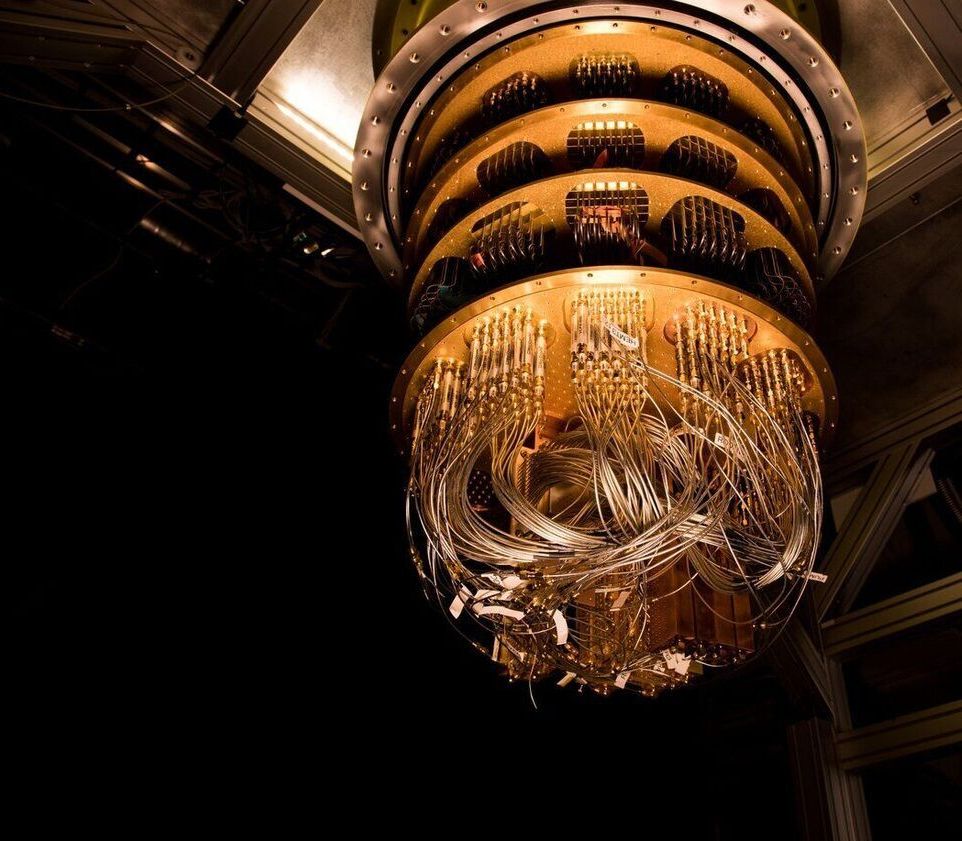
Quantum computing is a new paradigm in computing that utilizes the benefits of quantum mechanics to enhance the computing experience. Quantum computers will no longer rely on binary digits (0 and 1 states), that computers have relied on since the early beginnings, but will instead use quantum bits, which can be in a superposition of states. Quantum bits, or qubits, have the advantage of being in many states at once, offering parallel computing advantages. For example, they have long been regarded as far superior to classical computers for applications in data encryption.
Although the concept of quantum computers has been known for several decades, practical realizations are still lacking. The main limiting factor has been the critical influence of the environment on a qubit. Most physical systems need to be in perfectly controlled conditions in order to remain in the superposition state, whereas any interaction (mechanical, thermal, or other) with the environment perturbs this state and ruins the qubit. Such perturbation is termed “decoherence” that has plagued many potential qubit systems.
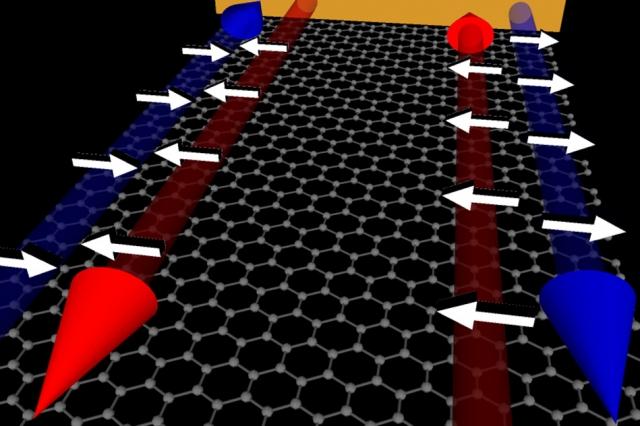
Graphene, having spurred research into numerous novel directions, is naturally also considered as a candidate material host for qubits. For example, back in 2013, a team of researchers from MIT found that graphene can be made into a topological insulator – meaning that electrons with one spin direction move around the graphene edges clockwise, whereas those that have the opposite spin move counterclockwise. They made this happen by applying two magnetic fields: one perpendicular to the graphene sheet, to make the electrons flow at sheet edges only, and another parallel to the sheet, that separates the two spin contributions. Electron spin has long been considered a candidate qubit, because it is inherently a quantum system that is in a superposition of states. In graphene, the spins move along the sheet edges robustly, without much decoherence. Furthermore, the same research showed switching the spin selection on and off, an important feature of q-bit transistors.