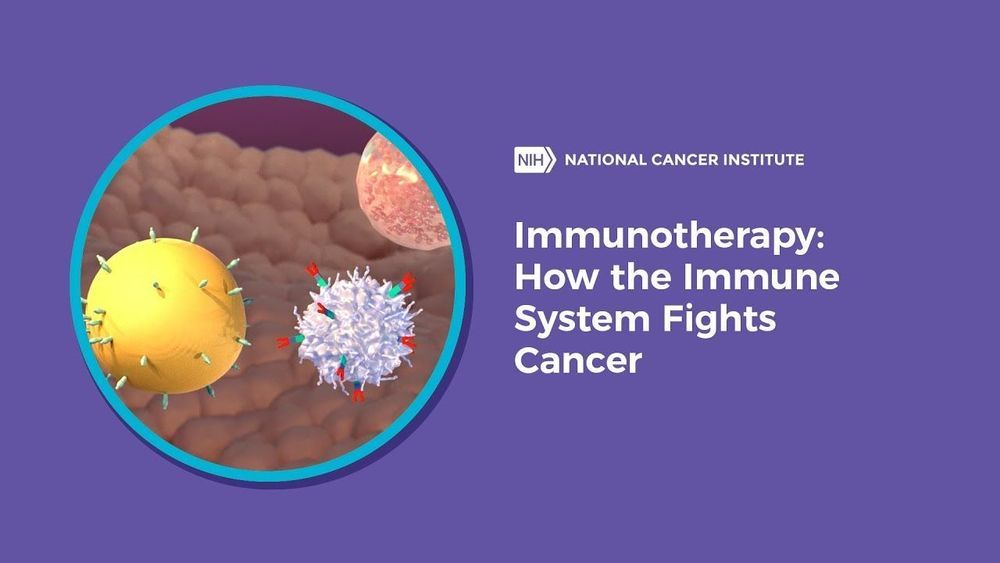
The recent clinical trial was only conducted on patients with lymphoma, but the researchers suggested their approach could be potentially used to treat other types of cancer — and that it could improve the efficacy of other immunotherapies, including checkpoint blockade.
“The in situ vaccine approach has broad implications for multiple types of cancer,” said Brody, the study’s lead author and the director of the Lymphoma Immunotherapy Program at The Tisch Cancer Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “This method could also increase the success of other immunotherapies such as checkpoint blockade.”
Related Articles Around the Web.