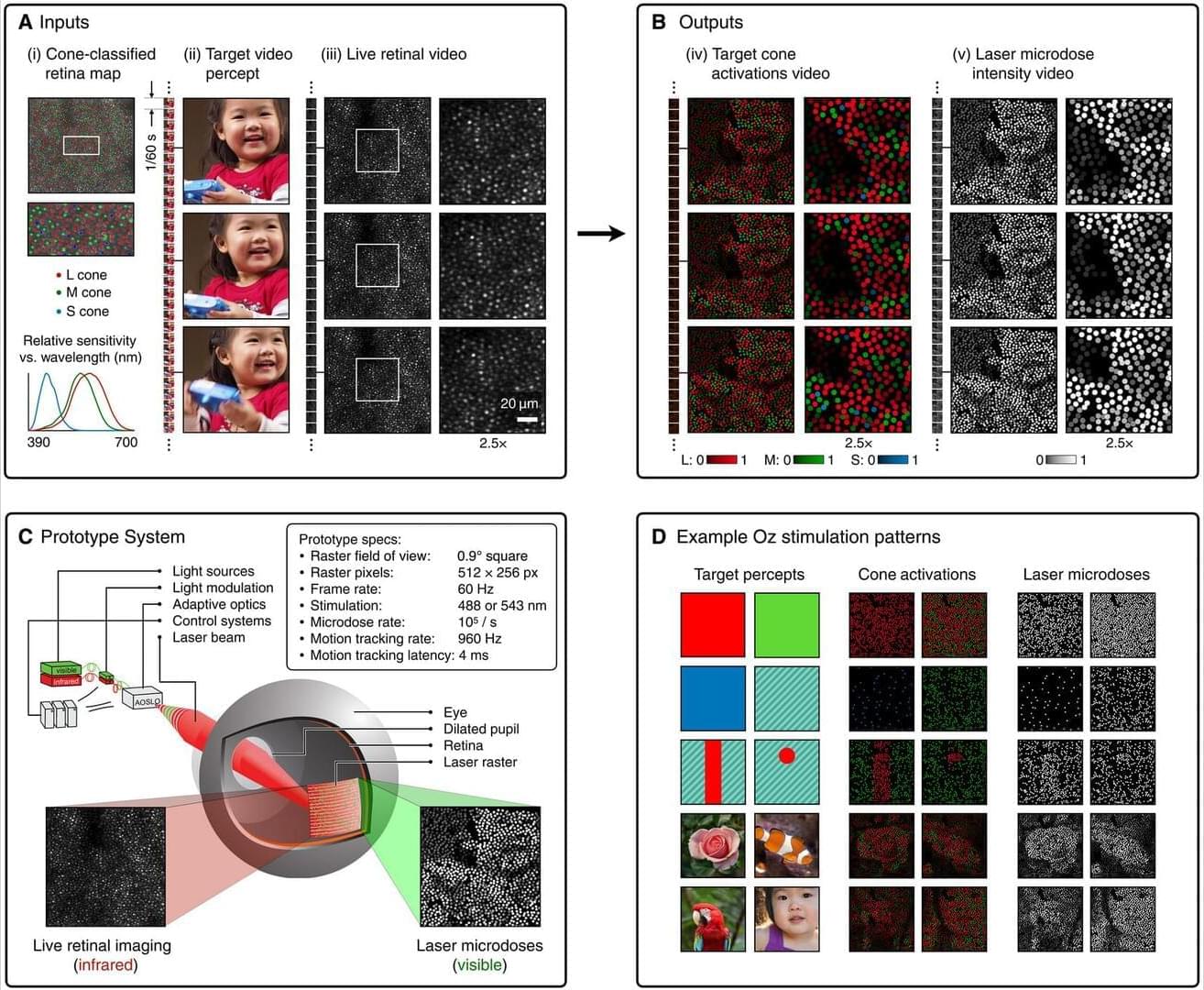
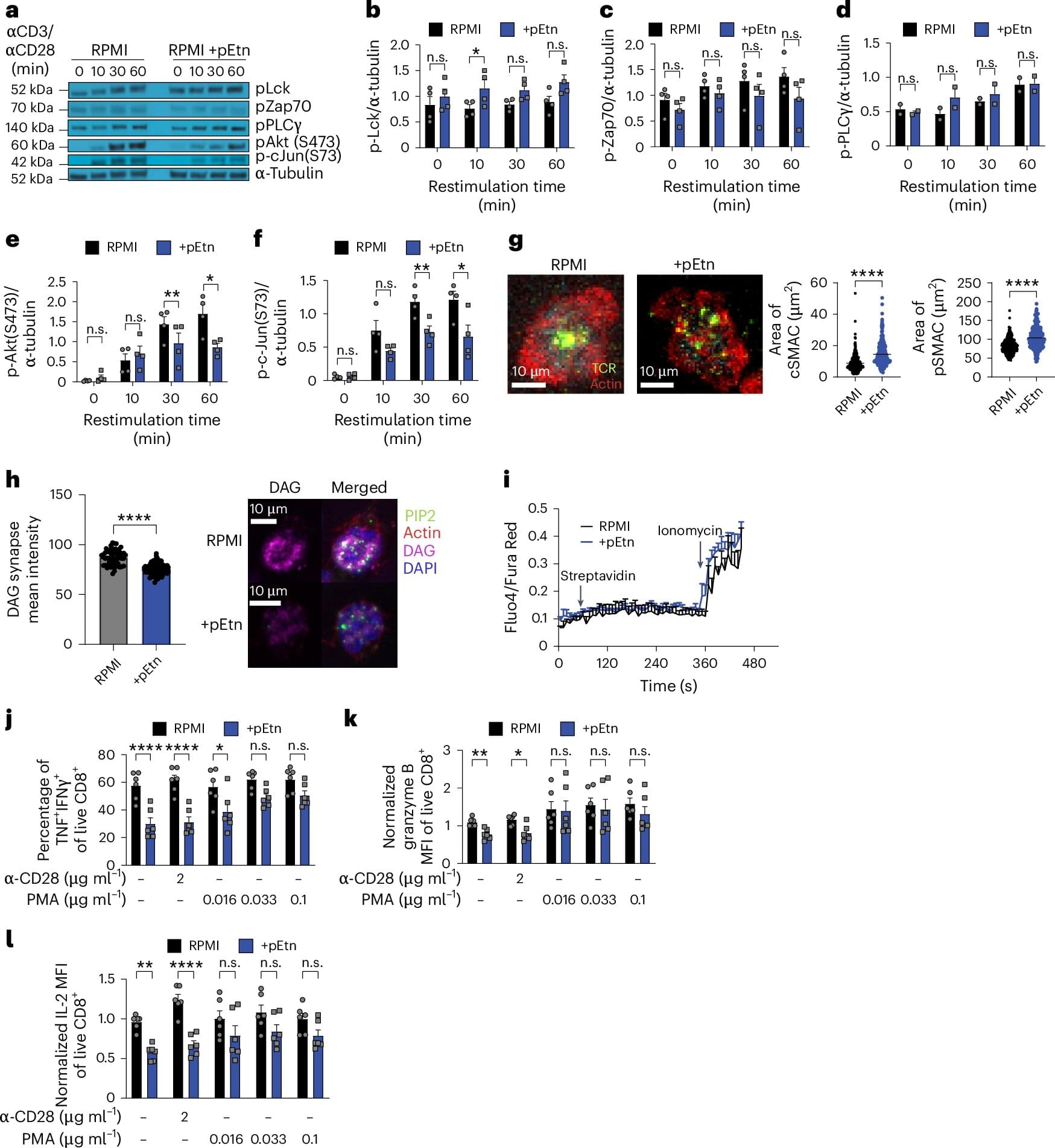
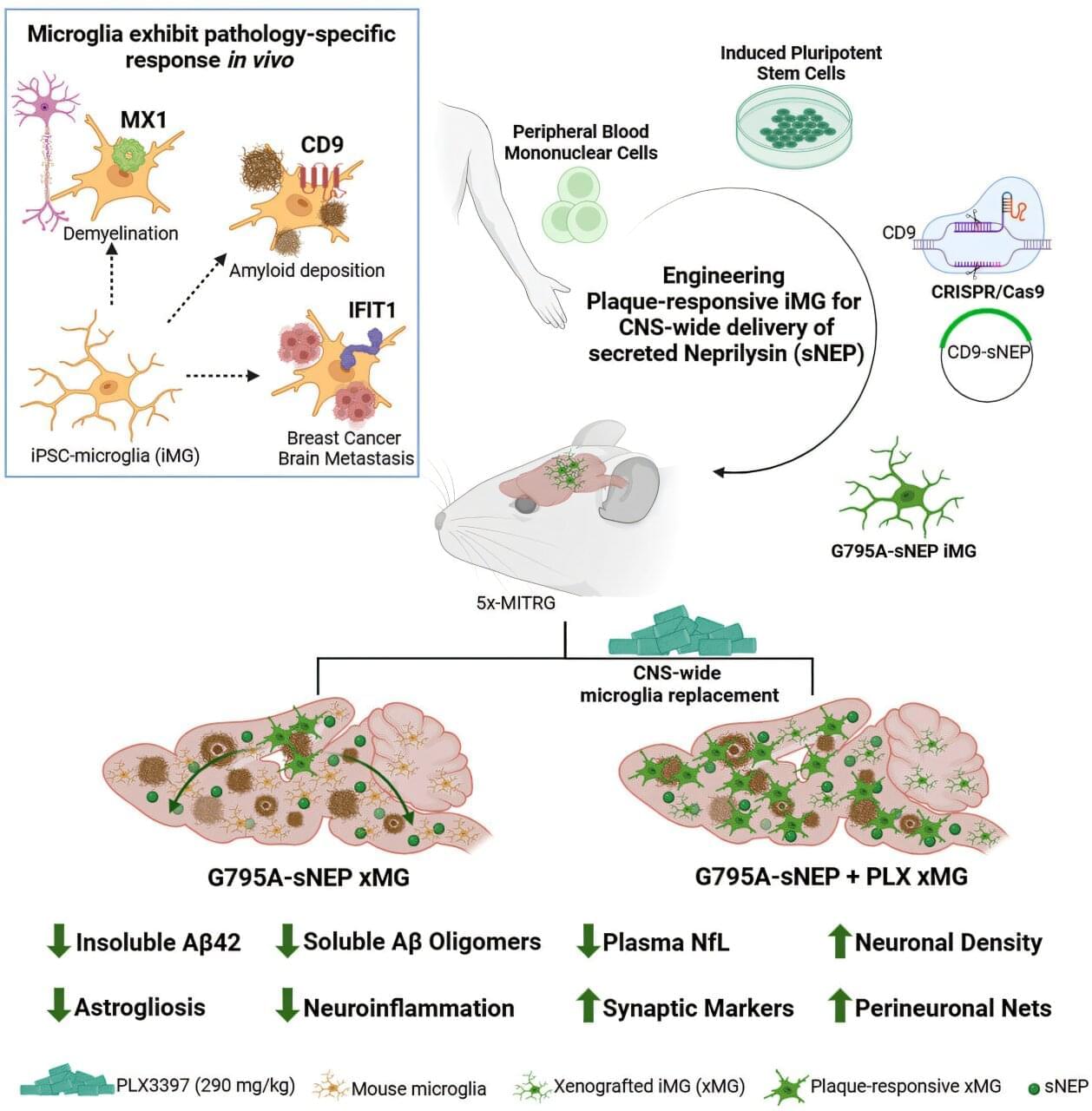
Neutron star mergers are collisions between neutron stars, the collapsed cores of what were once massive supergiant stars. These mergers are known to generate gravitational waves, energy-carrying waves propagating through a gravitational field, which emerge from the acceleration or disturbance of a massive body.
Collisions between neutron stars have been the topic of many theoretical physics studies, as a deeper understanding of these events could yield interesting insights into how matter behaves at extreme densities. The behavior of matter at extremely high densities is currently described by a theoretical framework known as the equation of state (EoS).
Recent astrophysics research has explored the possibility that EoS features, such as phase transitions or a quark-hadron crossover, could be inferred from the gravitational wave spectrum observed after neuron stars have merged. However, most of these theoretical works did not consider the effects of magnetic fields on this spectrum.