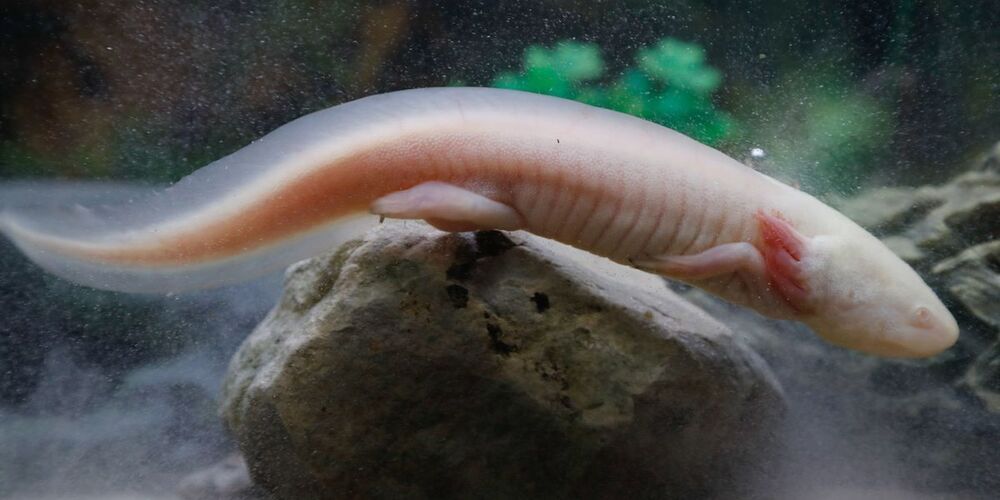
Researchers have recently discovered two of the genes that govern this weird-looking salamander’s ability to regenerate limbs, eyes, and even its brain.
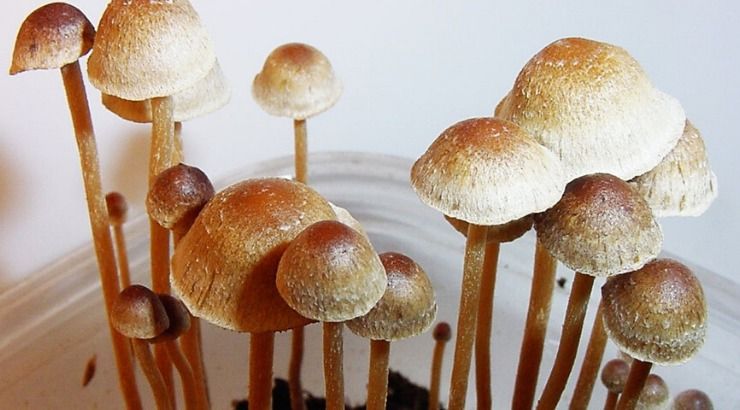
(TT) — Psilocybin, the active ingredient in the most commonly used psychedelic mushrooms, is coming closer to becoming a mainstream treatment for depression.

Everybody feels negative emotions once in a while, but these emotions have a stronger effect on your health than you may realize. Every time you think about regrets, experience resentment or replay bad memories in your head, your body suffers just as much as your mind. That’s why harboring negative emotions can lead to devastating long-term disease.
But there is one simple solution: forgiveness. Trouble is, our culture seems to perceive forgiveness as a sign of weakness, submission, or both. This makes it harder to actually do the work to forgive people who’ve done you harm.
Turbulence is everywhere—it rattles our planes and makes tiny whirlpools in our bathtubs—but it is one of the least understood phenomena in classical physics.
Turbulence occurs when an ordered fluid flow breaks into small vortices, which interact with each other and break into even smaller vortices, which interact with each other and so-on, becoming the chaotic maelstrom of disorder that makes white water rafting so much fun.
But the mechanics of that descent into chaos have puzzled scientists for centuries.
