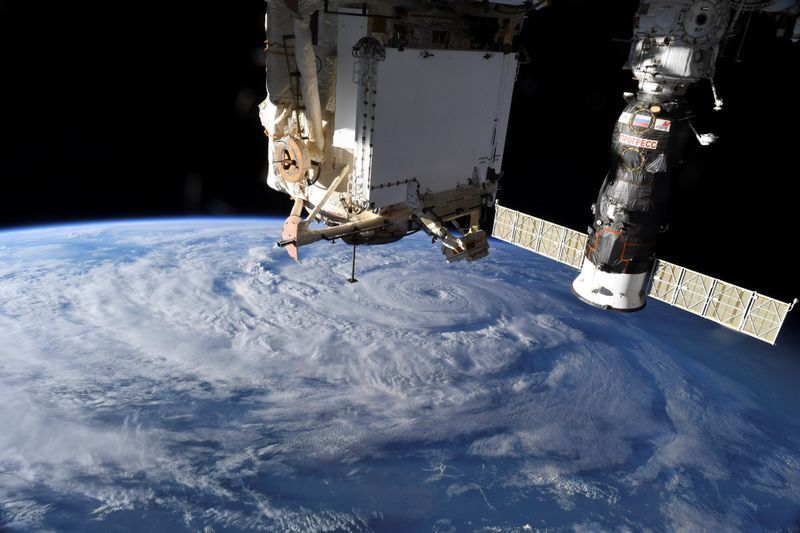
MOSCOW (Reuters) — The International Space Station is leaking air in above-normal volumes, but the leak presents no danger to the Russian-American crew, the Russian space agency Roscosmos said on Tuesday.
The leak has been localised to one section of a service module and the crew, made up of U.S. astronaut Chris Cassidy and Russian cosmonauts Anatoly Ivanishin and Ivan Vagner, plan to eliminate it in the coming days, Russia’s RIA news agency quoted Roscosmos executive director Sergei Krikalev as saying.
Roscosmos said additional air may be delivered to the station.