For an equitable end to the pandemic, the world needs vaccines that can safely reach rural and remote areas.



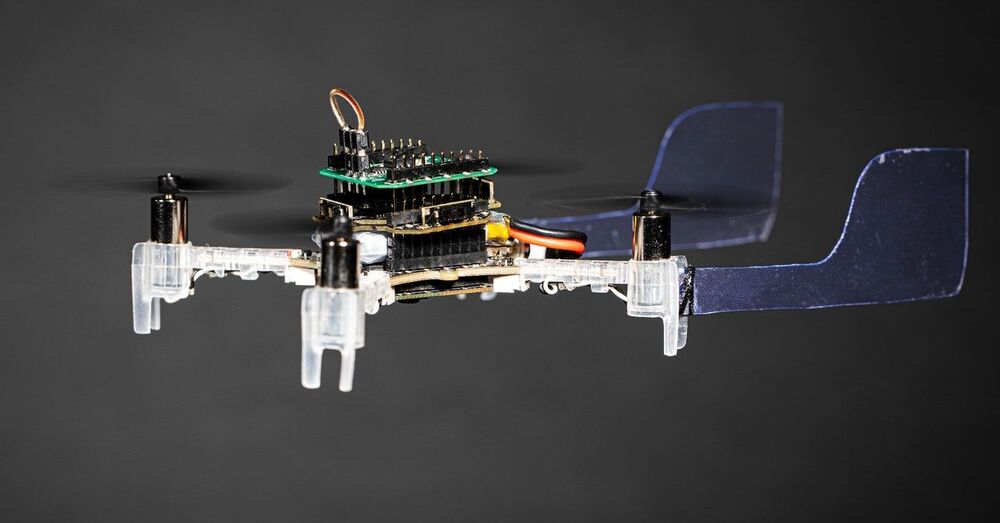
“It’s all thanks to the sacrifice of the hawk moth Manduca sexta, which is an extremely sensitive smeller, like other moths. When a moth picks up a scent, like that of a flower or a potential mate, the odors bind to proteins inside the antennae, and these proteins in turn activate neurons dedicated to specific chemicals. That means the antennae are producing electrical signals that researchers can tap into. In order to create a sort of moth-drone cyborg, mechanical engineer Melanie Anderson of the University of Washington cold-anesthetized a hawk moth in a freezer before removing its antennae. Then she cut both ends off of a single antenna and attached each to an itty-bitty wire hooked up to an electrical circuit. “A lot like a heart monitor, which measures the electrical voltage that is produced by the heart when it beats, we measure the electrical signal produced by the antenna when it smells odor,” says Anderson, lead author on a recent paper in the journal Bioinspiration and Biomimetics describing the research. “And very similarly, the antenna will produce these spike-shaped pulses in response to patches of odor.””
Researchers slap a living antenna on a drone to give the machine an insanely keen sense of smell. Ladies and gentlemen, meet the “Smellicopter.”

“For example, a number of animals benefit from solar-powered molecules. The pea aphid produces pigments that, with the aid of light, generate adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, the compound that powers reactions with cells. In addition, a stripe of yellow pigment on the exoskeleton of the Oriental hornet (Vespa orientalis) converts light to electricity, which could help to explain why these insects become more active during the middle of the day. Other animals make use of actual photosynthesis, using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce sugars and other vital compounds. Plants and algae rely on chloroplasts, structures within their cells, to carry out photosynthesis, but Elysia sea slugs can steal chloroplasts from algae they graze on, to help them live solely on photosynthesis for months… Many other animals reap benefits from photosynthesis by forming partnerships instead. For instance, most corals partner with photosynthetic symbiotic microbes known as zooxanthellae, while the eggs of spotted salamanders receive valuable oxygen from algae.”
If humans had green skin, for instance, what if it granted us the ability to perform photosynthesis, which plants use to live off of sunlight?
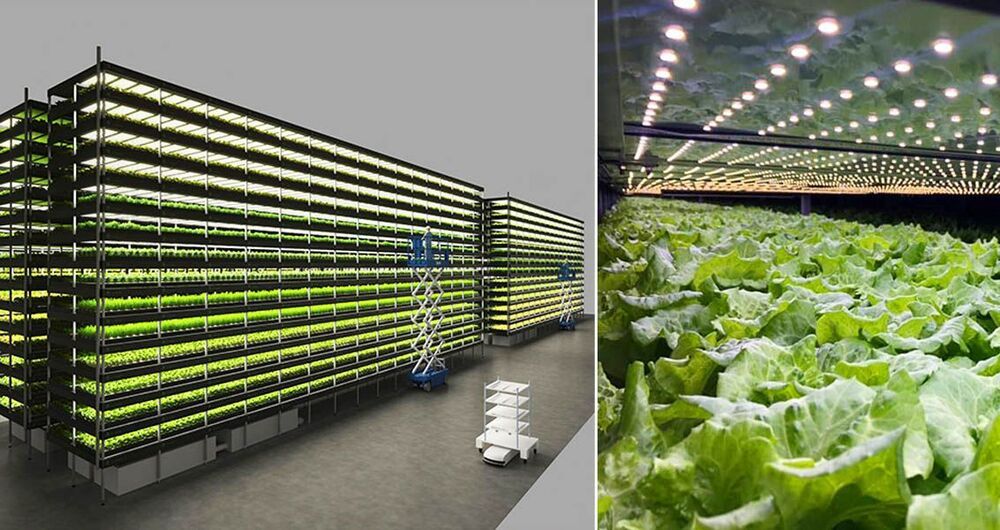