Betelgeuse has been the center of significant media attention lately. The red supergiant is nearing the end of its life, and when a star over 10 times the mass of the Sun dies, it goes out in spectacular fashion. With its brightness recently dipping to the lowest point in the last hundred years, many space enthusiasts are excited that Betelgeuse may soon go supernova, exploding in a dazzling display that could be visible even in daylight.
While the famous star in Orion’s shoulder will likely meet its demise within the next million years—practically couple days in cosmic time—scientists maintain that its dimming is due to the star pulsating. The phenomenon is relatively common among red supergiants, and Betelgeuse has been known for decades to be in this group.
Coincidentally, researchers at UC Santa Barbara have already made predictions about the brightness of the supernova that would result when a pulsating star like Betelgeuse explodes.
Scientists at the University of Sussex have measured a property of the neutron—a fundamental particle in the universe—more precisely than ever before. Their research is part of an investigation into why there is matter left over in the universe, that is, why all the antimatter created in the Big Bang didn’t just cancel out the matter.
The team—which included the Science and Technology Facilities Council’s (STFC) Rutherford Appleton Laboratory in the UK, the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) in Switzerland, and a number of other institutions—was looking into whether or not the neutron acts like an “electric compass.” Neutrons are believed to be slightly asymmetrical in shape, being slightly positive at one end and slightly negative at the other—a bit like the electrical equivalent of a bar magnet. This is the so-called “electric dipole moment” (EDM), and is what the team was looking for.
This is an important piece of the puzzle in the mystery of why matter remains in the Universe, because scientific theories about why there is matter left over also predict that neutrons have the “electric compass” property, to a greater or lesser extent. Measuring it then it helps scientists to get closer to the truth about why matter remains.
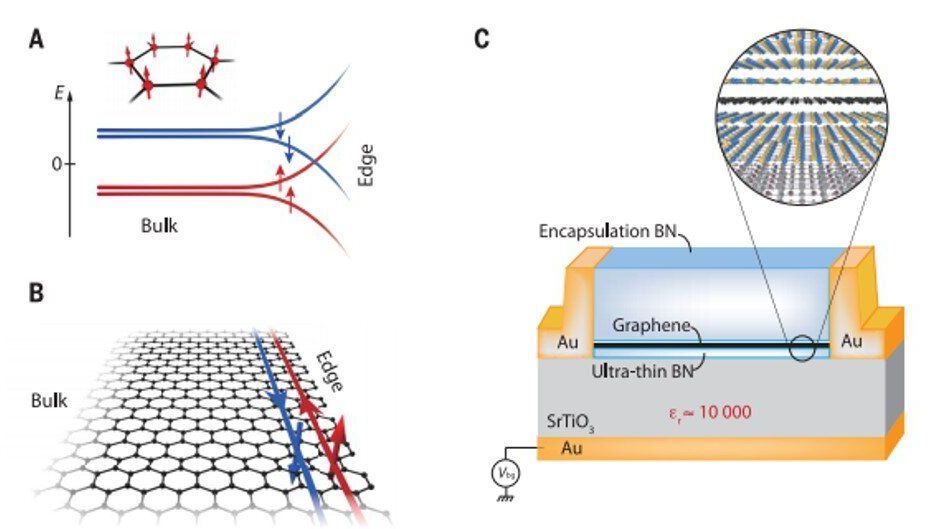
Materials that exhibit topological phases can be classified by their dimensionality, symmetries and topological invariants to form conductive-edge states with peculiar transport and spin properties. For example, the quantum Hall effect can arise in two-dimensional (2-D) electron systems subjected to a perpendicular magnetic field. When distinct characteristics of quantum Hall systems are compared with time-reversal symmetric (entropy conserved) topological insulators (TIs), they appear to rely on Coulomb interactions between electrons to induce a wealth of strongly correlated, topologically or symmetry-projected phases in a variety of experimental systems.
