A process called nucleation plays a critical role in many physical and biological phenomena that range from crystallization, melting and evaporation to the formation of clouds and the initiation of neurodegenerative diseases. However, nucleation is a challenging process to study experimentally, especially in its early stages, when several atoms or molecules start to form a new phase from a parent phase. Now, a team of physicists led by the University of California, Los Angeles has used a method called atomic electron tomography to study early-stage nucleation in four dimensions (that is, in three dimensions of space and across time) at atomic resolution.
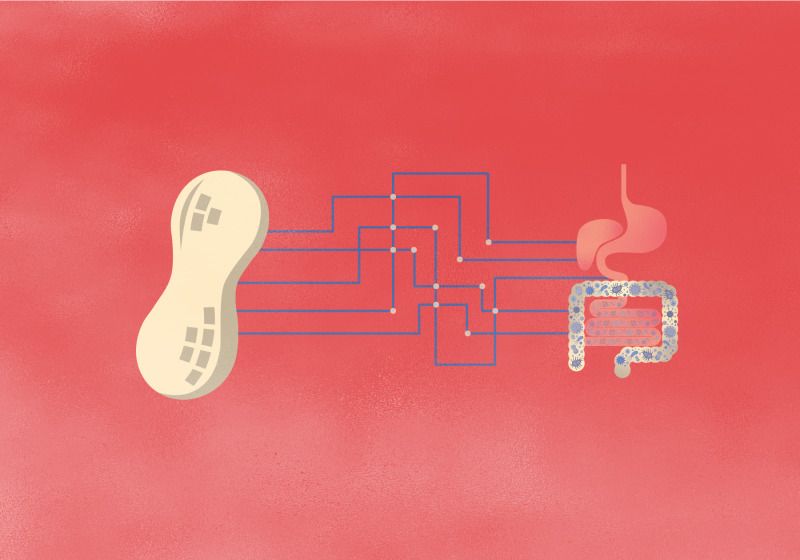
As evidence grows that gut bacteria play roles in the development and persistence of food allergies, researchers begin to explore microbe-based interventions.
Malware researchers discovered a new malicious campaign for Android devices that replaces legitimate apps with tainted copies built to push advertisements or hijack valid ad events.
Around 25 million devices have already been infected with what researchers have dubbed “Agent Smith,” after users installed an app from an unofficial Android store.
https://paper.li/e-1437691924#/
Forms of Transhumanism
Transhumanism takes a variety of overlapping forms united around a common commitment to use science and technology to improve human intellect and/or physiology. Many, though not all, are committed to Posthumanism; others focus on artificial intelligence and its implications for human life. All of them raise important worldview questions, though not always the same ones.
One early form of Transhumanism was Extropianism. The name comes from the neologism extropy, a word intended to convey the reversal of entropy. Its focus is on using science, technology, and reason to take control of human evolution through life extension technologies, uploading our minds into computers, etc. An optimistic philosophy, Extropianism expected to extend human lifespans indefinitely and to recover and heal people frozen cryogenically.
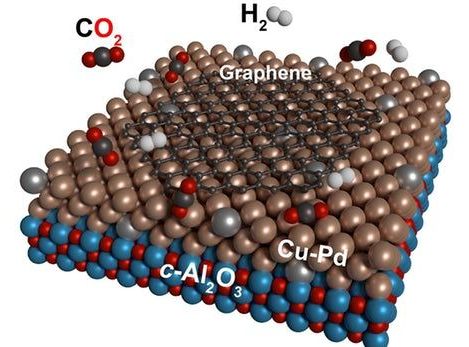
Carbon dioxide is kind of painted as the villain of the 21st century, and it’s not enough to just reduce our emissions now – we need to remove some of what’s already in the atmosphere. Now, researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have developed a simple way to turn the troublesome gas into a useful resource by converting it into the “wonder” material graphene.
Astaroth is, as demonologists will tell you, the Great Duke of Hell and part of the evil trinity. Microsoft, however, is warning that Astaroth malware is attacking Windows users with a fileless “invisible man” methodology. Here’s what you need to know.
