Pinning plasma within a set of magnetic fields offers physicists a new way to study clean energy, space weather and the inner workings of stars.
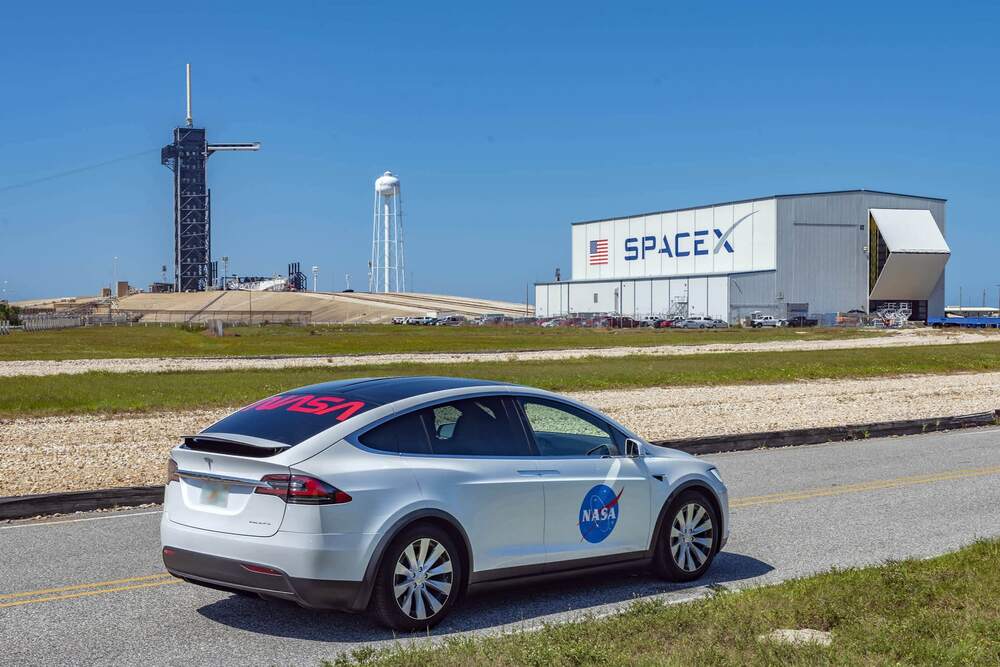



SpaceX wants to begin connecting moving vehicles – from cars and trucks to jets and ships – to its Starlink satellite internet network, according to a request the company filed with the Federal Communications Commission.
“This application would serve the public interest by authorizing a new class of ground-based components for SpaceX’s satellite system that will expand the range of broadband capabilities available to moving vehicles throughout the United States and to moving vessels and aircraft worldwide,” SpaceX director of satellite policy David Goldman wrote in a letter to the FCC filed on Friday.
Starlink is the company’s capital-intensive project to build an interconnected internet network with thousands of satellites, known in the space industry as a constellation, designed to deliver high-speed internet to consumers anywhere on the planet.

Researchers affiliated with Nvidia and Harvard today detailed AtacWorks, a machine learning toolkit designed to bring down the cost and time needed for rare and single-cell experiments. In a study published in the journal Nature Communications, the coauthors showed that AtacWorks can run analyses on a whole genome in just half an hour compared with the multiple hours traditional methods take.
Most cells in the body carry around a complete copy of a person’s DNA, with billions of base pairs crammed into the nucleus. But an individual cell pulls out only the subsection of genetic components that it needs to function, with cell types like liver, blood, or skin cells using different genes. The regions of DNA that determine a cell’s function are easily accessible, more or less, while the rest are shielded around proteins.
AtacWorks, which is available from Nvidia’s NGC hub of GPU-optimized software, works with ATAC-seq, a method for finding open areas in the genome in cells pioneered by Harvard professor Jason Buenrostro, one of the paper’s coauthors. ATAC-seq measures the intensity of a signal at every spot on the genome. Peaks in the signal correspond to regions with DNA such that the fewer cells available, the noisier the data appears, making it difficult to identify which areas of the DNA are accessible.
