 enrichment in Kupffer cells and hepatocytes.
Next, the researchers examined whether APOE ε4 CSF proteome changes were reflected in the plasma and used the GNPC dataset for plasma proteome profiling of AD, PDD, FTD, PD, ALS, and non-impaired controls. Fifty-eight plasma proteins associated with the APOE genotype were identified in non-impaired controls. CART modeling revealed that these 58 proteins could strongly differentiate between APOE ε4 carriers and non-carriers across neurodegenerative diseases, and this signature was found to be consistent across different sexes and racial groups.
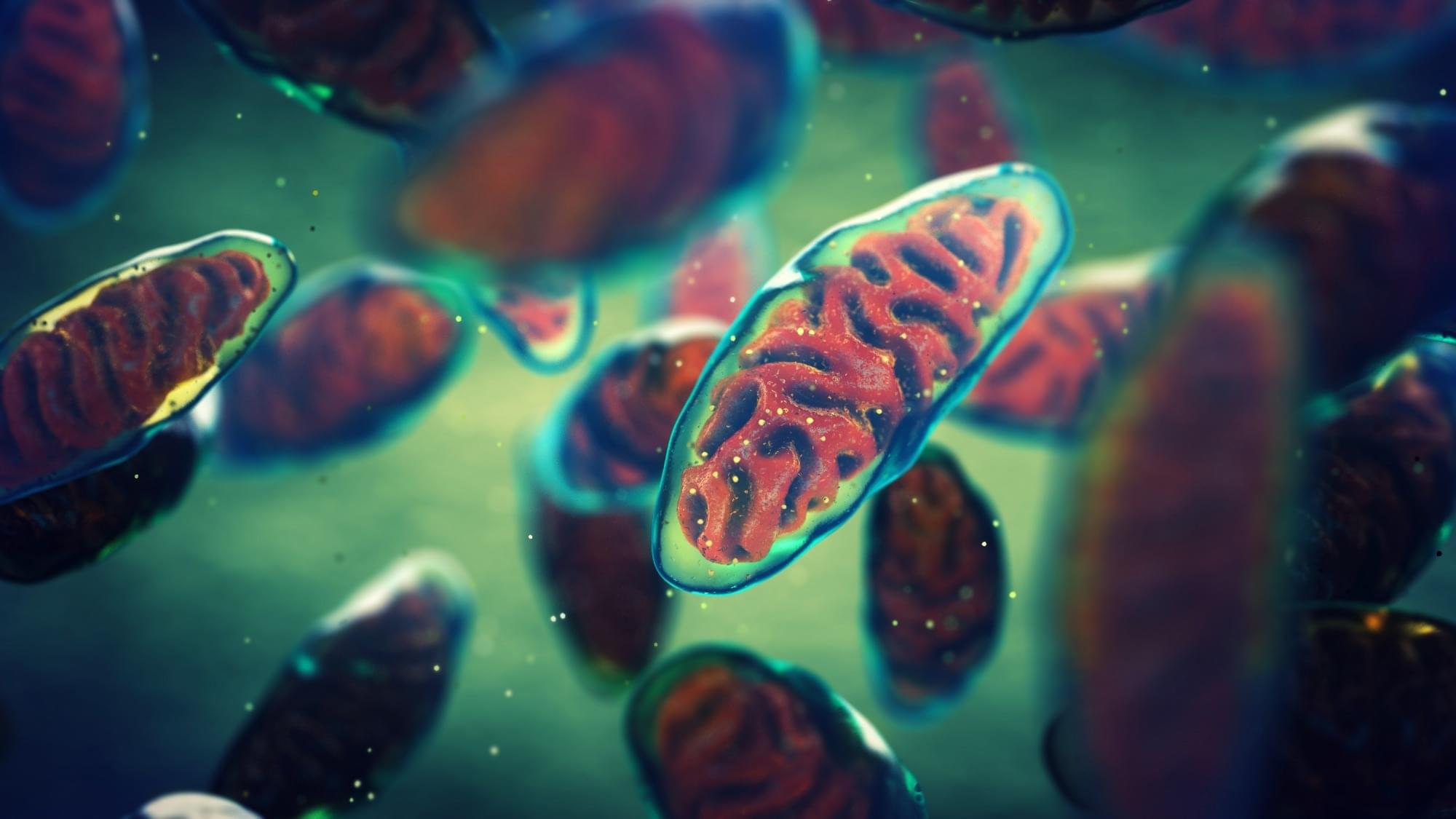
Researchers discovered that mitochondria-rich extracellular vesicles (Ti-mitoEVs) from skeletal muscle can deliver healthy mitochondria to damaged cells, restoring energy and promoting tissue repair in mice. The approach reversed acute muscle injury and chronic kidney disease, offering a promising new regenerative therapy.
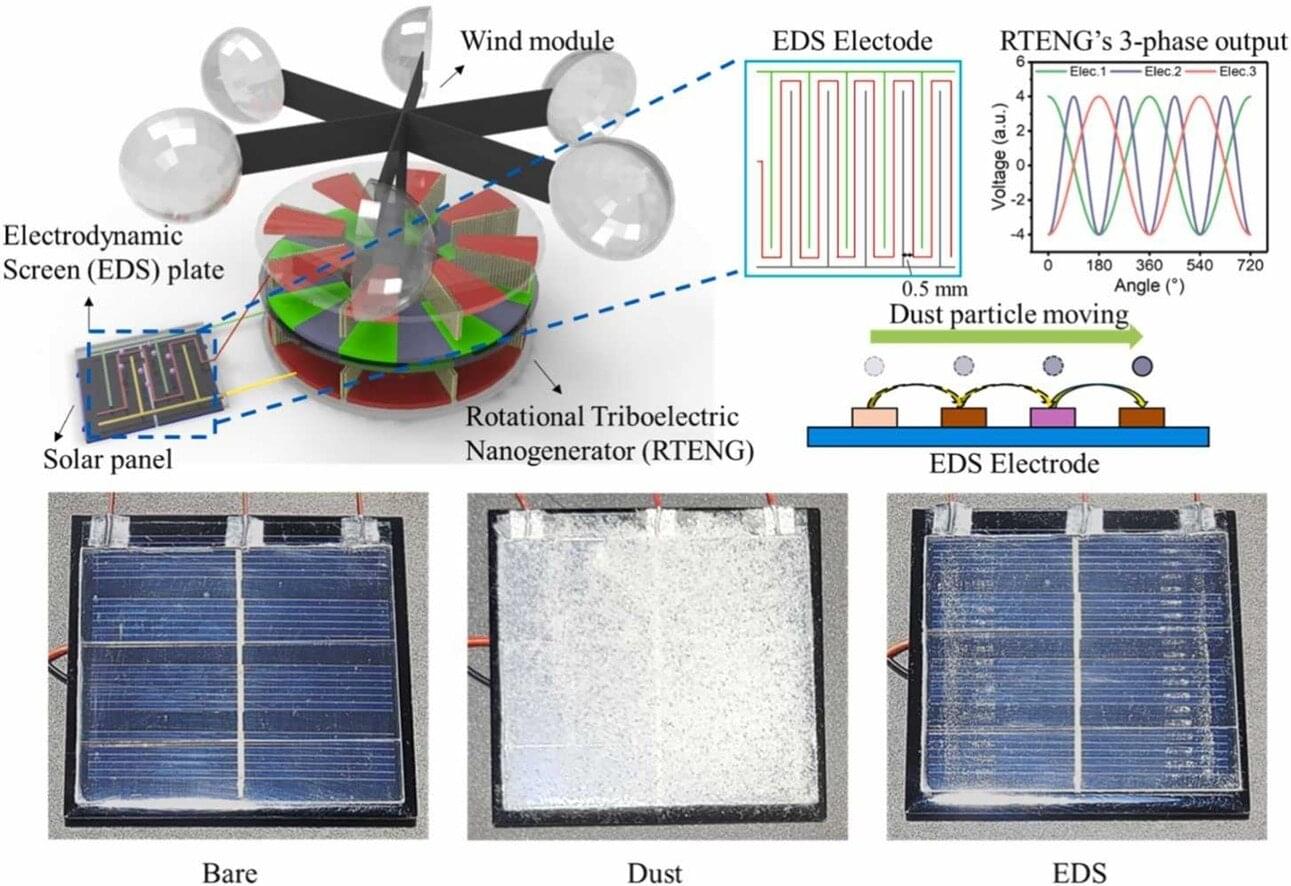
A collaborative research team has successfully developed a self-powered pollution prevention technology that can remove pollutants from the surface of solar panels without external power. This technology uses a wind-powered rotational triboelectric nanogenerator to generate power and combines said power with electrodynamic screen (EDS) technology to move dust in the desired direction for removal.
