Not all stars are created equally. Astronomers believe that the first stars to form after the Big Bang were mostly made of only hydrogen and helium with trace amounts of lithium, as the heavier elements formed later on by nuclear fusion inside the stars. When these stars went supernova, heavier elements spread throughout space and formed more stars. Each successive generation contained more heavy elements, and these elements also became successively heavier.
While most stars still contain mostly hydrogen and helium, they now contain many heavy elements as well, especially as they get older. These elements show up in spectrographic data when astronomers gather light from these distant stars. Stars are considered “pristine” when the data shows a lack of heavy elements—meaning they are likely very rare, older stars from earlier generations. And now, a group of astronomers, led by Alexander Ji from the University of Chicago, believe they have found the most pristine star on record. The group has documented their findings on the arXiv preprint server.
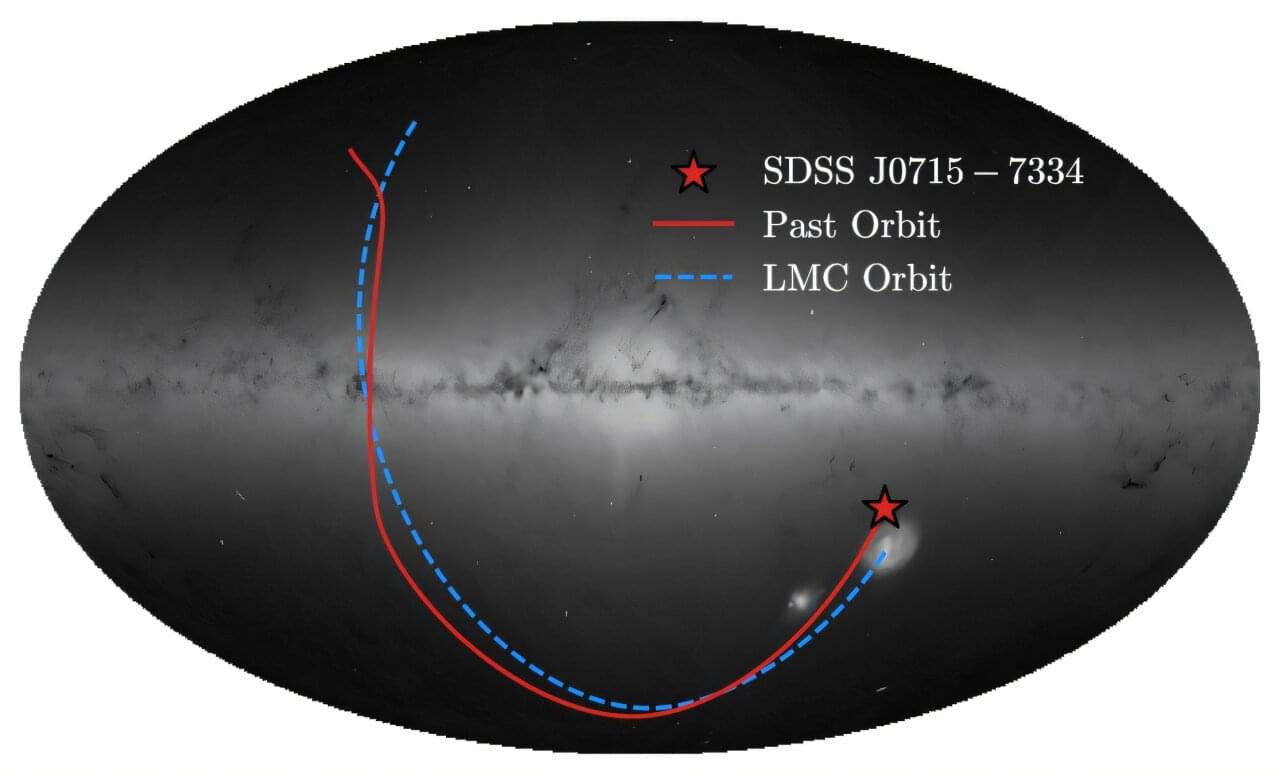
The star, referred to as SDSS J0715-7334, is a red giant purported to have the lowest metallicity—or heavy element content—ever found. The team’s detailed spectral and chemical analysis shows that SDSS J0715-7334 has a total metallicity “Z” of less than 7.8 × 10-7. This is compared to the next lowest metallicity star currently known, a star located in the Milky Way with a total metallicity of around 1.4 × 10-6.