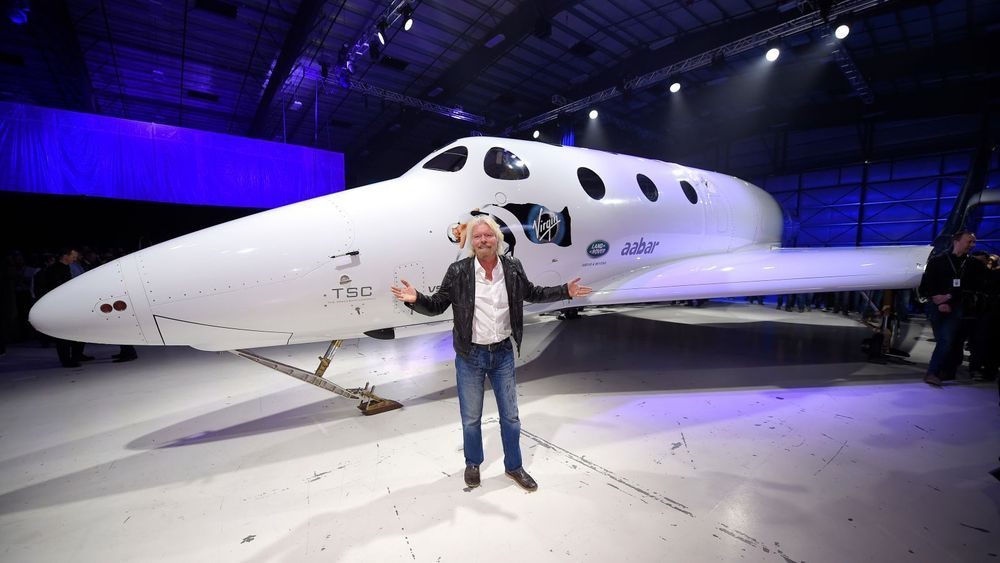
Virgin Galactic is preparing to become the first publicly traded spaceflight company, and the venture is setting a course to be profitable by August 2021, which would put it lightyears ahead of the profitability projections of another transportation-based company that simply moves people around on Earth: Uber.
The Wall Street Journal reports that Virgin Galactic is merging with Social Capital Hedosophia Holdings (SCH), which will take a 49 percent stake and invest about $800 million into the space tourism endeavor.
In 2016, Alpine Tech started a digital currency mining operation in Gondo, on the Italian border.
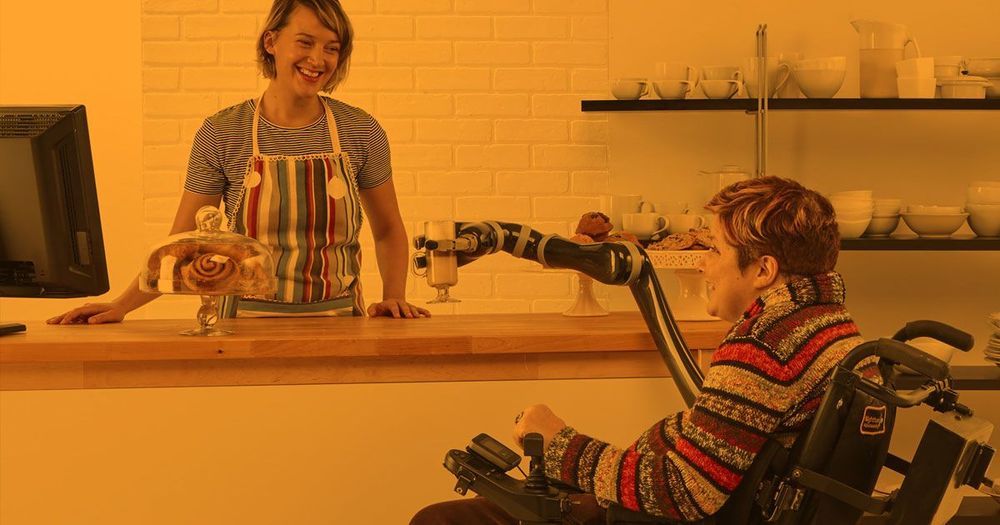
A new robot arm can help people who use wheelchairs better handle the day-to-day tasks that might otherwise be too challenging or awkward.
The Jaco, a robotic arm made by the tech company Kinova Robotics, can attach to a wheelchair and operate as a sort of third arm, according to Digital Trends — helping people with limited mobility go about their lives with a greater degree of independence.
The technical challenges are not as daunting as the social and diplomatic ones, says bioengineer Kevin Esvelt at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Media Lab in Cambridge, who was among the first to build a CRISPR-based gene drive. “Technologies like this have real-world consequences for people’s lives that can be nearly immediate.”
Altering the genomes of entire animal populations could help to defeat disease and control pests, but researchers worry about the consequences of unleashing this new technology.