More than 100 years ago in his autobiography, Nikola Tesla reflected on the first time he had the idea to control the weather. Now, China is spending billions to prove that weather modification is possible.
Tesla wrote:
“One day, as I was roaming in the mountains, I sought shelter from an approaching storm. The sky became overhung with heavy clouds but somehow the rain was delayed until, all of a sudden, there was a lightning flash and a few moments after a deluge. This observation set me thinking. It was manifest that the two phenomena were closely related, as cause and effect, and a little reflection led me to the conclusion that the electrical energy involved in the precipitation of the water was inconsiderable, the function of lightning being much like that of a sensitive trigger.”
Help support our video productions http://www.patreon.com/scifri.
Produced by Luke Groskin.
Filmed by Christian Baker.
Music by Audio Network.
Additional Footage and Stills Provided by Joel Simon, Pond5, Shutterstock, Nic Symbios, Pit Schuni (C.C. BY 2.0)Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (C.C. BY 2.0), Eleni Katafori, Bradely Smith, Loic Royer, Alexander Reben.
Inspired by the forces behind evolution, artist and tool designer Joel Simon programmed a network of computers to blend and “breed” together images over and over using users’ preferences as its guide. Although thousands of users, breeding millions of bizarre and beautiful images, Joel’s goal was more conceptual: He wanted to see if the system could evolve art and what types of forms might emerge from the process.
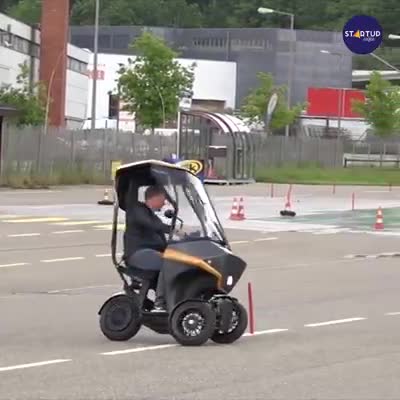



Solar powered vehicle.
Electric vehicle that can be operated only with solar power.
More info: https://bit.ly/2LKaMsw
