HSC J023336-053022, a massive galaxy cluster located approximately 4 billion light-years away from Earth, is heating the material within it to hundreds of millions of degrees Celsius — over 25 times hotter than the core of the Sun.


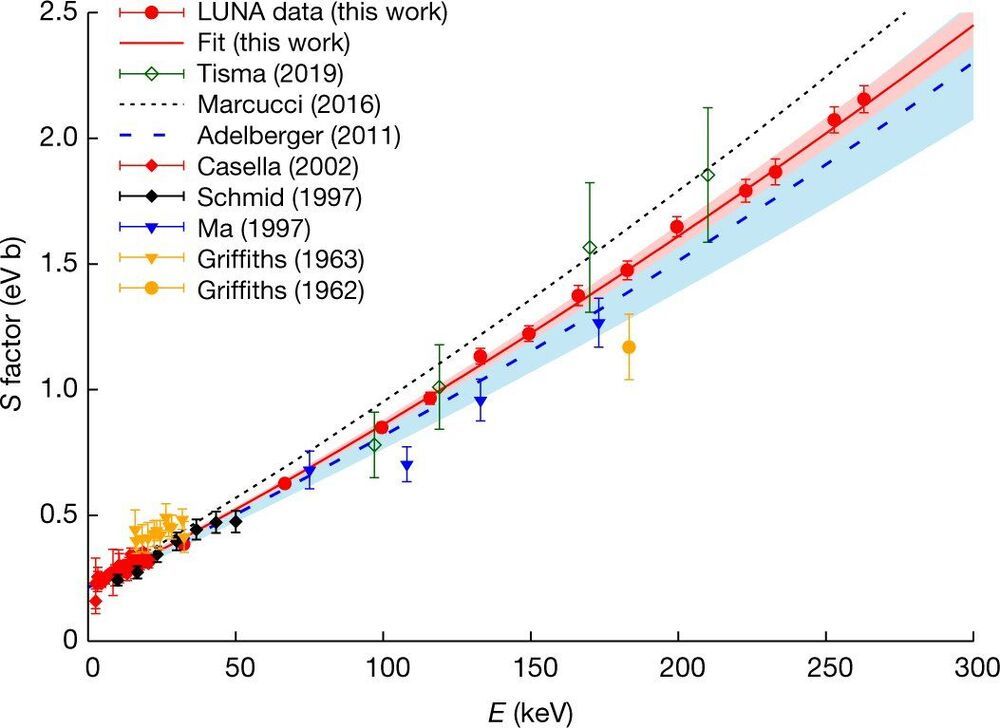
A large team of researchers affiliated with a host of institutions in Italy, the U.K and Hungary has carried out the most precise measurements yet of deuterium fusing with a proton to form helium-3. In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes their effort and how they believe it will contribute to better understanding the events that transpired during the first few minutes after the Big Bang.
Astrophysics theory suggests that the creation of deuterium was one of the first things that happened after the Big Bang. Therefore, it plays an important role in Big Bang nucleosynthesis—the reactions that happened afterward that led to the production of several of the light elements. Theorists have developed equations that show the likely series of events that occurred, but to date, it has been difficult to prove them correct without physical evidence. In this new effort, the researchers working at the Laboratory for Underground Nuclear Astrophysics in Italy have carried out experiments to simulate those first few minutes, hoping to confirm the theories.
The work was conducted deep under the thick rock cover of the Gran Sasso mountain to prevent interference from cosmic rays —it involved firing a beam of protons at a deuterium target—deuterium being a form of hydrogen with just one proton and one neutron—and then measuring the rate of fusion. But because the rate of fusion is so low, the bombardment had to be carried out many times—the team carried out their work nearly every weekend for three years.
Ira Pastor, ideaXme life sciences ambassador and CEO Bioquark interviews Dr. Michelle Francl the Frank B. Mallory Professor of Chemistry, at Bryn Mawr College, and an adjunct scholar of the Vatican Observatory.
Ira Pastor comments:
Today, we have another fascinating guest working at the intersection of cutting edge science and spirituality.
Dr. Michelle Francl is the Frank B. Mallory Professor of Chemistry, at Bryn Mawr College, a distinguished women’s college in the suburbs of Philadephia, as well as an adjunct scholar of the Vatican Observatory.
Dr. Francl has a Ph.D. in chemistry from University of California, Irvine, did her post-doctoral research at Princeton University, and has taught physical chemistry, general chemistry, and mathematical modeling at Bryn Mawr College since 1986. In addition Dr. Francl has research interests in theoretical and computational chemistry, structures of topologically intriguing molecules (molecules with weird shapes), history and sociology of science, and the rhetoric of science.
Dr. Francl is noted for developing new methodologies in computational chemistry, is on a list of the 1,000 most cited chemists, is a member of the editorial board for the Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, is active in the American Chemical Society, and the author of “The Survival Guide for Physical Chemistry”. In 1994, she was awarded the Christian R. and Mary F. Lindback Award by Bryn Mawr College for excellence in teaching.
A group of researchers led by Sir Andre Geim and Dr. Alexey Berdyugin at The University of Manchester have discovered and characterized a new family of quasiparticles named ‘Brown-Zak fermions’ in graphene-based superlattices.
The team achieved this breakthrough by aligning the atomic lattice of a graphene layer to that of an insulating boron nitride sheet, dramatically changing the properties of the graphene sheet.
The study follows years of successive advances in graphene-boron nitride superlattices which allowed the observation of a fractal pattern known as the Hofstadter’s butterfly—and today (Friday, November 13) the researchers report another highly surprising behavior of particles in such structures under applied magnetic field.



Japanese researchers have created a mind-controllable Gundam robot, turning one of the anime’s most exciting technological concepts into reality.
The model, based on the mobile suit Zaku, has been available through Bandai’s Zeonic Technics package since last year, but that version requires manual programming on a smartphone app.
【課題】 来週から休暇に入る受講生は、この機会にミニチュアザクを組み立てて、課題に挑戦をして欲しい 今回の課題はプログラムだ。アクションコードに音声をプログラムした。 簡単に音声は追加出来るぞ。 #ジオニックテクニクス #ZEONICTECHNICS pic.twitter.com/rX5OSisXs1
China Launches 6G Satellite and Nokia seals the deal with NASA for 4G moon network.