Circa 2015
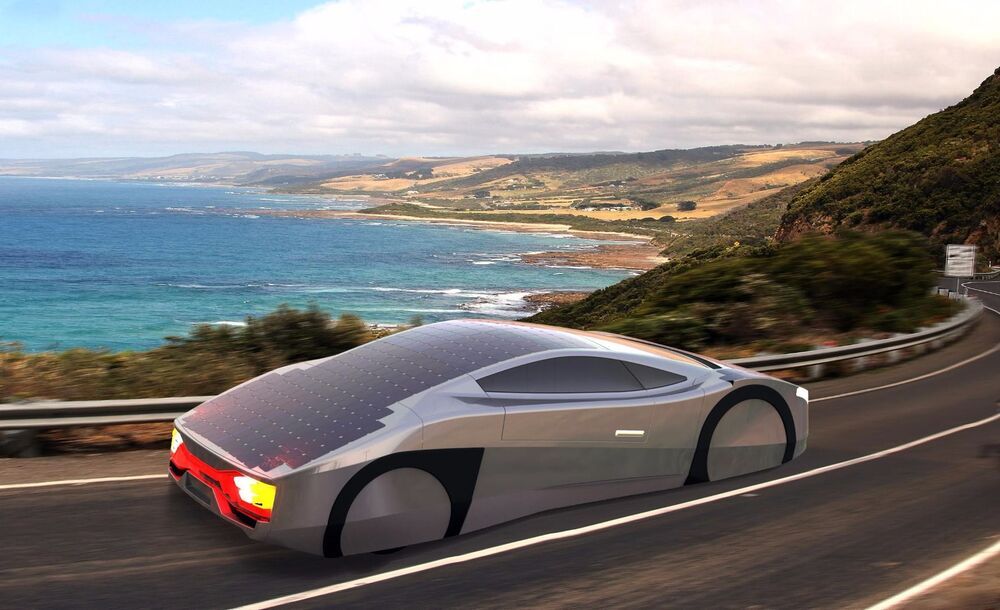
If you’ve ever scanned the comments section on an electric car or bike article, you’ll be familiar with this complaint: “that’s not green, it’s just a coal-powered vehicle.” Well, not this one. The Immortus is an electric car built to generate its own power through some 7 sq m (75 sq ft) of solar photovoltaic paneling. You can charge its battery off the mains if you have to, but if conditions are sunny, the inbuilt solar panels alone will let you drive at more than 60 km/h (37 mph) for an unlimited distance.
The Immortus is based on solar race car technology with the project originally founded by Australia’s Aurora Solar Car Team, which has competed in a bunch of solar race events across the world. Hence the light weight and the shape of the Immortus, which combines maximal sun exposure with extreme aerodynamics, including covered wheels.
Unlike the solar racers, though, it’s designed to approach practicality on the road, with a 0–100 km/h (62 mph) time that will be less than seven seconds and a top speed over 150 km/h (93 mph). It’s also a two-seater with a modest luggage capacity for daily driving. Melbourne-based EVX Ventures, creators of the Immortus, even list fun as a priority, saying it should handle like a well-balanced sports car.