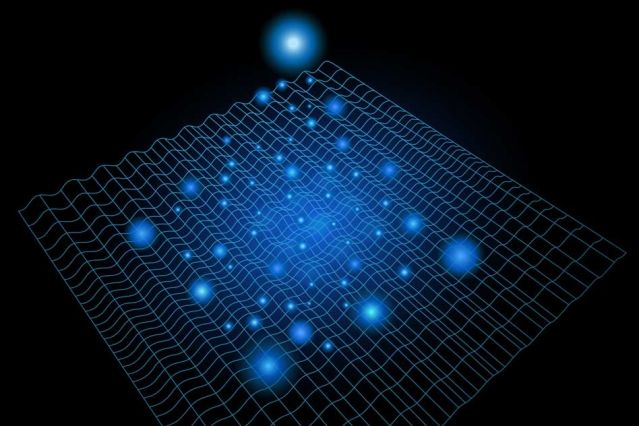
Physics experiment with ultrafast laser pulses produces a previously unseen phase of matter.
“Politicians should read science fiction, not westerns and detective stories.”– Arthur C. Clarke.
In Confiant’s “Demand Quality Report for Q3 2019”, the ad fraud and security company analyzed 120 billion ad impressions between January 1st and September 20th that flowed through their systems in order to provide a breakdown of different malicious ad campaigns.
While Confiant’s report also discussed low quality ads and banner ads that appear in video slots, we will focus on the detected malicious ads and the campaigns that utilize them.
A malicious ad is defined by Confiant as one that performs unwanted behavior such as a forced redirect to scams, cryptojacking, or ads that infect a visitor’s device.
Microsoft security analysts reveal that cryptocurrency-stealing malware “Dexphot” already infected 80,000 computers earlier this year.
Microsoft reveals that new crypto-stealing malware “Dexphot” already infected 80,000 devices earlier this year.
Merck now holds 22 CRISPR-related patents worldwide across nine different geographies.
- Patents cover Paired Cas9 Nickase CRISPR genome-editing technology to advance gene therapy and research.
DARMSTADT, Germany, Nov. 26, 2019 /PRNewswire/ — Merck, a leading science and technology company, today announced that the Japan Patent Office and the Intellectual Property Office of Singapore have each allowed the company’s patent application for the use of paired CRISPR nickases, bringing Merck’s number of patents to 22 worldwide.
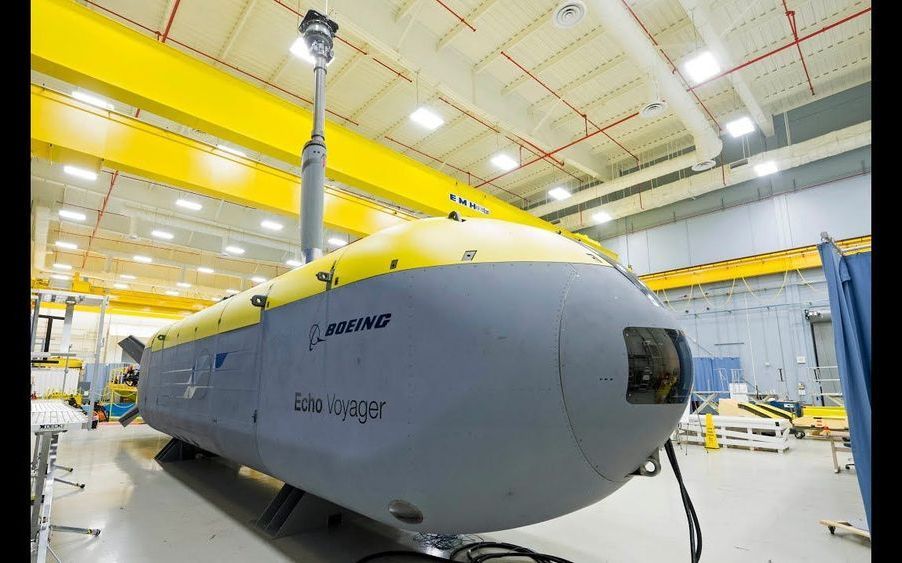
The US Navy has awarded Boeing contracts worth a total of $274.4m to produce five Orca Extra Large Unmanned Undersea Vehicles (XLUUVs). Based on Boeing’s Echo Voyager prototype UUV, the 15.5m-long submersible could be used for mine countermeasures, anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, electronic warfare and strike missions. Berenice Baker finds out more.
