Plan to draw up legal definition of ‘ecocide’ attracts support from European countries and small island nations.


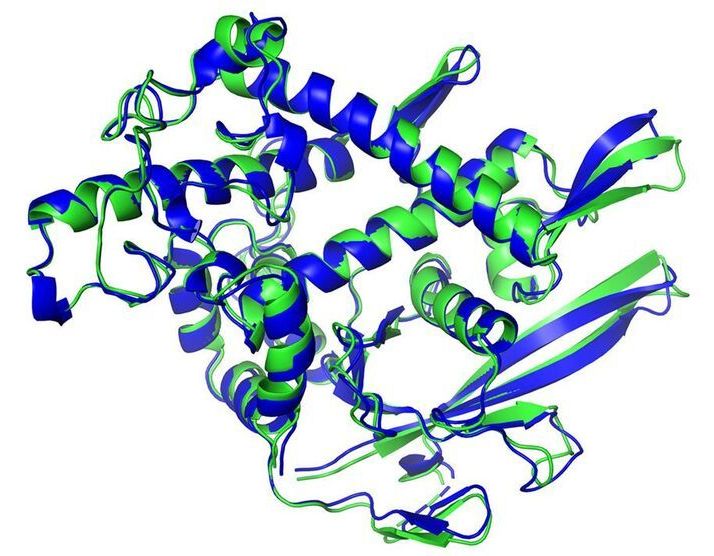
Artificial intelligence (AI) has solved one of biology’s grand challenges: predicting how proteins curl up from a linear chain of amino acids into 3D shapes that allow them to carry out life’s tasks. Today, leading structural biologists and organizers of a biennial protein-folding competition announced the achievement by researchers at DeepMind, a U.K.-based AI company. They say the DeepMind method will have far-reaching effects, among them dramatically speeding the creation of new medications.
A long-standing and incredibly complex scientific problem concerning the structure and behaviour of proteins has been effectively solved by a new artificial intelligence (AI) system, scientists report.
DeepMind, the UK-based AI company, has wowed us for years with its parade of ever-advancing neural networks that continually trounce humans at complex games such as chess and Go.
All those incremental advancements were about much more than mastering recreational diversions, however.
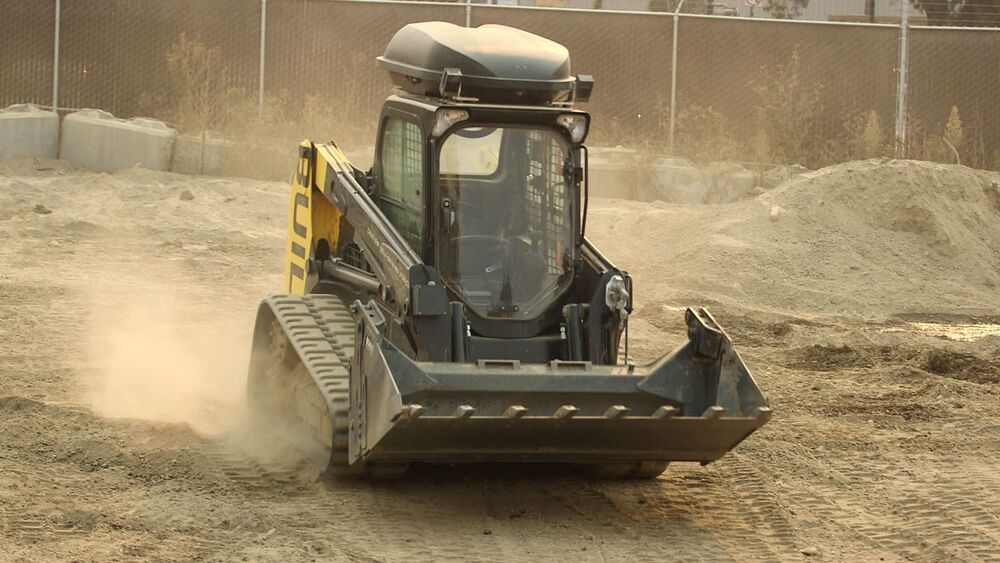


