Google is now the fourth Big Tech company to beat the milestone.



Gaithersburg, Md.-based Novavax said the funding will allow the company to participate in Operation Warp Speed, the government’s program that has a goal of supporting the development of hundreds of millions of vaccine doses by 2021. The funding granted to Novavax will support the late-stage clinical development of the vaccine candidate, including a pivotal Phase III study. Additionally, the funds will be used to establish large-scale manufacturing in order to deliver 100 million doses of NVX‑CoV2373 by the end of the year.
Stanley C. Erck, president and chief executive officer of Novavax, said the company was honored to partner with Operation Warp Speed, a program that is supporting multiple shots on goal against COVID-19 by backing multiple vaccine projects, including Moderna’s mRNA program and AstraZeneca’s vaccine candidate.
“The pandemic has caused an unprecedented public health crisis, making it more important than ever that industry, government and funding entities join forces to defeat the novel coronavirus together. We are grateful to the U.S. government for its confidence in our technology platform, and are working tirelessly to develop and produce a vaccine for this global health crisis,” Erck said in a statement.


Study after study has shown that statins can prevent heart attacks, strokes and death in middle-aged adults. But in 28 major clinical trials of statins, only 2 percent of participants have been 75 years or older. This means that even though older adults are at greater risk of heart disease and death, there is scant data on whether statins should be prescribed for them.
A new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and VA Boston Healthcare System leverages national data from the U.S. Veterans Health Administration Services and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to shed new light on the role statins may play for older adults who have not yet experienced a heart attack, stroke or other cardiovascular event. In their retrospective analysis, the researchers found that the risk of dying from any cause was lower by 25 percent among veterans who were using statins compared to those who were not treated with statins. The risk of dying from a cardiovascular event, such as a heart attack or stroke, was lower by 20 percent. The team’s results are published in JAMA.
“Based on these data, age is not a reason to not prescribe statins,” said lead and corresponding author Ariela Orkaby, MD, MPH, a physician scientist at VA Boston Health Care System and in the Division of Aging at the Brigham. “Statins are commonly studied and prescribed for middle-aged adults but understudied in people over age 75. One of the most remarkable things about our results is that we found the benefit of statins held true regardless of whether a person was older or younger or had a condition such as dementia.”

There is no really useful treatments for Pancreatic Cancer, also it’s really deadly. So this sounds like awesome science news! “Cancer cells in the pancreas seem to thrive off this hyperactive cholesterol synthesis. The team thinks this is probably because they are taking advantage of other molecules generated by the same pathway. They’re able to keep the pathway running and maintain their supply thanks to an enzyme called sterol O-acyltransferase 1 (SOAT1), which converts free cholesterol to its stored form and which pancreatic cancer cells have in abundance.” “When the researchers eliminated the SOAT1 enzyme through genetic manipulation, preventing cells from converting and storing their cholesterol, cancer cells stopped proliferating. In animal experiments, eliminating the enzyme stalled tumor growth.”
Scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have found that they can stop the growth of pancreatic cancer cells by interfering with the way the cells store cholesterol. Their findings in mice and lab-grown pancreas models point toward a new strategy for treating the deadly disease.
The study, reported in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, was led by CSHL Professor David Tuveson’s team wanted to know why pancreatic cancer cells, like many cancer cells, manufacture abundant amounts of cholesterol. Cholesterol is an essential component of cell membranes, but the research team determined that pancreatic cancer cells make far more of it than they need to support their own growth. “This is unusual, because the cholesterol pathway is one of the most regulated pathways in metabolism,” says Tobiloba Oni, a graduate student in Tuveson’s lab.
Most cells make only as much cholesterol as they need, quickly shutting down the synthesis pathway once they have enough, Oni explains. But he and his colleagues, including Giulia Biffi, a former postdoctoral fellow in Tuveson’s lab, found that cancer cells convert most of the cholesterol they make into a form that can be stored within the cell. Free cholesterol never accumulates, and the synthesis pathway keeps churning out more.

