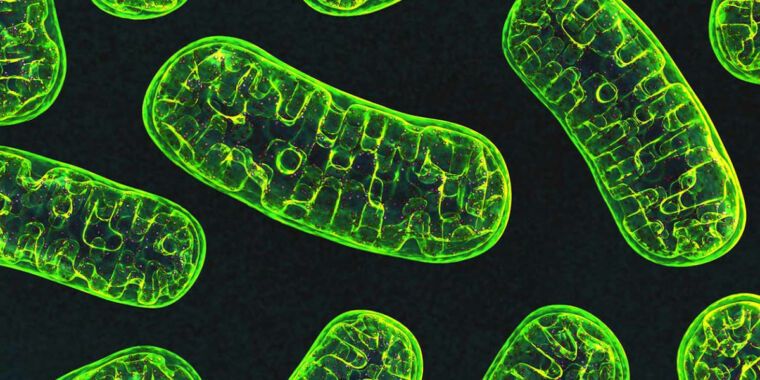
The “powerhouse of the cell” is apparently not necessary for animal life.

Human urine is an promising material in the future where an enormous amount of urine is produced by rapidly growing population.

Scientists from Imperial College London have proposed a new regulatory framework for assessing the impact of AI, called the Human Impact Assessment for Technology (HIAT).
The researchers believe the HIAT could identify the ethical, psychological and social risks of technological progress, which are already being exposed in a growing range of applications, from voter manipulation to algorithmic sentencing.

