Your favorite TV show isn’t the only place where guest stars might appear. Keep an eye on the sky for the second half of 2024 and you might be able to witness a rare astronomical event.
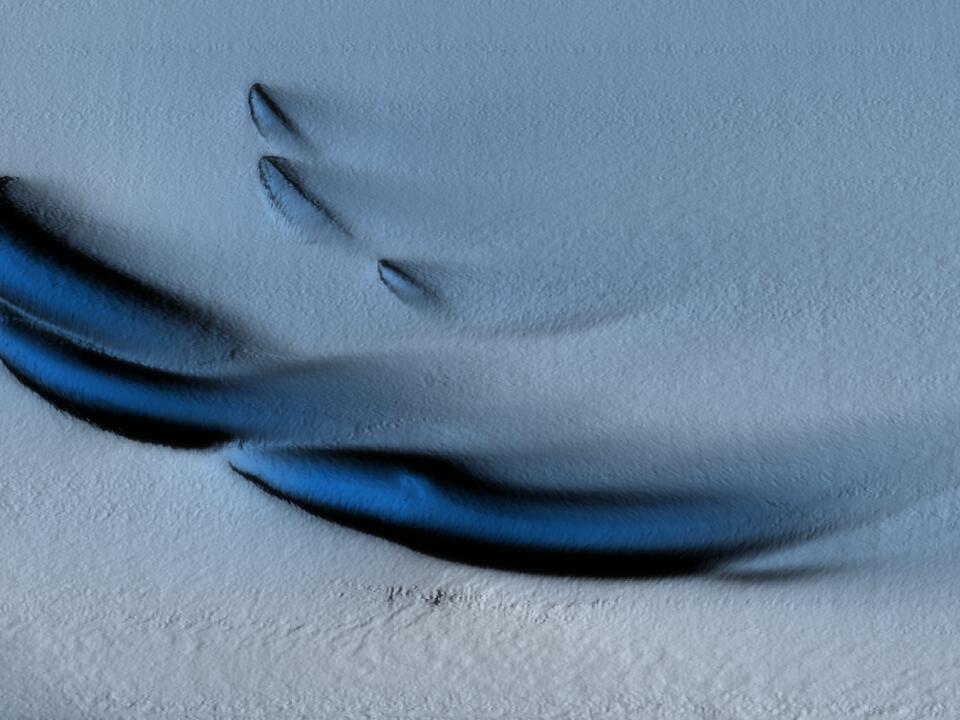
The unusual patterns, found beneath West Antarctica’s Doston Ice Shelf, could help scientists to better understand how glaciers erode.
🌏 Get NordVPN 2Y plan + 4 months extra here plus up to 20 GB Saily data voucher ➼ https://NordVPN.com/sabine It’s risk-free with Nord’s 30-day money-back guarantee! ✌
Physicists say that they might have solved a long standing problem: How do supermassive black holes manage to merge to larger ones. Their idea: dark matter gets the job done. Or does it? I’ve had a look.
Paper: https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract…
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
Calculations show that nerve fibres in the brain could emit pairs of entangled particles, and this quantum phenomenon might explain how different parts of the brain work together.
Have you ever considered the possibility that our reality might be an intricately crafted computer simulation? There is a name for this theory — Simulation Hypothesis — and it is now being tested in quantum lab experiments.
Though it may initially resemble a plot from the latest sci-fi blockbuster, a dedicated group of researchers is rigorously exploring this intriguing concept.
They are investigating the philosophical implications and technological advancements that could render such a simulation plausible.
New theoretical research finds that it’s impossible to form a black hole with the energy of light particles alone, poking a hole in Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
When two black holes collide, space and time shake and energy spreads out like ripples in a pond. These gravitational waves, predicted by Einstein in 1916, were observed for the first time by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) telescope in September 2015.
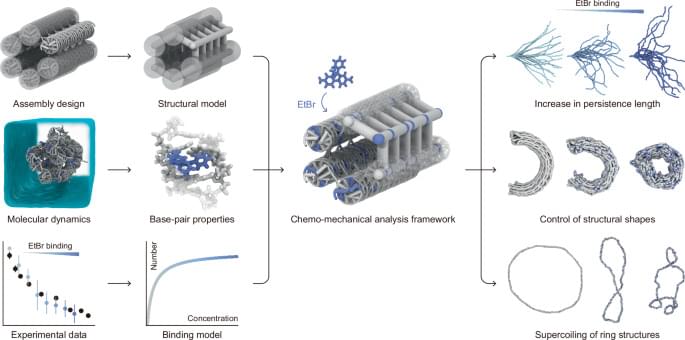
Chemo-mechanical deformation of structured DNA assemblies driven by DNA-binding ligands is promising for biological and therapeutic applications, but it is elusive how to effectively model and predict their effects on the deformation and mechanical properties of DNA structures. Here, the authors present a computational framework for simulating chemo-mechanical change of structured DNA assemblies, using ethidium bromide intercalation as an example.
A New Hint of Life on Mars
Posted in alien life
An exploration of the newly discovered rock on Mars that seems to show tantalizing hints that it may be evidence of past microbial life living on Mars and how we may be very close to finally finding evidence of extraterrestrial life.
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel: