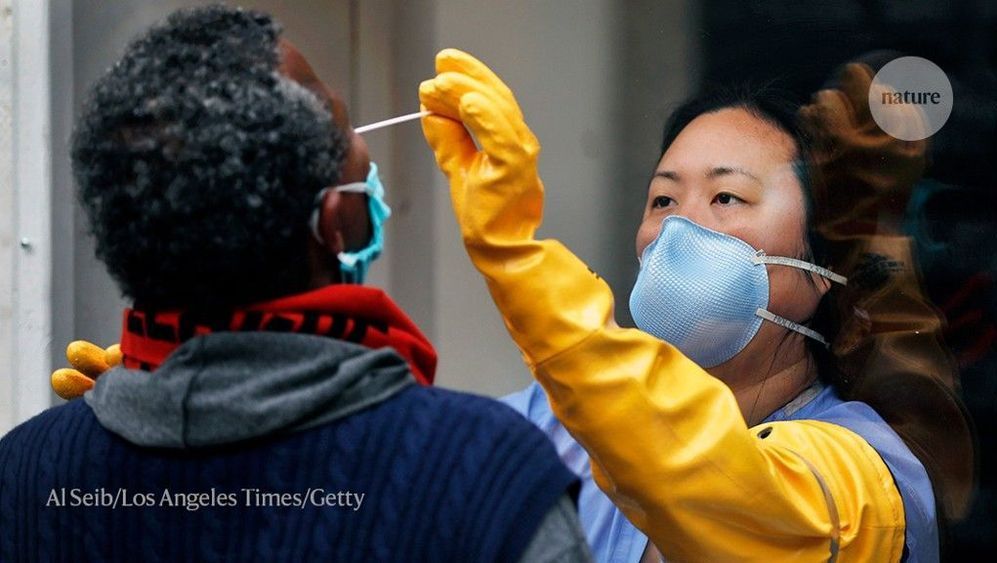
The kit has been granted approval under ‘emergency use’ provisions, and should help to ease testing backlogs in the country.


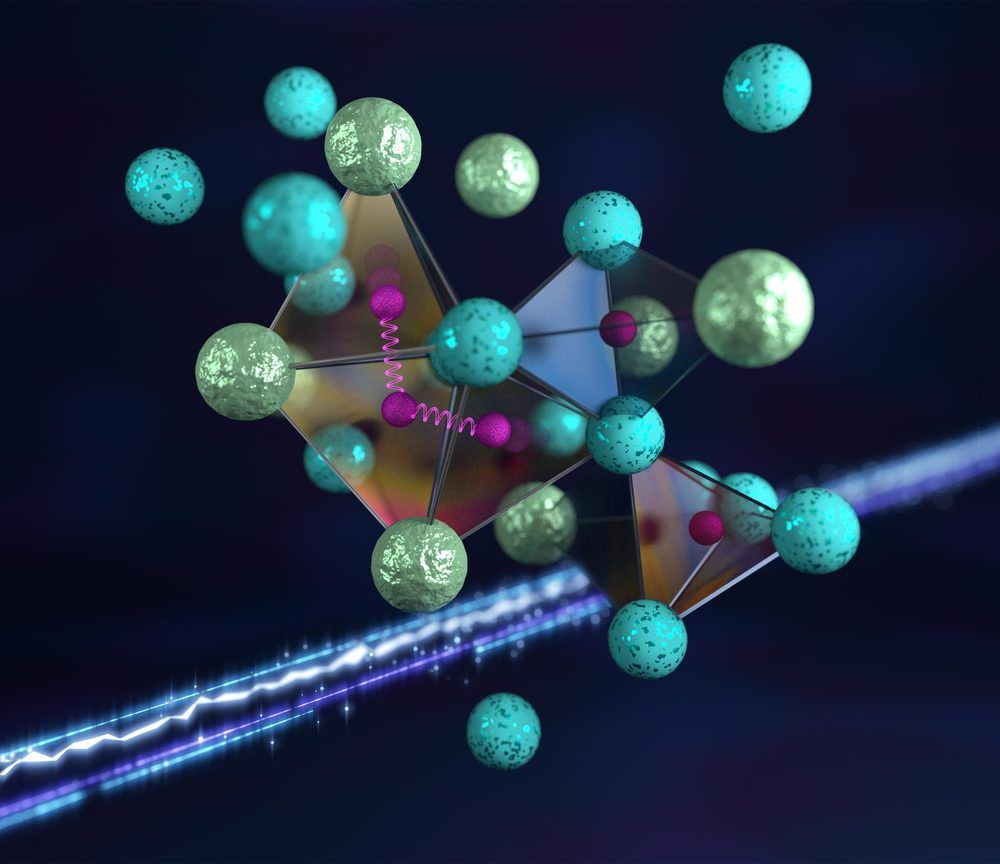
An international team of researchers has discovered the hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride material are much more tightly spaced than had been predicted for decades — a feature that could possibly facilitate superconductivity at or near room temperature and pressure.
Such a superconducting material, carrying electricity without any energy loss due to resistance, would revolutionize energy efficiency in a broad range of consumer and industrial applications.
The scientists conducted neutron scattering experiments at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory on samples of zirconium vanadium hydride at atmospheric pressure and at temperatures from −450 degrees Fahrenheit (5 K) to as high as −10 degrees Fahrenheit (250 K) — much higher than the temperatures where superconductivity is expected to occur in these conditions.
Circa 2016
Researchers build “teeny, tiny structures” that can change infrared to visible light.
Remember that famous Bin Laden raid? It would have been impossible without night vision — specifically, a pair of $65,000 L-3 Ground Panoramic Night Vision Goggles. But even those top-of-the-line NVGs — former Navy SEAL Matt Bissonette compared other night-vision systems to “looking through toilet paper tubes” — are heavy, clunky, and odd-looking. Now researchers from Australia have developed a material that can make infrared light visible, raising the possibility of night-vision goggles as thin as glass and free of external power.
Conventional night vision goggles look a bit like binoculars and require electricity. Here’s how they work: An “objective lens” in front collects low-level and near-infrared light, whose photons are converted by a photocathode into electrons. The goggles use thousands of volts of electricity to send the electrons down a vacuum-sealed tube into a plate with millions of tiny holes. Pushing the electrons through the holes releases other electrons in a chain reaction called cascaded secondary emission. The effect: where there was one electron, there are now hundreds, all in the same pattern as the original photons. When the electrons hit the final layer, which is covered in phosphorescent material, what was dark becomes light.
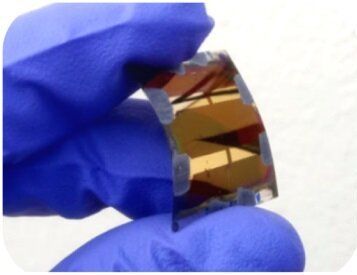
A revolution is underway in the development of autonomous wireless sensors, low-power consumer electronics, smart homes, domotics and the Internet of Things. All the related technologies require efficient and easy-to-integrate energy harvesting devices for their power. Billions of wireless sensors are expected to be installed in interior environments in coming decades.
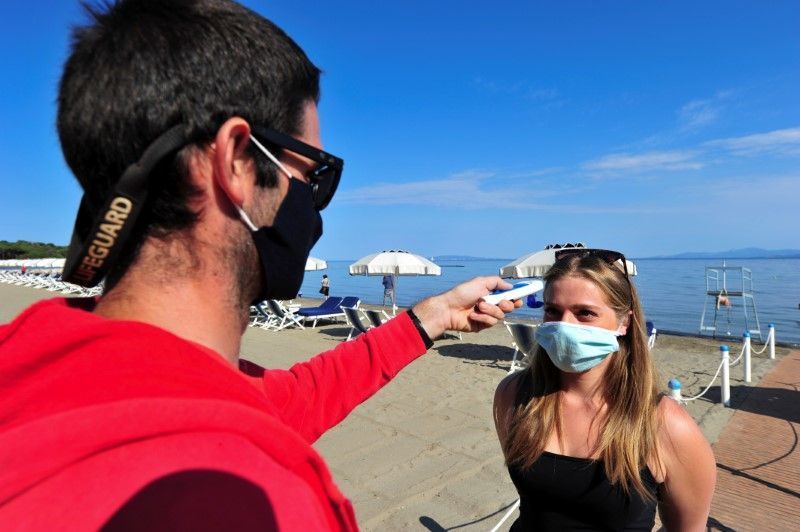