For now, it’s a simple network. But, it could be an important first step toward smarter and more adaptive prosthetics and brain-computer interfaces — and potentially lay the groundwork for a world where neural implants create real brain networks.
“On one side it sets the basis for a novel scenario that was never encountered during natural evolution, where biological and artificial neurons are linked together and communicate across global networks; laying the foundations for the Internet of Neuro-electronics,” Themis Prodromakis, a nanotechnology researcher and director at the University of Southampton’s Centre for Electronics Frontiers said in a press release.
“On the other hand, it brings new prospects to neuroprosthetic technologies, paving the way towards research into replacing dysfunctional parts of the brain with AI chips.”
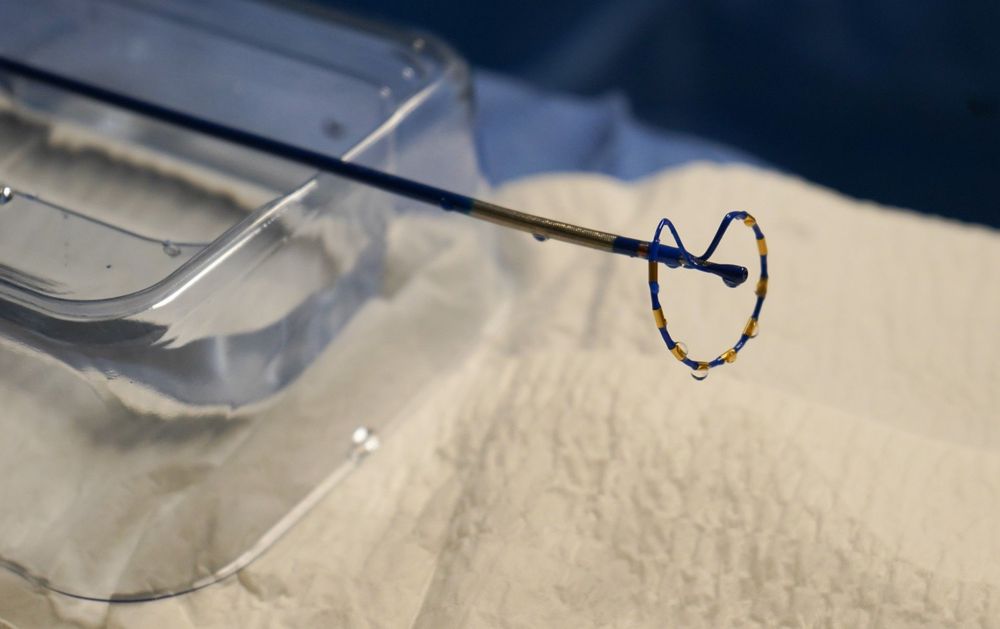
Cardiologists at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center are the first in the United States to test a new type of ablation technology for patients suffering from atrial fibrillation, a common type of irregular heartbeat.
The team is participating in a global clinical trial to assess pulsed field ablation (PFA) technology to treat patients with atrial fibrillation. Developed by.
Ogba Educational Clinic
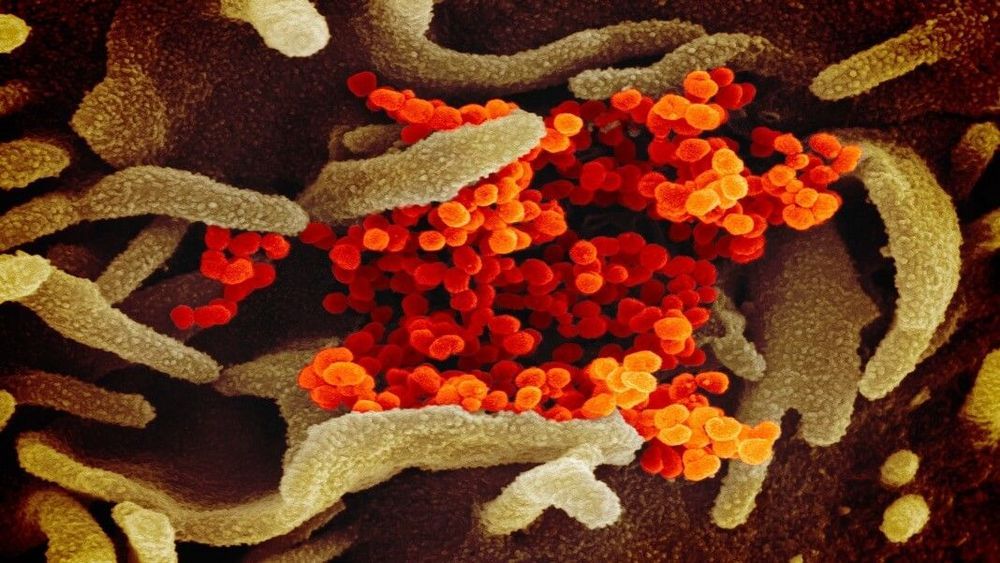
A nightmarish scene was burnt into my memory nearly two decades ago: Changainjie, Beijing’s normally chaotic “fifth avenue,” desolate without a sign of life. Schools shut, subways empty, people terrified to leave their homes. Every night the state TV channels reported new cases and new deaths. All the while, we had to face a chilling truth: the coronavirus, SARS, was so novel that no one understood how it spread or how to effectively treat it. No vaccines were in sight. In the end, it killed nearly 1,000 people.
It’s impossible not to draw parallels between SARS and the new coronavirus outbreak, COVID-19, that’s been ravaging China and spreading globally. Yet the response to the two epidemics also starkly highlights how far biotech and global collaborations have evolved in the past two decades. Advances in genetic sequencing technologies, synthetic biology, and open science are reshaping how we deal with potential global pandemics. In a way, the two epidemics hold up a mirror to science itself, reflecting both technological progress and a shift in ethos towards collaboration.
Let me be clear: any response to a new infectious disease is a murky mix of science, politics, racism, misinformation, and national egos. It’s naïve to point to better viral control and say it’s because of technology alone. Nevertheless, a comparison of the two outbreaks dramatically highlights how the scientific world has changed, for the better, in the last two decades.


D-Wave today announced the launch of Leap 2, the latest version of its quantum cloud service that gives developers real-time access to its hardware quantum systems.
As the company notes, Leap 2 was built with the feedback of thousands of developers in mind who used the previous generation of the service since it launched 18 months ago.
At the core of Leap 2 is D-Wave’s new hybrid solver that can handle complex problems with up to 10,000 variables. As a hybrid system, D-Wave uses both classical and quantum hardware to solve these problems.

Planetary imaging is a fun and rewarding hobby that allows beginners and advanced amateur astronomers to delve into astronomical imaging without much of the expense and complexity of deep space astrophotography. There are also quite a few opportunities for planetary imagers to contribute to some significant scientific research. However, it is important to first understand what equipment is needed to successfully capture images of the solar system. In addition, some basic understanding of our atmosphere and optics are required, which will be addressed in this write-up.