At the quantum level, the past and the future are indiscernible. That could have profound effects on the world we can see.


Researchers at the University of Tokyo have developed a 3D cooling system that uses boiling water to dissipate heat from microchips up to seven times more efficiently than conventional methods.
Until now, Google’s Android XR glasses had only appeared in carefully curated teaser videos and limited hands-on previews shared with select publications. These early glimpses hinted at the potential of integrating artificial intelligence into everyday eyewear but left lingering questions about real-world performance. That changed when Shahram Izadi, Google’s Android XR lead, took the TED stage – joined by Nishtha Bhatia – to demonstrate the prototype glasses in action.
The live demo showcased a range of features that distinguish these glasses from previous smart eyewear attempts. At first glance, the device resembles an ordinary pair of glasses. However, it’s packed with advanced technology, including a miniaturized camera, microphones, speakers, and a high-resolution color display embedded directly into the lens.
The glasses are designed to be lightweight and discreet, with support for prescription lenses. They can also connect to a smartphone to leverage its processing power and access a broader range of apps.
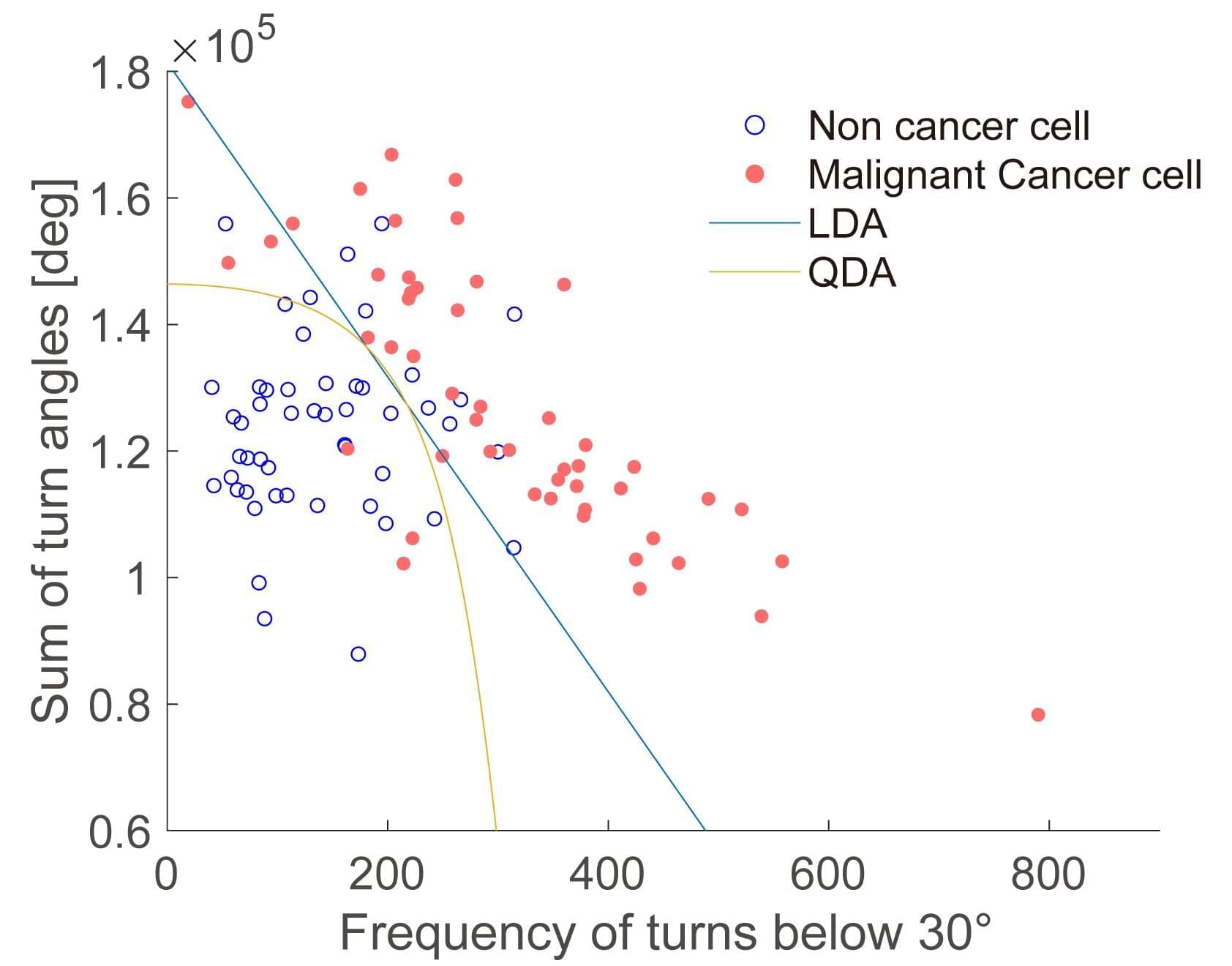
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma cells and healthy fibroblasts on a dish and found that tracking and analysis of their paths can be used to differentiate them with up to 94% accuracy.
Beyond diagnosis, their technique may also shed light on cell motility-related functions, like tissue healing. The paper is published in the journal PLOS ONE.
While scientists and medical experts have been looking at cells under the microscope for many centuries, most studies and diagnoses focus on their shape, what they contain, and where different parts are located inside. But cells are dynamic, changing over time, and are known to be able to move.