The European Union has confirmed that American citizens will not be allowed to enter its borders as the bloc begins to ease travel restrictions imposed earlier this year in response to the pandemic. Travelers from America, as well as Brazil and Russia, have been barred from entry because of their countries’ inability to contain the spread of the coronavirus.
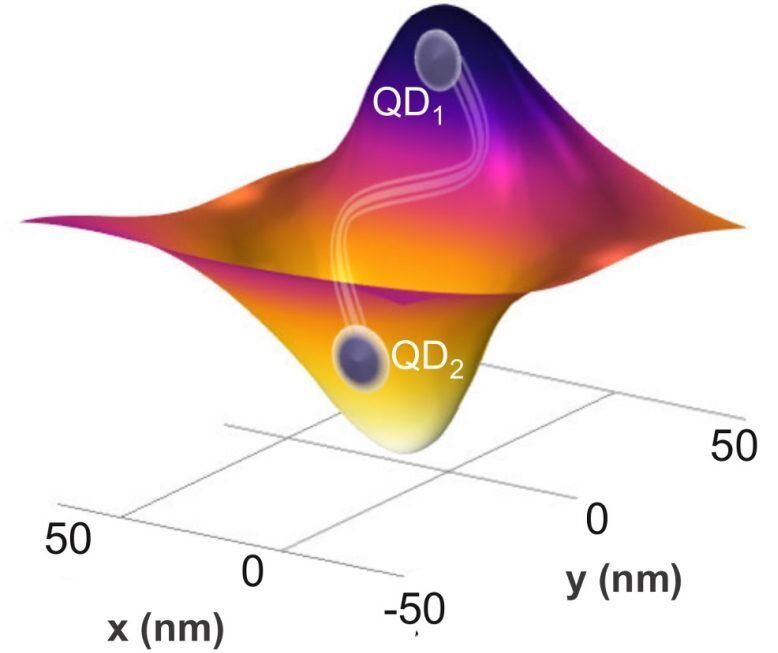
Researchers at CRANN and Trinity’s School of Physics have created an innovative new device that will emit single particles of light, or photons, from quantum dots that are the key to practical quantum computers, quantum communications, and other quantum devices.
The team has made a significant improvement on previous designs in photonic systems via their device, which allows for controllable, directional emission of single photons and which produces entangled states of pairs of quantum dots.
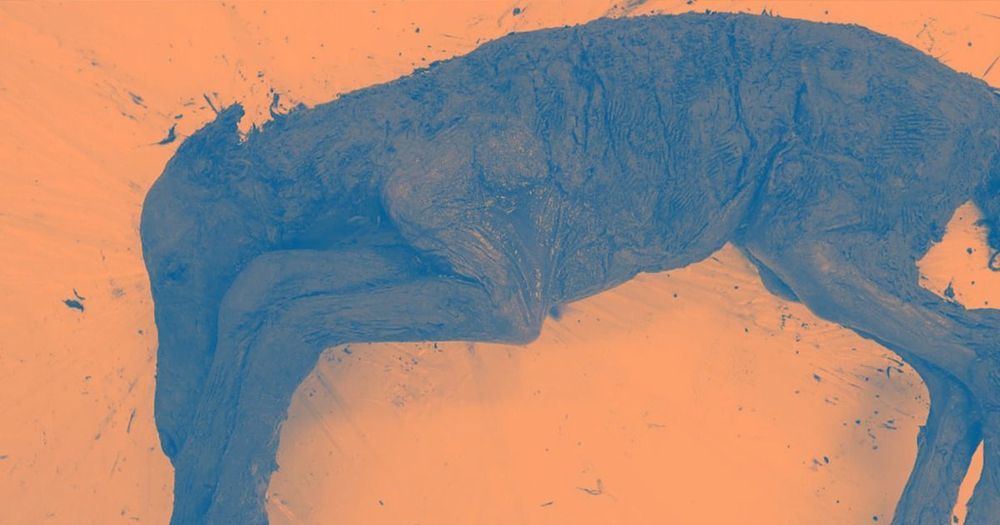
Horse to Water
In addition to liquid blood, scientists conducting the autopsy found intact organs and tissues.
“We can now claim that this is the best-preserved Ice Age animal ever found in the world,” Semyon Grigoyev, head of the Mammoth Museum in Yakutsk, Russia, told Russian news agency TASS, as per The Siberian Times.

In fact, in a recent paper in Royal Society Open Science, researchers showed that AI tasked with maximizing returns is actually disproportionately likely to pick an unethical strategy in fairly general conditions. Fortunately, they also showed it’s possible to predict the circumstances in which this is likely to happen, which could guide efforts to modify AI to avoid it.
The fact that AI is likely to pick unethical strategies seems intuitive. There are plenty of unethical business practices that can reap huge rewards if you get away with them, not least because few of your competitors dare use them. There’s a reason companies often bend or even break the rules despite the reputational and regulatory backlash they could face.
Those potential repercussions should be of considerable concern to companies deploying AI solutions, though. While efforts to build ethical principles into AI are already underway, they are nascent and in many contexts there are a vast number of potential strategies to choose from. Often these systems make decisions with little or no human input and it can be hard to predict the circumstances under which they are likely to choose an unethical approach.
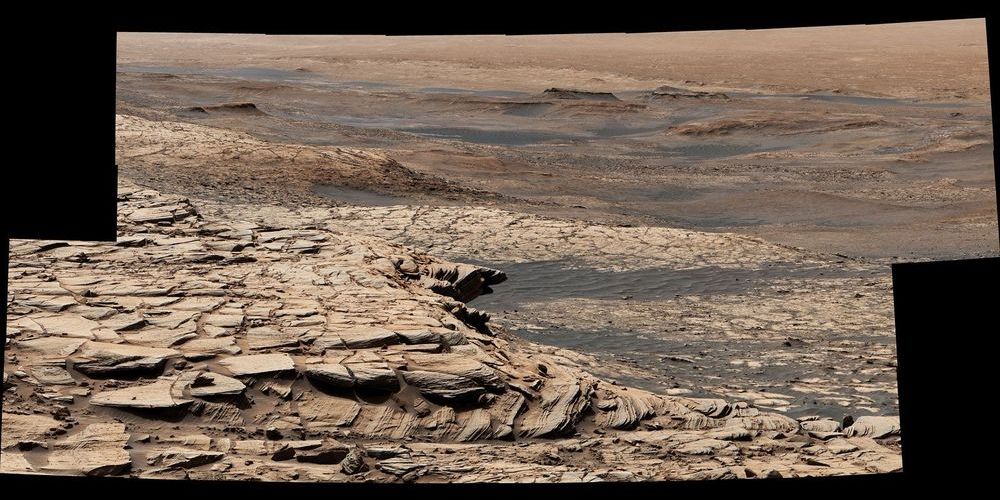

After more than a year in a clay-rich region, Curiosity is making a mile-long journey around some deep sand so that it can explore higher up Mount Sharp.
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover has started a road trip that will continue through the summer across roughly a mile (1.6 kilometers) of terrain. By trip’s end, the rover will be able to ascend to the next section of the 3-mile-tall Martian (5-kilometer-tall) mountain it’s been exploring since 2014, searching for conditions that may have supported ancient microbial life.
Located on the floor of Gale Crater, Mount Sharp is composed of sedimentary layers that built up over time. Each layer helps tell the story about how Mars changed from being more Earth-like — with lakes, streams and a thicker atmosphere — to the nearly-airless, freezing desert it is today.