ROME (Reuters) — The new coronavirus is losing its potency and has become much less lethal, a senior Italian doctor said on Sunday.
“In reality, the virus clinically no longer exists in Italy,” said Alberto Zangrillo, the head of the San Raffaele Hospital in Milan in the northern region of Lombardy, which has borne the brunt of Italy’s coronavirus contagion.
“The swabs that were performed over the last 10 days showed a viral load in quantitative terms that was absolutely infinitesimal compared to the ones carried out a month or two months ago,” he told RAI television.

#ICYMI: NASA astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley aboard the SpaceX Dragon Endeavour arrived at the International Space Station and docked today, May 31, 2020, at the station’s Harmony port at 10:16 a.m. ET.
Following soft capture, 12 hooks were closed to complete a hard capture at 10:27 a.m. ET.
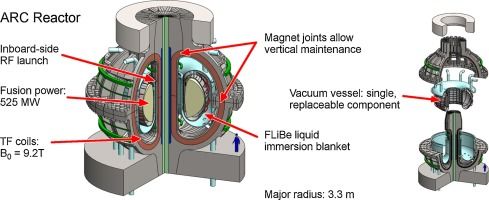
Circa 2015
The affordable, robust, compact (ARC) reactor is the product of a conceptual design study aimed at reducing the size, cost, and complexity of a combined fusion nuclear science facility (FNSF) and demonstration fusion Pilot power plant. ARC is a ∼200–250 MWe tokamak reactor with a major radius of 3.3 m, a minor radius of 1.1 m, and an on-axis magnetic field of 9.2 T. ARC has rare earth barium copper oxide (REBCO) superconducting toroidal field coils, which have joints to enable disassembly. This allows the vacuum vessel to be replaced quickly, mitigating first wall survivability concerns, and permits a single device to test many vacuum vessel designs and divertor materials. The design point has a plasma fusion gain of Qp ≈ 13.6, yet is fully non-inductive, with a modest bootstrap fraction of only ∼63%. Thus ARC offers a high power gain with relatively large external control of the current profile. This highly attractive combination is enabled by the ∼23 T peak field on coil achievable with newly available REBCO superconductor technology. External current drive is provided by two innovative inboard RF launchers using 25 MW of lower hybrid and 13.6 MW of ion cyclotron fast wave power. The resulting efficient current drive provides a robust, steady state core plasma far from disruptive limits. ARC uses an all-liquid blanket, consisting of low pressure, slowly flowing fluorine lithium beryllium (FLiBe) molten salt. The liquid blanket is low-risk technology and provides effective neutron moderation and shielding, excellent heat removal, and a tritium breeding ratio ≥ 1.1. The large temperature range over which FLiBe is liquid permits an output blanket temperature of 900 K, single phase fluid cooling, and a high efficiency helium Brayton cycle, which allows for net electricity generation when operating ARC as a Pilot power plant.