The new facility is a product of the partnership between Danish startup Nordic Harvest and Taiwanese tech company YesHealth Group. It’s an indoor farm that covers an area of over 75000 square feet, situated just on the outskirts of Copenhagen. Featuring a 14-shelf grow rack system, it boasts an annual production capacity of about 1000 tons of greens. That’s almost equivalent to the capacity of farms covering an area that’s the size of 20 soccer fields!

Research papers come out far too rapidly for anyone to read them all, especially in the field of machine learning, which now affects (and produces papers in) practically every industry and company. This column aims to collect the most relevant recent discoveries and papers — particularly in but not limited to artificial intelligence — and explain why they matter.

A membrane between what is inside the solar system and the outside. 😃
NASA‘s New Horizons spacecraft has helped scientists study a mysterious phenomenon at the edge of the Solar System, where particles from the Sun and interstellar space interact.
This region, about 100 times further from the Sun than Earth, is where uncharged hydrogen atoms from interstellar space meet charged particles from our Sun. The latter extend out from our Sun in a bubble called the heliosphere.
At the point where the two interact, known as the heliopause, it’s thought there is a build-up of hydrogen from interstellar space. This creates a sort of “wall”, which scatters incoming ultraviolet light.
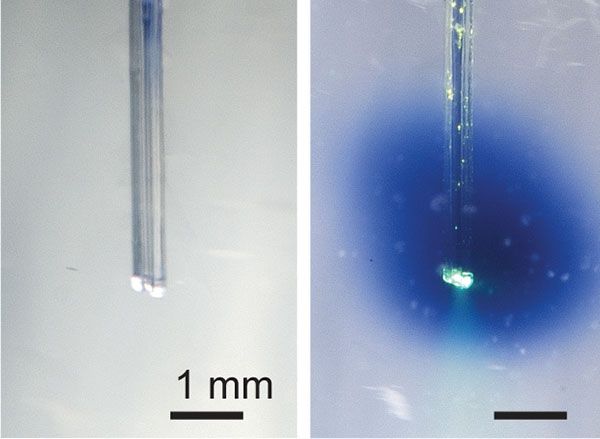
When taken orally or intravenously, medications typically travel throughout the body, producing unwanted side effects. MIT scientists are working on an alternative, that delivers both light and a light-activated drug directly to the target area.
So-called “photoswitchable” drugs contain light-sensitive molecules that essentially switch the drug on when exposed to a flash of light. This means that a pharmaceutical could remain inactive when moving through the bloodstream or digestive tract, only becoming active once it reached the place it was needed. As a result, few if any side effects would occur.
That said, how could a flash of light be delivered precisely to the target area, right when the drug was present at that location? Well, that’s where a device developed by the MIT researchers comes into play.

Scientists have developed a machine-learning method that crunches massive amounts of data to help determine which existing medications could improve outcomes in diseases for which they are not prescribed.
The intent of this work is to speed up drug repurposing, which is not a new concept—think Botox injections, first approved to treat crossed eyes and now a migraine treatment and top cosmetic strategy to reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
But getting to those new uses typically involves a mix of serendipity and time-consuming and expensive randomized clinical trials to ensure that a drug deemed effective for one disorder will be useful as a treatment for something else.