The findings are published in the journal Nano Energy. The team was led by Professor Juhyuck Lee from the Department of Energy Science and Engineering, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology, along with Dr. Wanchul Seung at Global Technology Research, Samsung Electronics.
The dust that gathers on the surface of solar panels causes a significant reduction in power production efficiency. EDS technology, designed to address this problem, uses electric fields to remove dust from the surface, and it is noted for environments that are not easily accessible, such as deserts, mountains, and space, as it does not require cleaning equipment or personnel. Traditional EDS technology, however, requires high voltage and, consequently, external power, and it has the disadvantage of additional maintenance costs.
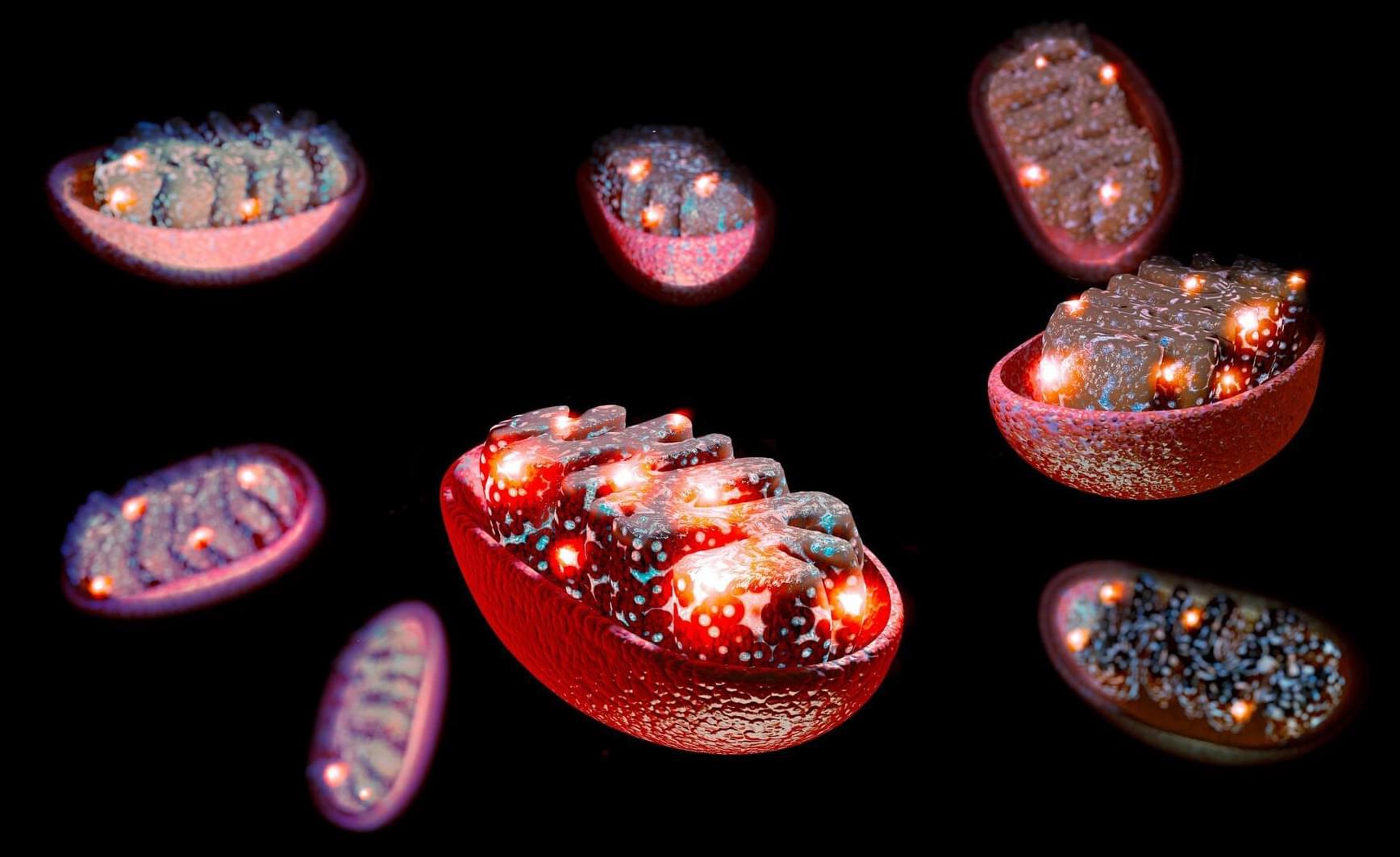
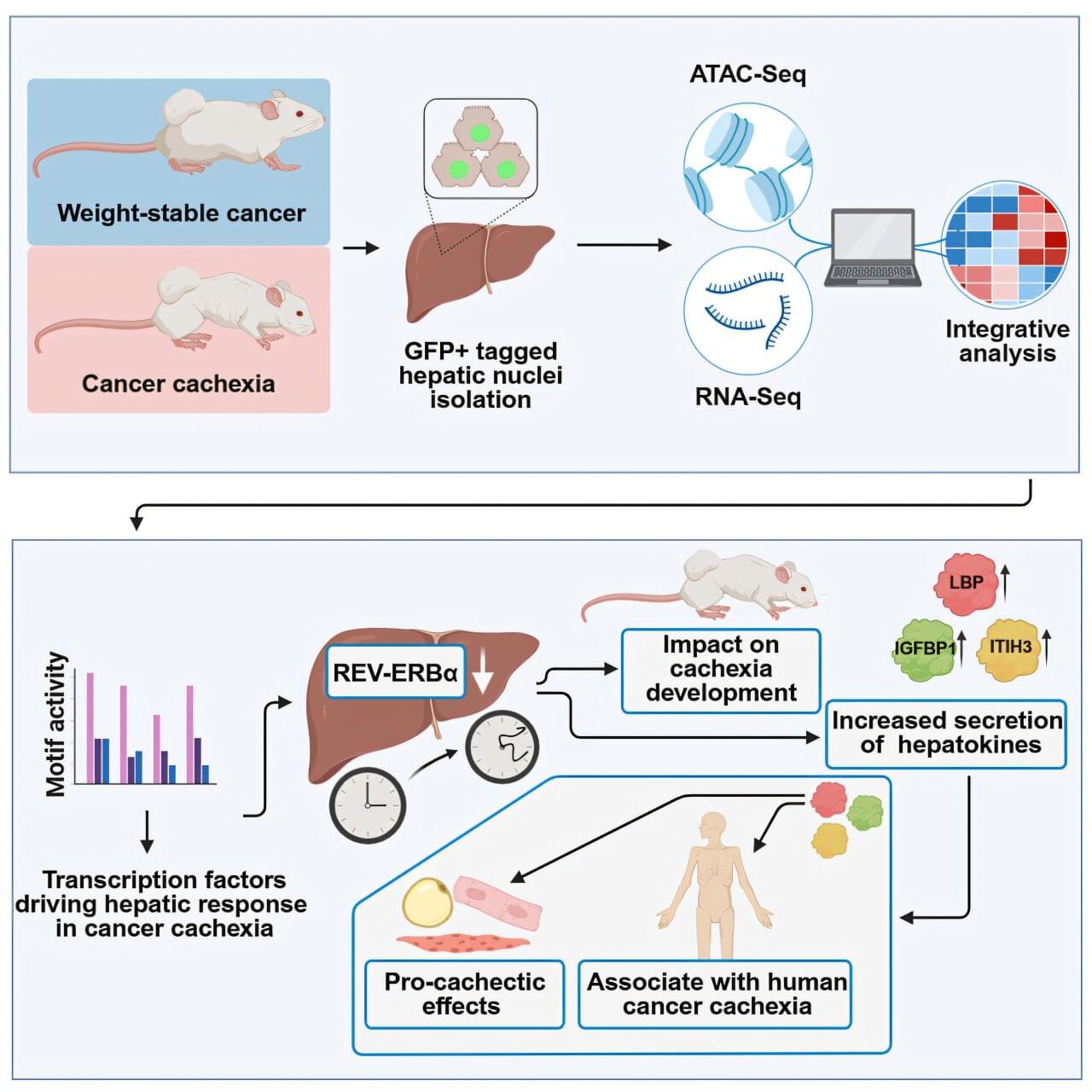
Many people with cancer experience dramatic loss of muscle and fat tissue. In many cases, even the heart muscle is affected, which further weakens the body. This wasting syndrome, known as cachexia, affects around half of all cancer patients. It is a major cause of therapy resistance, complications, and increased mortality.
Researchers from Helmholtz Munich, in collaboration with Heidelberg University Hospital, the Technical University of Munich, and the German Center for Diabetes Research have now identified a previously overlooked driver of cachexia: the liver. It responds systemically to tumors in other organs—such as the intestine or pancreas—and contributes to tissue wasting by releasing specific signaling molecules.
The study is published in the journal Cell.