A newly-designed atomic clock uses entangled atoms to keep time even more precisely than its state-of-the-art counterparts. The design could help scientists detect dark matter and study gravity’s effect on time.



Such primordial black holes (PBHs) could account for all or part of dark matter, be responsible for some of the observed gravitational waves signals, and seed supermassive black holes found in the center of our Galaxy and other galaxies. They could also play a role in the synthesis of heavy elements when they collide with neutron stars and destroy them, releasing neutron-rich material. In particular, there is an exciting possibility that the mysterious dark matter, which accounts for most of the matter in the universe, is composed of primordial black holes. The 2020 Nobel Prize in physics was awarded to a theorist, Roger Penrose, and two astronomers, Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Ghez, for their discoveries that confirmed the existence of black holes. Since black holes are known to exist in nature, they make a very appealing candidate for dark matter.
The recent progress in fundamental theory, astrophysics, and astronomical observations in search of PBHs has been made by an international team of particle physicists, cosmologists and astronomers, including Kavli IPMU members Alexander Kusenko, Misao Sasaki, Sunao Sugiyama, Masahiro Takada and Volodymyr Takhistov.
To learn more about primordial black holes, the research team looked at the early universe for clues. The early universe was so dense that any positive density fluctuation of more than 50 percent would create a black hole. However, cosmological perturbations that seeded galaxies are known to be much smaller. Nevertheless, a number of processes in the early universe could have created the right conditions for the black holes to form.


Once, at a friend’s wedding, he left a group of guests mildly incensed for suggesting that near-future humans might live well into their 100s. A similar thing happens at dinner parties, where the responses are more polite but no less sceptical. Eventually, he says, “I think we are very likely to have a drug that treats ageing in the next 10 years.” Steele believes we will be hopelessly unlucky if scientists don’t make a breakthrough within that time, given how many human trials are in progress or upcoming. And although these breakthroughs won’t result in treatments that extend our lives by 100 years, they will give us enough extra time to ensure we’re alive for subsequent breakthroughs, subsequent treatments, subsequent additions in lifespan and so on.
The biologist Andrew Steele thinks ageing is a disease that can be treated. But if we had a cure for getting old, what would that mean for us?
D. MBA) MalaysiaPresident, World Talent Economy Forum (WTEF)
Topic: Space policy.
Moderator-Sharif Uddin Ahmed Rana (Ph. D. MBA) Malaysia.
President, World Talent Economy Forum (WTEF)
Moderator-Sharif Uddin Ahmed Rana (Ph. D. MBA) Malaysia.
President, World Talent Economy Forum (WTEF)
U.S. Navy Chief Artificial Intelligence Officer, and AI Portfolio Manager, Office of Naval Research.
Brett Vaughan is the U.S. Navy Chief Artificial Intelligence (AI) Officer and AI Portfolio Manager at the Office of Naval Research (ONR).
Mr. Vaughan has 30 years of Defense Intelligence and Technology expertise with strengths in military support, strategic communications, geospatial intelligence (GEOINT), Naval Intelligence and Navy R&D.
He spent two decades in various roles at the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), an additional 10 years in intelligence roles in the Office of the Chief of Naval Operations, and was recently appointed to his current role in 2019.
Mr. Vaughan has Master’s Degrees in Environmental Science from Johns Hopkins University, and in National Security and Strategic Studies from the Naval War College, as well as a Bachelor’s Degree in Geography and Cartography, from University of Mary Washington.
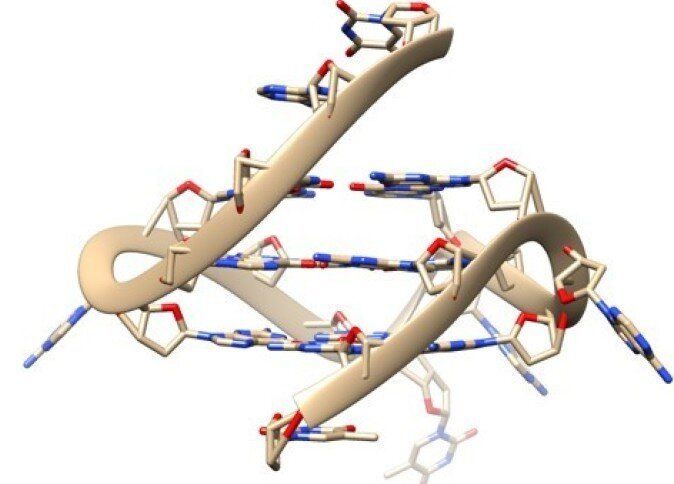
New probes allow scientists to see four-stranded DNA interacting with molecules inside living human cells, unraveling its role in cellular processes.
DNA usually forms the classic double helix shape of two strands wound around each other. While DNA can form some more exotic shapes in test tubes, few are seen in real living cells.
However, four-stranded DNA, known as G-quadruplex, has recently been seen forming naturally in human cells. Now, in new research published today in Nature Communications, a team led by Imperial College London scientists have created new probes that can see how G-quadruplexes are interacting with other molecules inside living cells.


At the same time, there was indeed more action. In one major victory, Amazon, Microsoft, and IBM banned or suspended their sale of face recognition to law enforcement, after the killing of George Floyd spurred global protests against police brutality. It was the culmination of two years of fighting by researchers and civil rights activists to demonstrate the ineffective and discriminatory effects of the companies’ technologies. Another change was small yet notable: for the first time ever, NeurIPS, one of the most prominent AI research conferences, required researchers to submit an ethics statement with their papers.
So here we are at the start of 2021, with more public and regulatory attention on AI’s influence than ever before. My New Year’s resolution: Let’s make it count. Here are five hopes that I have for AI in the coming year.