A Twitter teardown of digital pregnancy tests reveals the complicated 8-bit processor inside. These digital tests still use a paper strip to record the test, and literally read the result and convert it into an LCD display.



Just playing around with the SpaceX footage from last nights SN6 hop. Enlarged and enhanced the video so we could zoom in on SN6 and the 2nd half of the video I slow it down X5.

Nuclear startup NuScale has received a landmark final safety evaluation report (FSER) for its modular reactor design, making it the first American modular design to reach this point. NuScale’s design uses classic nuclear fission water reactor technology in a much smaller form factor, which contrasts with the escalating sizes of most current nuclear plant construction around the world.
☢️ You like nuclear. So do we. Let’s nerd out over nuclear together.
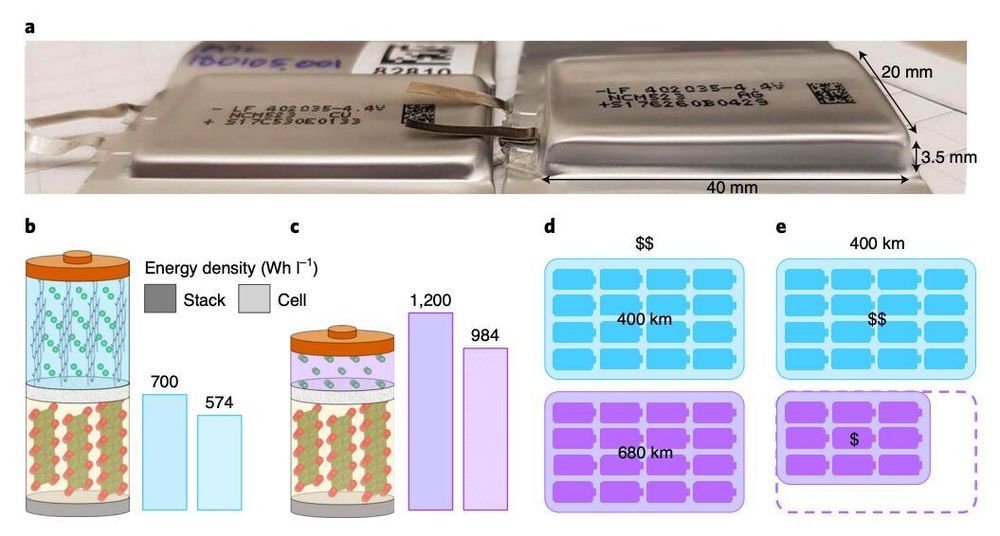
Batteries with high energy densities could enable the creation of a wider range of electric vehicles, including flying vehicles that can transport humans in urban environments. Past studies predict that to support the operation of vehicles capable of take-off and landing, batteries require energy densities of approximately 400 Wh kg-1 at the cell level, which is approximately 30% higher than the energy density of most existing lithium-ion (Li-ion) cells.
In addition to powering flying vehicles, high-energy cells (i.e., single units within a battery that convert chemical into electrical energy) could increase the distance that electric cars can travel before they need to be charged again. They may also reduce overall fabrication costs for electric vehicles, as similar results could be achieved using fewer but better-performing cells.
Anode-free lithium metal cells are particularly promising for creating batteries with higher energy densities. While they use the same cathode as Li-ion cells, these cells store energy via an electroplated lithium metal instead of a graphite host, and they can have energy densities that are 60% greater than those of Li-ion cells.

For years, researchers have aimed to learn more about a group of metal oxides that show promise as key materials for the next generation of lithium-ion batteries because of their mysterious ability to store significantly more energy than should be possible. An international research team, co-led by The University of Texas at Austin, has cracked the code of this scientific anomaly, knocking down a barrier to building ultra-fast battery energy storage systems.
The team found that these metal oxides possess unique ways to store energy beyond classic electrochemical storage mechanisms. The research, published in Nature Materials, found several types of metal compounds with up to three times the energy storage capability compared with materials common in today’s commercially available lithium-ion batteries.
By decoding this mystery, the researchers are helping unlock batteries with greater energy capacity. That could mean smaller, more powerful batteries able to rapidly deliver charges for everything from smartphones to electric vehicles.
A hand-held video game console allowing indefinite gameplay might be a parent’s worst nightmare.
But this Game Boy is not just a toy. It’s a powerful proof-of-concept, developed by researchers at Northwestern University and the Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in the Netherlands, that pushes the boundaries of battery-free intermittent computing into the realm of fun and interaction.
Instead of batteries, which are costly, environmentally hazardous and ultimately end up in landfills, this device harvests energy from the sun—and the user. These advances enable gaming to last forever without having to stop and recharge the battery.
Qualcomm Technologies announced Monday that it conducted the first successful extended range 5G data call over mmWave.
Range has been a key obstacle for cellphone carriers as they move to mmWave technology to take advantage of faster 5G speeds. Qualcomm’s breakthrough could speed up deployment of 5G smartphones.
Qualcomm reported that it conducted a 5G call over a 2.36 mile distance, double the distance that it had projected when it unveiled its new antenna system last year. Qualcomm worked with Casa Systems, an ultra-broadband provider, and Ericsson, the multinational telecommunications company, on the project.
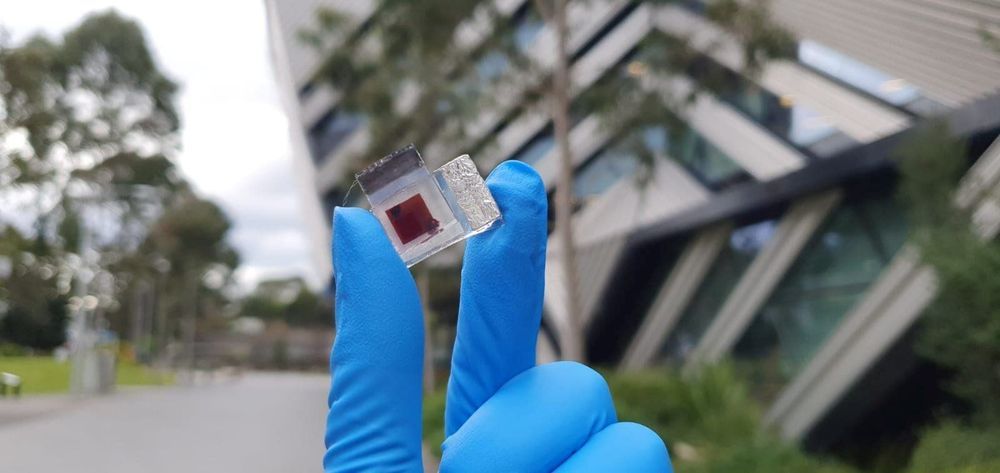
Dye-sensitized solar cells used in low-light conditions could perform more consistently thanks to improved understanding of the role additives play in optimizing electrolytes.
Laptops and mobile phones, among other devices, could be charged or powered indoors, away from direct sunlight, using dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs), which have achieved efficiencies of up to 34% at 1000 lux from a fluorescent lamp.
Copper-based electrolytes containing various combinations of additives have been used to achieve these efficiencies, with varying results to date.