Perseverance will scour mud and clay in Jezero’s river delta and shorelines for signs of microbe communities.




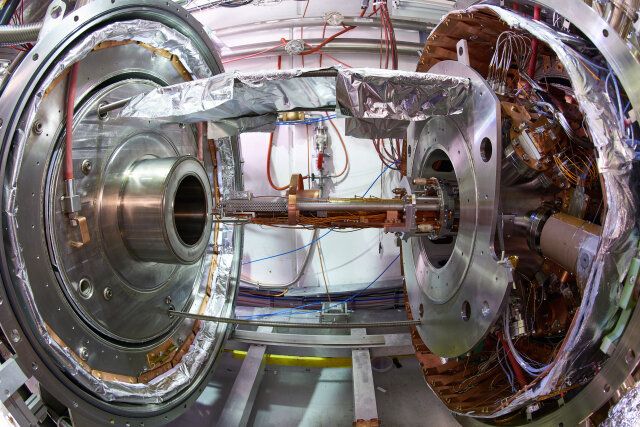
It’s a fundamental law of physics that even the most ardent science-phobe can define: matter falls down under gravity. But what about antimatter, which has the same mass but opposite electrical charge and spin? According to Einstein’s general theory of relativity, gravity should treat matter and antimatter identically. Finding even the slightest difference in their free-fall rate would therefore lead to a revolution in our understanding. While the free fall of matter has been measured with an accuracy of around one part in 100 trillion, no direct measurement for antimatter has yet been performed due to the difficulty in producing and containing large quantities of it.

How much does a power system’s reliability depend on the temperature? Electric power system generator resource adequacy modeling is designed to help determine capacity requirements for electric power system operators across the United States. While calculating resource adequacy requirements has been done for a century, it requires ongoing attention as the generation mix is constantly expanding and changing. A new paper contributes to these ongoing reliability considerations by using a unique data set to determine how both low and high temperatures reduce the reliability of coal, gas, diesel, hydroelectric, and nuclear power generators and thus affect the amount of generation markets should contract for.

Although some researchers are reluctant to share genome data, the field is generally viewed as generous compared with other disciplines. Still, the repositories meant to foster sharing often present barriers to those uploading and downloading data. Researchers tell tales of spending months or years tracking down data sets, only to find dead ends or unusable files. And journal editors and funding agencies struggle to monitor whether scientists are sticking to their agreements.
Data sharing was a core principle that led to the success of the Human Genome Project 20 years ago. Now scientists are struggling to keep information free.

A novel computer algorithm, or set of rules, that accurately predicts the orbits of planets in the solar system could be adapted to better predict and control the behavior of the plasma that fuels fusion facilities designed to harvest on Earth the fusion energy that powers the sun and stars.
The algorithm, devised by a scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), applies machine learning, the form of artificial intelligence (AI) that learns from experience, to develop the predictions. “Usually in physics, you make observations, create a theory based on those observations, and then use that theory to predict new observations,” said PPPL physicist Hong Qin, author of a paper detailing the concept in Scientific Reports. “What I’m doing is replacing this process with a type of black box that can produce accurate predictions without using a traditional theory or law.”
Qin (pronounced Chin) created a computer program into which he fed data from past observations of the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, and the dwarf planet Ceres. This program, along with an additional program known as a “serving algorithm,” then made accurate predictions of the orbits of other planets in the solar system without using Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation. “Essentially, I bypassed all the fundamental ingredients of physics. I go directly from data to data,” Qin said. “There is no law of physics in the middle.”

UK-based BenevolentAI has dosed the first patient in its first-in-human clinical trial of its novel multi-target drug, BEN-2293, for treating atopic dermatitis (AD).
Designed and developed using BenevolentAI’s scientific and technical expertise, BEN-2293 is a potent and selective small-molecule Pan-Trk antagonist formulated for topical delivery.
BenevolentAI has dosed the first patient in its clinical trial of its novel multi-target drug, BEN-2293, for treating atopic dermatitis (AD).
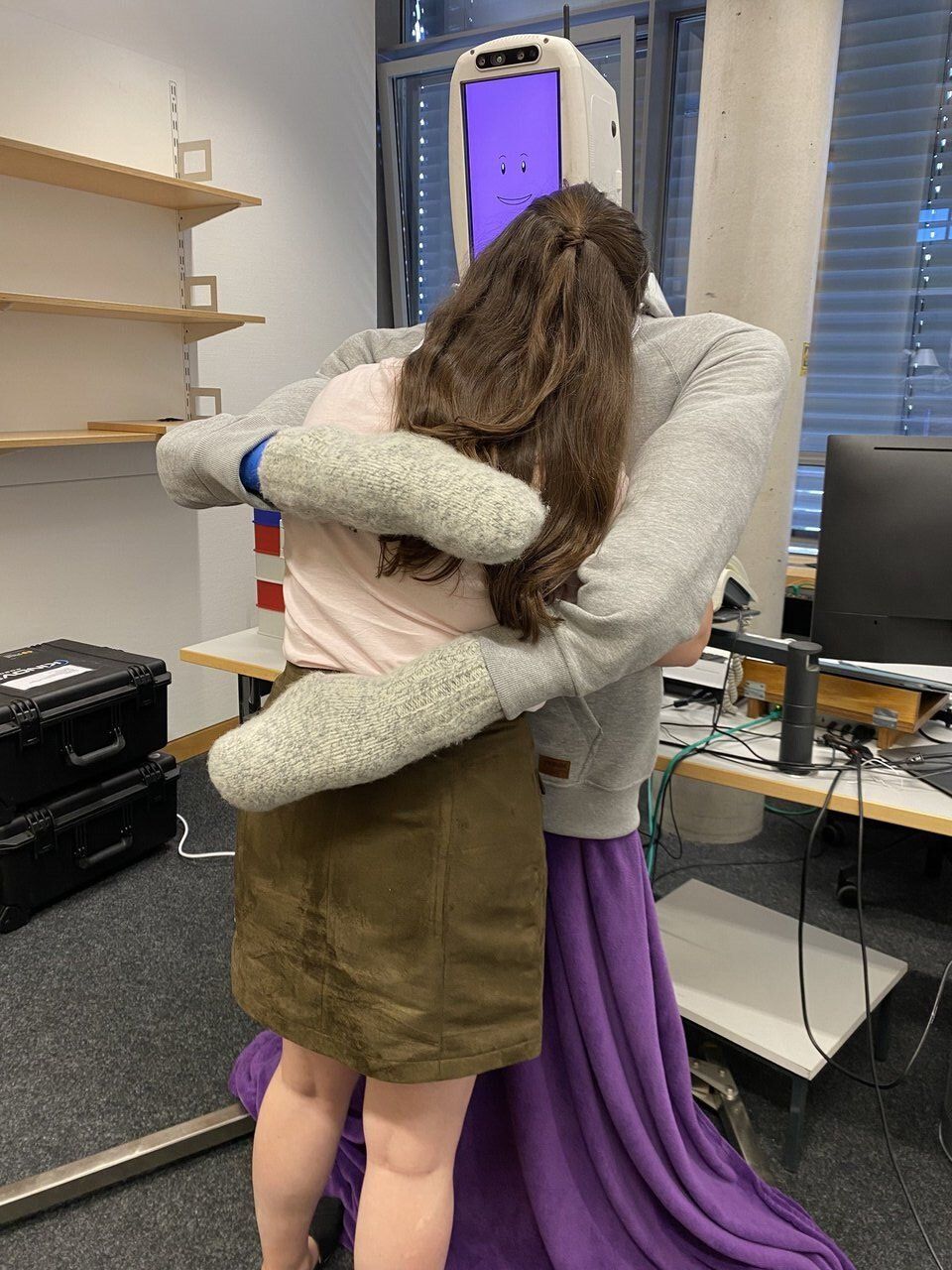


Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) and ETH Zürich have recently created HuggieBot 2.0, a robot that can hug users at their request. This robot, set to be presented at the ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) in March, builds on a previous robotic system created by Alexis E. Block, one of the authors, during her Master’s degree.