Astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have captured a striking photo of GAL-CLUS-022058–38303, the largest and one of the most complete Einstein rings known in the Universe.


Put a robot in a tightly-controlled environment and it can quickly surpass human performance at complex tasks, from building cars to playing table tennis. But throw these machines a curve ball and they’re in trouble—just check out this compilation of some of the world’s most advanced robots coming unstuck in the face of notoriously challenging obstacles like sand, steps, and doorways.
The reason robots tend to be so fragile is that the algorithms that control them are often manually designed. If they encounter a situation the designer didn’t think of, which is almost inevitable in the chaotic real world, then they simply don’t have the tools to react.
Rapid advances in AI have provided a potential workaround by letting robots learn how to carry out tasks instead of relying on hand-coded instructions. A particularly promising approach is deep reinforcement learning, where the robot interacts with its environment through a process of trial-and-error and is rewarded for carrying out the correct actions. Over many repetitions it can use this feedback to learn how to accomplish the task at hand.
Elon Musk has been a vocal critic of artificial intelligence, calling it an “existential threat to humanity”. He is wrong, right?
Musk is heavily invested in AI research himself through his OpenAI and NeuroLink ventures, and believes that the only safe road to AI involves planning, oversight & regulation. He recently summarized this, saying:
“My recommendation for the longest time has been consistent. I think we ought to have a government committee that starts off with insight, gaining insight… Then, based on that insight, comes up with rules in consultation with industry that give the highest probability for a safe advent of AI.”
Across dozens of media appearances, Musk’s message about AI has indeed been remarkably consistent. He says it’s dangerous, and says it needs regulation, or else “AI could turn humans into an endangered species”.
A bit of everything here from hallmarks of aging to epigenetic reprogramming(which effects telomeres, gene expression, etc) and even diet.
In this talk given at Ending Age-Related Diseases 2020, Dr. Kris Verburgh of the Free University of Brussels discusses the methods by which people might lead longer, healthier lives. While some of these methods involve the use of advanced rejuvenation biotechnology techniques, others are simpler to implement and require a minimum amount of technology, such as nutrition and exercise, along with health-monitoring technology that already exists in the public space.
HOW CAN YOU SUPPORT US?
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
LEAF / Lifespan.io is a 501©(3) nonprofit organization. Everything we’ve done thus far and everything we will do in the future is thanks to your support — please stand with us to fight the diseases of aging and increase healthy human lifespan.
► Support us with monthly donations by becoming a Lifespan Hero: https://www.lifespan.io/hero.
► Make a one-time donation and learn about other ways to support us here: http://lifespan.io/support.
► Learn more, and help us #CrowdsourceTheCure: https://www.lifespan.io.
► Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/user/LifespanIO
JOIN US
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
Join us, and together, we can overcome diseases like Alzheimer’s, heart disease, and cancer by addressing their shared source: the aging processes themselves.
#Research #Aging #Funding #LEAF #Biotech #Nutrition #Rejuvenation #Lifespan



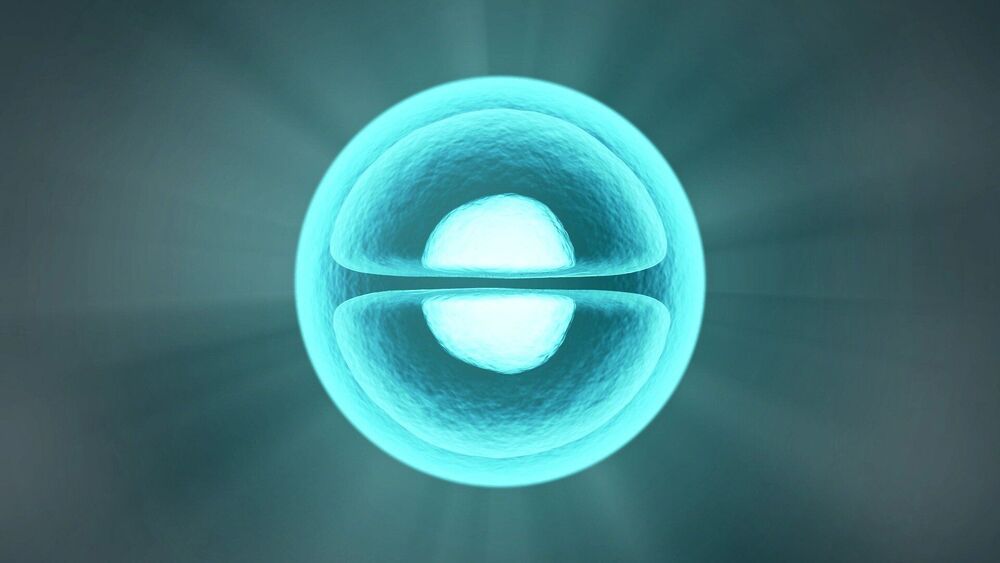
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and University College London have rebuilt a human thymus, an essential organ in the immune system, using human stem cells and a bioengineered scaffold. Their work is an important step towards being able to build artificial thymi which could be used as transplants.
The thymus is an organ in the chest where T lymphocytes, which play a vital role in the immune system, mature. If the thymus does not work properly or does not form during foetal development in the womb, this can lead to diseases such as severe immunodeficiency, where the body cannot fight infectious diseases or cancerous cells, or autoimmunity, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the patient’s own healthy tissue.
In their proof-of-concept study, published in Nature Communications today, the scientists rebuilt thymi using stem cells taken from patients who had to have the organ removed during surgery. When transplanted into mice, the bioengineered thymi were able to support the development of mature and functional human T lymphocytes.

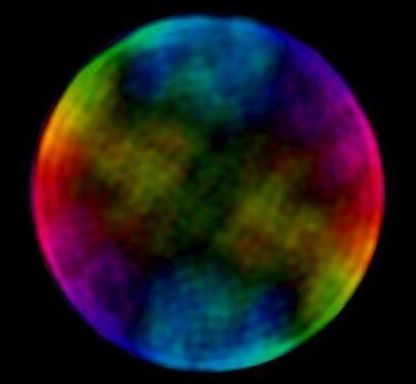
Blue Moon. Strawberry Moon. Supermoon. Snow Moon. Blood Moon. Earth’s favourite satellite buddy has a name for every occasion. Yet the most glorious view of the full Moon we’ve seen to date has no name.
That’s probably because it’s not indicative of an occasion, but a way of looking at our satellite. With your naked eyes, you would never see the rainbowy, soap-bubble-like view of the Moon as pictured above.
But that’s what it looks like to the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), an incredibly powerful radio telescope array located in the desert of Western Australia.