Low-impact treadmill
Posted in futurism
The Michelin Vision tire concept does not need to be inflated, is specifically manufactured through 3D printing, and is biodegradable.
Microsoft security engineers detailed today a new malware strain that has been infecting Windows computers since October 2018 to hijack their resources to mine cryptocurrency and generate revenue for the attackers.
Named Dexphot, this malware reached its peak in mid-June this year, when its botnet reached almost 80,000 infected computers.
Since then, the number of daily infections has been slowly going down, as Microsoft claims it deployed countermeasures to improve detections and stop attacks.
NOTE FROM TED: Please do not look to this talk for medical advice. This talk, which was filmed at a TEDx event, contains strong assertions about multiple sclerosis and lifestyle medicine that lack sufficient scientific evidence for general prescription. TEDx events are independently organized by volunteers. The guidelines we give TEDx organizers are described in more detail here: http://storage.ted.com/tedx/manuals/tedx_content_guidelines.pdf
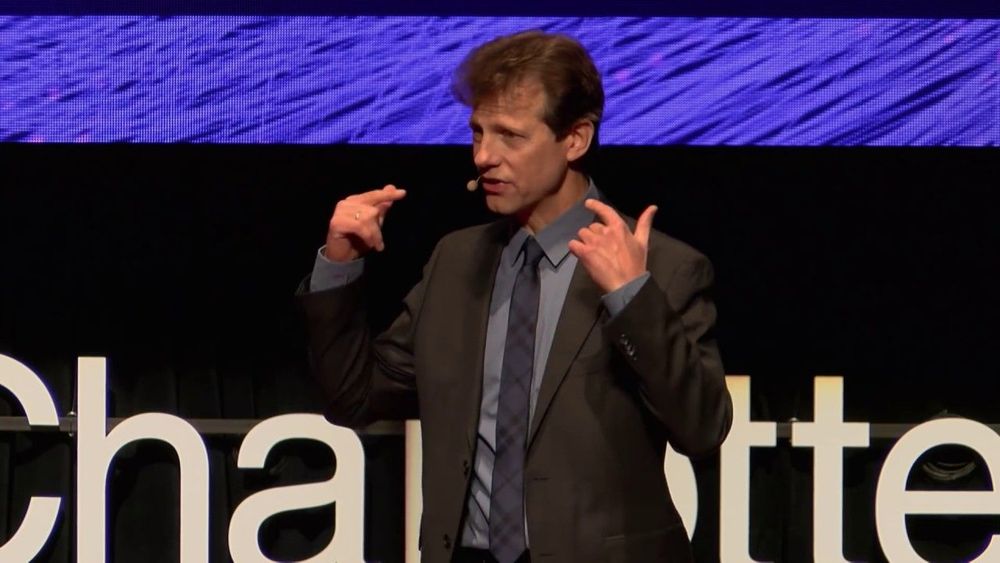
After a shocking diagnosis that would begin stripping Bob Cafaro of his ability to perform, sheer willpower and changes to his daily life allow him to beat all odds.
Bob Cafaro played chamber music full time and served on the faculty of the University of Virginia until 1983 when he became a regular with the Metropolitan Opera Orchestra. He later joined the Baltimore Symphony and in 1985 became a member of the Philadelphia Orchestra. In 1999, Bob was stricken with a virulent case of Multiple Sclerosis, which left him nearly blind and without the use of his hands. Defying what doctors had told him, he made a complete and remarkable recovery and has since written a book, been a member of The Rachmaninov Trio since 2003, and has grown passionate in his involvement with volunteer and outreach activities.
This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community.