Two DARPA-developed technologies – a novel decision aid for mission commanders and a rapid software integration tool – played a critical role in the recent Air Force demonstration of the Advanced Battle Management System (ABMS).
The Adapting Cross-domain Kill-webs (ACK) program and the System-of-systems Technology Integration Tool Chain for Heterogeneous Electronic Systems (STITCHES) were among a number of technologies employed in the Aug. 31 – Sep. 4 ABMS on-ramp demonstration, which involved attacks using live aircraft, ships, air defense batteries, and other assets.
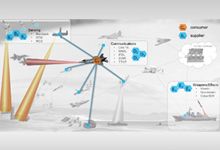
ACK is developing a decision aid for mission commanders to assist them with rapidly identifying and selecting options for tasking – and re-tasking – assets within and across organizational boundaries. Specifically, ACK assists users with selecting sensors, effectors, and support elements across military domains (space, air, land, surface, subsurface, and cyber) that span the different military services to deliver desired effects on targets. Instead of limited, monolithic, pre-defined kill chains, these more disaggregated forces can be used to formulate adaptive “kill webs” based on all of the options available.