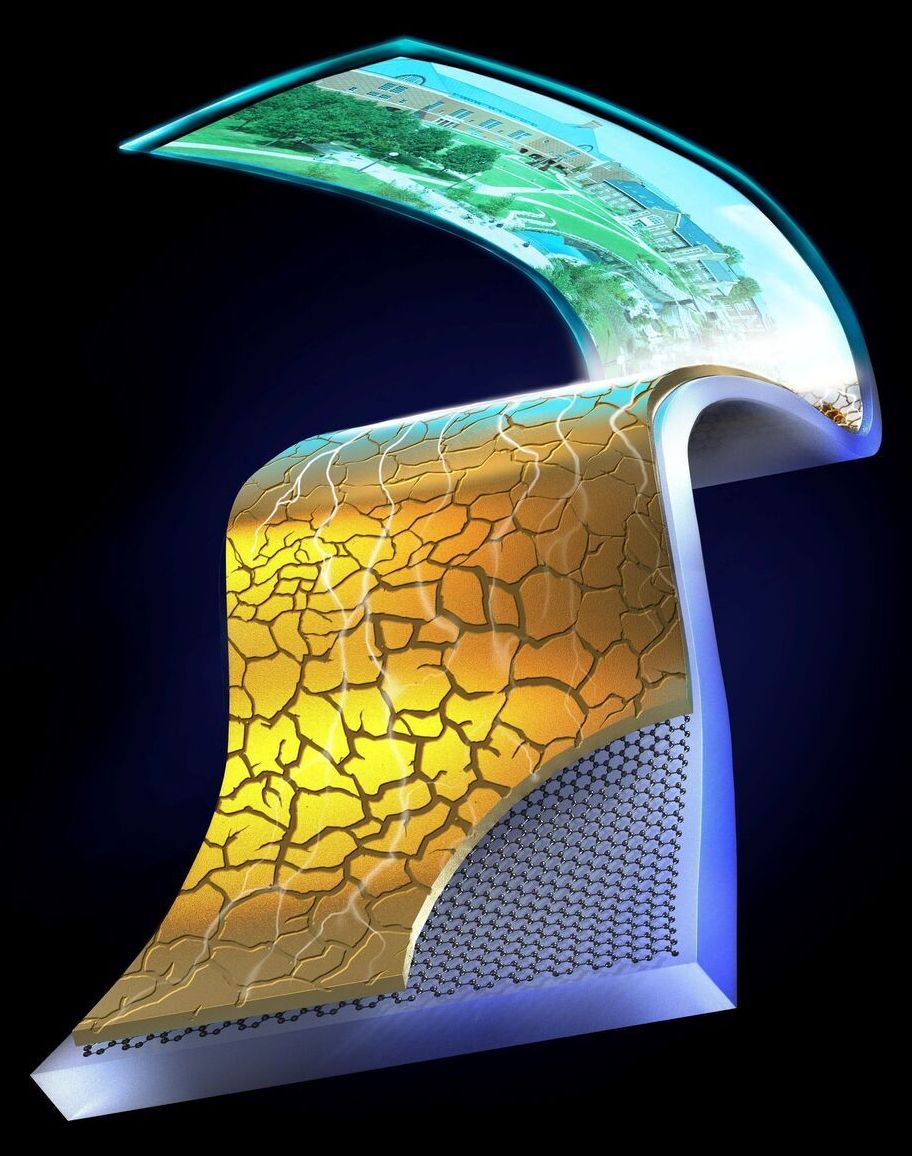
Flexible electrodes, electronic components that conduct electricity, are of key importance for the development of numerous wearable technologies, including smartwatches, fitness trackers and health monitoring devices. Ideally, electrodes inside wearable devices should retain their electrical conductance when they are stretched or deformed.
Many flexible electrodes developed so far are made of metal thin films placed on elastic substrates. While some of these electrodes are flexible and conduct electricity well, sometimes, the metal films are fractured, which can result in sudden electricity disconnection.
Researchers at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have recently introduced a new design that could enable the development of strain-resilient flexible electrodes that conduct electricity well, even when they are stretched or deformed. This design, outlined in a paper published in Nature Electronics, involves the introduction of a thin, two-dimensional (2-D) interlayer, which reduces the risk of fractures and retains electrical connections of metal films.
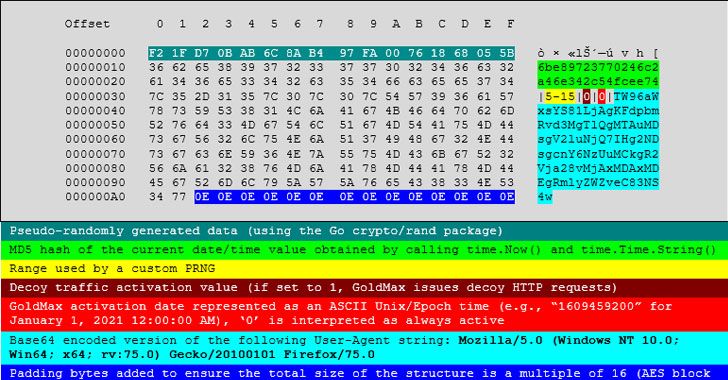
FireEye and Microsoft on Thursday said they discovered three more malware strains in connection with the SolarWinds supply-chain attack, including a “sophisticated second-stage backdoor,” as the investigation into the sprawling espionage campaign continues to yield fresh clues about the threat actor’s tactics and techniques.
Dubbed GoldMax (aka SUNSHUTTLE), GoldFinder, and Sibot, the new set of malware adds to a growing list of malicious tools such as Sunspot, Sunburst (or Solorigate), Teardrop, and Raindrop that were stealthily delivered to enterprise networks by alleged Russian operatives.