In a new report now on Science, Louis Veyrat and a research team in materials science, quantum optics and optoelectronics in France, China and Japan tuned the ground state of the graphene zeroth Landau level i.e. orbitals occupied by charged particles with discrete energy values. Using suitable screening of the Coulomb interaction with the high dielectric constant of a strontium titanate (SrTiO3) substrate, they observed robust helical edge transport at magnetic fields as low as 1 Tesla, withstanding temperatures of up to 110 kelvin across micron-long distances. These versatile graphene platforms will have applications in spintronics and topological quantum computation.
Topological insulators (TIs), i.e., a material that behaves as an insulator in its interior but retains a conducting surface state, with zero Chern number have emerged as quantum Hall topological insulators (QHTIs) arising from many-body interacting Landau levels. They can be pictured as two independent copies of quantum Hall systems with opposite chirality, but the experimental system is at odds with the described scenario, where a strong insulating state is observed on increasing the perpendicular magnetic field in charge-neutral, high-mobility graphene devices.
Synthetic biology researchers at Northwestern University have developed a system that can rapidly create cell-free ribosomes in a test tube, then select the ribosome that can perform a certain function.
The system, called ribosome synthesis and evolution (RISE), is an important step toward using ribosomes beyond their natural capabilities. The key feature of RISE is the ability to evolve ribosomes without cell viability constraints. The result could be new ways to synthesize materials, like nylon, or therapies, like new antibiotics that could address rising antibiotic resistance.
“Ribosomes have an extraordinary capability as the protein synthesis machinery of the cell,” said Michael Jewett, Walter P. Murphy Professor of Chemical and Biological Engineering and director of the Center for Synthetic Biology at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering, who led the research. “But to synthesize proteins beyond those found in nature, we have to design and modify the ribosome to work with non-natural substrates. Developing ribosomes in vitro is an important part of that system, and we are very excited to have this new capability.”
Boards and management teams can easily find themselves either stepping on each other’s toes – or, conversely, functioning in parallel universes. So how do you find the perfect balance? Top tips on achieving a Venn-like state from Patrick Dunne – a serial social entrepreneur, chair of the EY foundation and the author of a new book on governance.
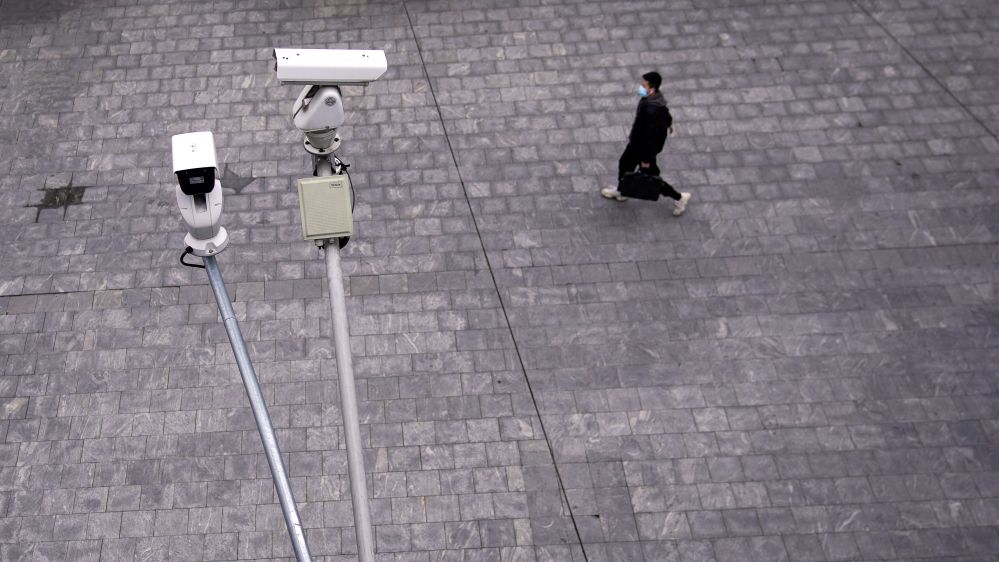
Authorities in China step up surveillance and roll out new artificial intelligence tools to fight deadly epidemic.