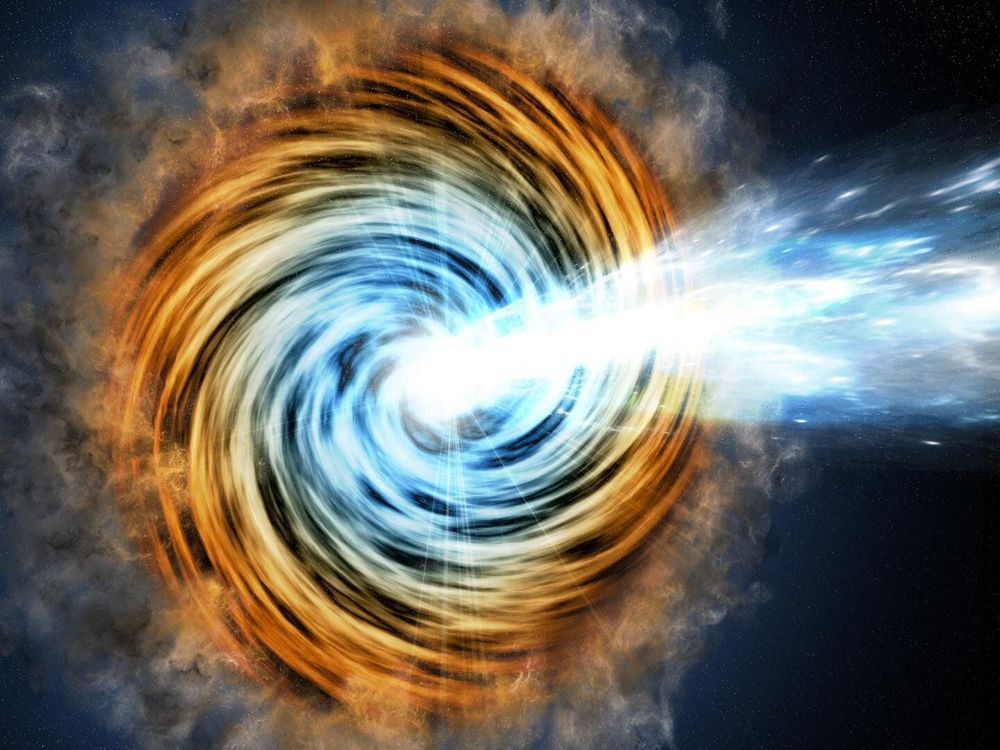
An international team of astronomers has identified one of the rarest known classes of gamma-ray emitting galaxies, called BL Lacertae, within the first 2 billion years of the age of the Universe. The team, that has used one of the largest optical telescope in the world, Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC), located at the Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos (Garafía, La Palma), consists of researchers from the Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM, Spain), DESY (Germany), University of California Riverside and Clemson University (USA). Their finding is published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Only a small fraction of galaxies emits gamma rays, which are the most extreme form of light. Astronomers believe that these highly energetic photons originate from the vicinity of a supermassive black hole residing at the centers of these galaxies. When this happens, they are known as active galaxies. The black hole swallows matter from its surroundings and emits jets or, in other words, collimated streams of matter and radiation. Few of these active galaxies (less than 1%) have their jets pointing by chance toward Earth. Scientists call them blazars and are one of the most powerful sources of radiation in the universe.
Blazars come in two flavors: BL Lacertae (BL Lac) and flat-spectrum radio-quasars (FSRQs). Our current understanding about these mysterious astronomical objects is that FSRQs are relatively young active galaxies, rich in dust and gas that surround the central black hole. As time passes, the amount of matter available to feed the black hole is consumed and the FSRQ evolves to become a BL Lac object. “In other words, BL Lacs may represent the elderly and evolved phase of a blazar’s life, while FSRQs resemble an adult,” explains Vaidehi Paliya, a DESY researcher who participated in this program.