There’s a lot of buzz around self-driving cars, but autonomous driving technology could revolutionize the construction industry first. That industry hasn’t changed much over the last several decades, according to some experts, making it an ideal candidate for automation.
“The way we build today is largely unchanged from the way we used to build 50 years ago,” said Gaurav Kikani, vice president of Built Robotics. “Within two years, I think we’re really going to turn the corner, and you’re going to see an explosion of robotics being used on construction sites.”
The industry is also faced with a labor shortage that the Covid-19 pandemic has further complicated.
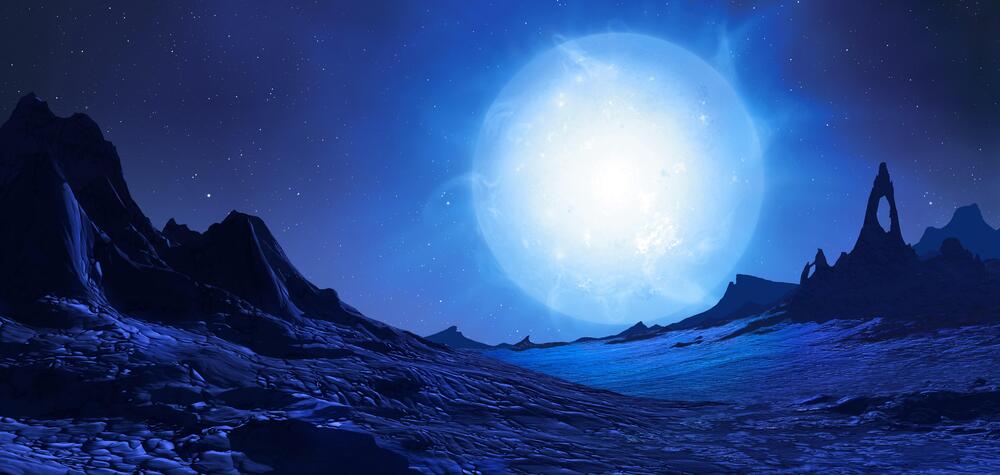

Shockingly, Carroll notes that if our own Earth had formed just one percent farther away from the Sun, it would have suffered a runaway glaciation. By contrast, one percent further in and Earth would have suffered a runaway greenhouse and the fate that befell present-day Venus. “The habitable zone is a planetary tightrope,” writes Carroll.
However, the book does cover the possibility that super-earths and/or gas giant planets that lie in their parent stars’ habitable zones might also harbor planet-sized moons. As the book notes, it’s an idea that Hollywood director James Cameron’s embraced in his ground-breaking movie “Avatar.”
“Envisioning Exoplanets” also offers the reader capsule summaries of the various detection techniques that astronomers have used through the years to remotely explore and characterize these far-flung worlds.
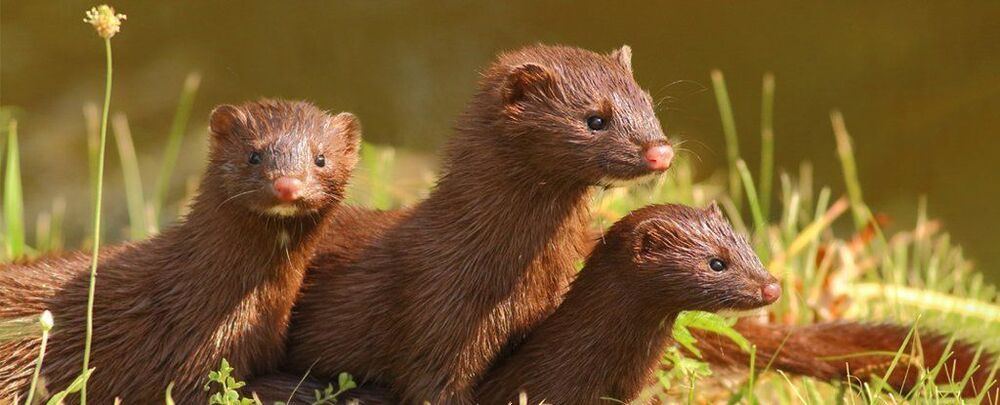


More than 100 SARS-CoV-2 infected mink may have escaped from Danish fur farms, raising the risk that these escapees could spread the novel coronavirus to wild animals, creating a new reservoir for the virus, The Guardian reported.
“Every year, a few thousand mink escape,” and this year, an estimated 5 percent of these escaped animals may have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, Sten Mortensen, veterinary research manager at the Danish Veterinary and Food Administration, told The Guardian.
These mink may be spreading the coronavirus to wild animals, even as millions of mink still on farms are being culled to prevent spread of the virus.
