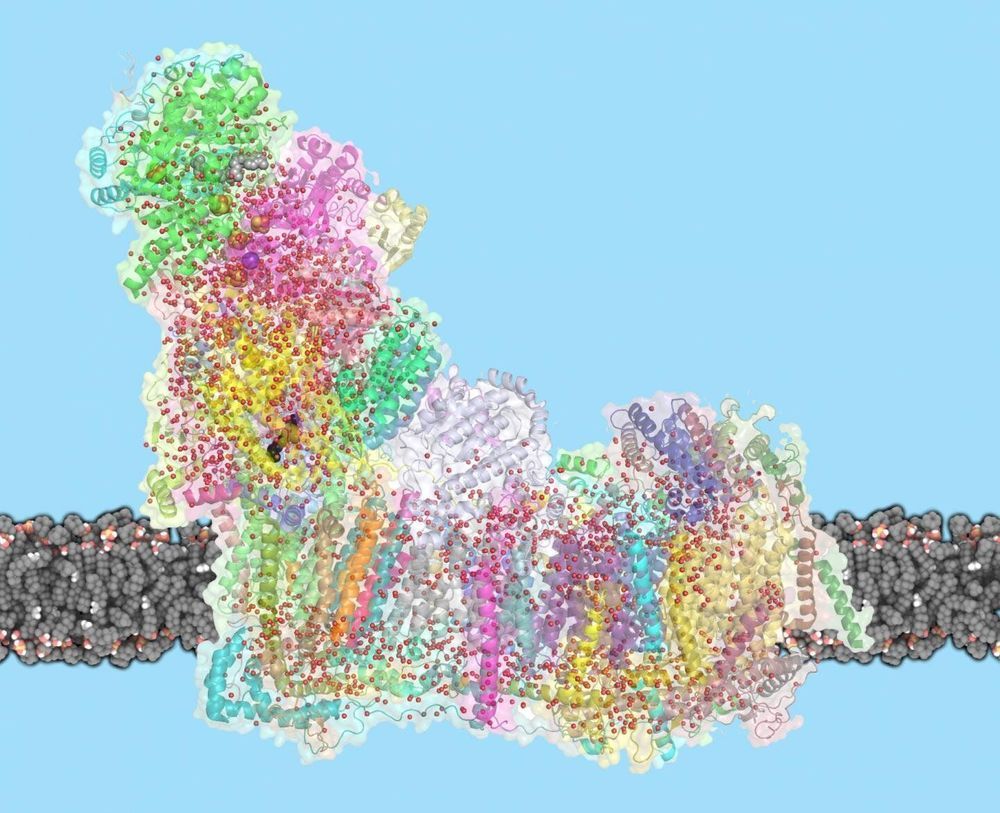
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells, generating energy that supports life. A giant molecular proton pump, called complex I, is crucial: It sets in motion a chain of reactions, creating a proton gradient that powers the generation of ATP, the cell’s fuel. Despite complex I’s central role, the mechanism by which it transports protons across the membrane has so far been unknown. Now, Leonid Sazanov and his group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria) have solved the mystery of how complex I works: Conformational changes in the protein combined with electrostatic waves move protons into the mitochondrial matrix. This is the result of a study published today in Science.
Complex I is the first enzyme in the respiratory chain, a series of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The respiratory chain is responsible for most of the cell’s energy production. In this chain, three membrane proteins set up a gradient of protons, moving them from the cell’s cytoplasm into the mitochondrial inner space, called the matrix. The energy for this process comes mostly from the electron transfer between NADH molecules, derived from the food we eat, and oxygen that we breathe. ATP synthase, the last protein in the chain, then uses this proton gradient to generate ATP.
Complex I is remarkable not only because of its central role in life, but also for its sheer size: with a molecular weight of 1 Megadalton, the eukaryotic complex I is one of the biggest membrane proteins. Its size also makes complex I hard to study. In 2016, Sazanov and his group were the first to solve the structure of mammalian complex I, following on their 2013 structure of a simpler bacterial enzyme. But the mechanism by which complex I moves protons across the membrane has remained controversial. “One idea was that a part of complex I works like a piston, to open and close channels through which protons travel”, explains Sazanov. “Another idea was that residues at the center of complex I act as a driver. It turns out that an even more unusual mechanism is at work.”