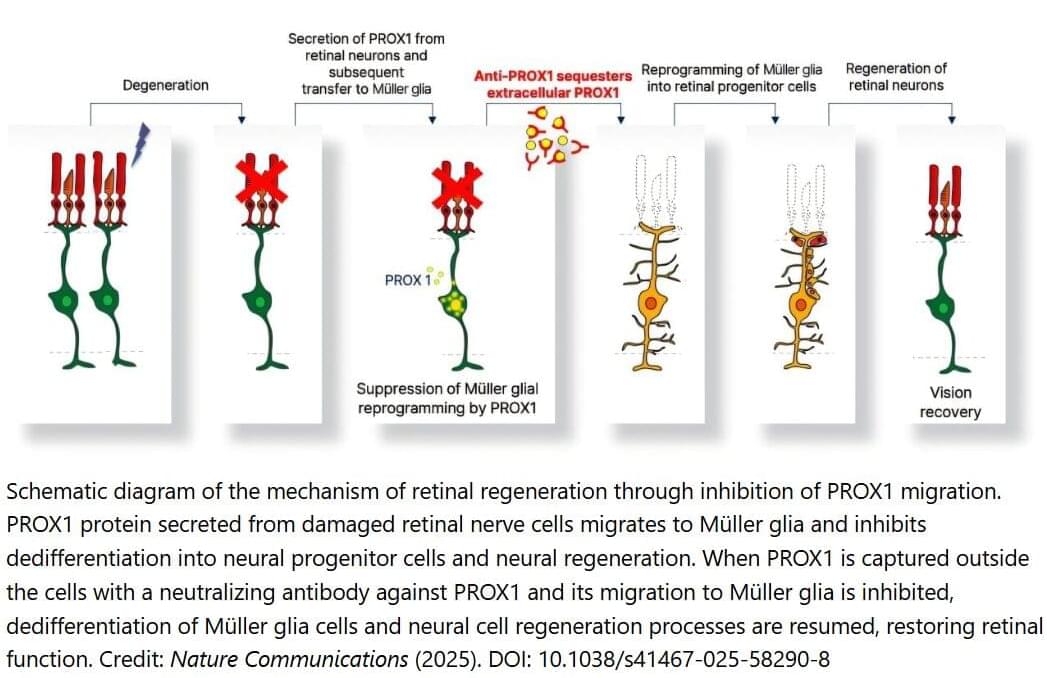
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet more than 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have successfully slowed disease progression, no effective therapy has been developed to restore already lost vision—until now.
KAIST researchers led by Professor Jinwoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences have successfully developed a novel drug to restore vision through retinal nerve regeneration. The research is published in the journal Nature Communications. The study was co-authored by Dr. Eun Jung Lee of Celliaz Inc. and Museong Kim, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST, as joint first authors.
The research team successfully induced neural regeneration and vision recovery in a disease-model mouse by administering a compound that blocks the PROX1 (Prospero Homeobox 1) protein, which suppresses retinal regeneration. The effect lasted for more than six months.
Are black holes really cosmic shredders—or are they complex quantum structures storing everything they consume? Discover the revolutionary Supermaze Hypothesis and Fuzzball Theory in this deep dive into black hole physics, quantum mechanics, and string theory. This could change everything we know about the universe!
Paper link : https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.
Chapters:
00:00 Introduction.
00:44 Inside the Supermaze – A New Perspective from String Theory.
02:42 The Fuzzball Revolution – Solving the Information Paradox.
04:43 Scientific Debate and the Road to the Theory of Everything.
06:57 Outro.
07:16 Enjoy.
MUSIC TITLE: Starlight Harmonies.
MUSIC LINK: https://pixabay.com/music/pulses-star… our website for up-to-the-minute updates: www.nasaspacenews.com Follow us Facebook: / nasaspacenews Twitter:
/ spacenewsnasa Join this channel to get access to these perks:
/ @nasaspacenewsagency #NSN #NASA #Astronomy#BlackHole #SupermazeHypothesis #FuzzballTheory #QuantumPhysics #StringTheory #MTheory #EventHorizon #HawkingRadiation #InformationParadox #CosmicMysteries #QuantumGravity #Branes #QuantumMaze #PhysicsExplained #SpaceTime #BlackHoleTheory #Astrophysics #Cosmology #QuantumUniverse #TheoryOfEverything #BlackHoleInfoParadox #StephenHawking #SamirMathur #NicholasWarner #QuantumEntanglement #ScienceExplained #GravitationalWaves #LIGO #EventHorizonTelescope #QuantumReality.
Visit our website for up-to-the-minute updates:
www.nasaspacenews.com.
Follow us.

is a universal constant for functions approaching chaos via period doubling. It was discovered by Feigenbaum in 1975 (Feigenbaum 1979) while studying the fixed points of the iterated function.
From the gritty realities of founding an AI startup to the global AI race and the future of superhuman intelligence, Eric Schmidt, former Google CEO and current CEO of Relativity Space shares hard truths, leadership insights, and a bold vision for AI’s next frontier. Will the US reclaim the lead, or is China set to dominate?
Timestamps:
0:00 Intro.
1:36 Eric Schmidt Introduces himself.
2:06 The Founder’s Journey: Joining Early Stage Company vs. Founding.
4:20 Why Sometimes Is It Better to Join NOT as a Founder?