“Disembodied Brains: Understanding our Intuitions on Human-Animal Neuro-Chimeras and Human Brain Organoids” by John H. Evans Book Link: https://amzn.to/40SSifF “Introduction to Organoid Intelligence: Lecture Notes on Computer Science” by Daniel Szelogowski Book Link: https://amzn.to/3Eqzf4C “The Emerging Field of Human Neural Organoids, Transplants, and Chimeras: Science, Ethics, and Governance” by The National Academy of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine Book Link: https://amzn.to/4hLR1Oe (Affiliate links: If you use these links to buy something, I may earn a commission at no extra cost to you.) Playlist: • Two AI’s Discuss: The Quantum Physics… The hosts explore the ethical and scientific implications of brain organoids and synthetic biological intelligence (SBI). Several sources discuss the potential for consciousness and sentience in these systems, prompting debate on their moral status and the need for ethical guidelines in research. A key focus is determining at what point, if any, brain organoids or SBI merit moral consideration similar to that afforded to humans or animals, influencing research limitations and regulations. The texts also examine the use of brain organoids as a replacement for animal testing in research, highlighting the potential benefits and challenges of this approach. Finally, the development of “Organoid Intelligence” (OI), combining organoids with AI, is presented as a promising but ethically complex frontier in biocomputing. Our sources discuss several types of brain organoids, which are 3D tissue cultures derived from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) that self-organize to model features of the developing human brain. Here’s a brief overview: • Cerebral Organoids: This term is often used interchangeably with “brain organoids”. They are designed to model the human neocortex and can exhibit complex brain activity. These organoids can replicate the development of the brain in-vitro up to the mid-fetal period. • Cortical Organoids: These are a type of brain organoid specifically intended to model the human neocortex. They are formed of a single type of tissue and represent one important brain region. They have been shown to develop nerve tracts with functional output. • Whole-brain Organoids: These organoids are not developed with a specific focus, like the forebrain or cerebellum. They show electrical activity very similar to that of preterm infant brains. • Region-specific Organoids: These are designed to model specific regions of the brain such as the forebrain, midbrain, or hypothalamus. For example, midbrain-specific organoids can contain functional dopaminergic and neuromelanin-producing neurons. • Optic Vesicle-containing Brain Organoids (OVB-organoids): These organoids develop bilateral optic vesicles, which are light sensitive, and contain cellular components of a developing optic vesicle, including primitive corneal epithelial and lens-like cells, retinal pigment epithelia, retinal progenitor cells, axon-like projections, and electrically active neuronal networks. • Brain Assembloids: These are created when organoids from different parts of the brain are placed next to each other, forming links. • Brainspheres/Cortical Spheroids: These are simpler models that primarily resemble the developing in-vivo human prenatal brain, and are particularly useful for studying the cortex. Unlike brain organoids, they do not typically represent multiple brain regions. • Mini-brains: This term has been debunked in favor of the more accurate “brain organoid”. These various types of brain organoids offer diverse models for studying brain development, function, and disease. Researchers are also working to improve these models by incorporating features like vascularization and sensory input. #BrainOrganoids #organoid #Bioethics #OrganoidIntelligence #WetwareComputing #Sentience #ArtificialConsciousness #Neuroethics #AI #Biocomputing #NeuralNetworks #ConsciousnessResearch #PrecautionaryPrinciple #AnimalTestingAlternatives #ResearchEthics #EmergingTechnology #skeptic #podcast #synopsis #books #bookreview #ai #artificialintelligence #booktube #aigenerated #documentary #alternativeviews #aideepdive #science #hiddenhistory #futurism #videoessay #ethics
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Tesla FSD Just Shocked Joe Rogan
Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology is rapidly advancing, impressing users and analysts alike, while navigating challenges in the auto industry and broader economic factors.
Questions to inspire discussion.
Tesla’s FSD Progress.
🚗 Q: How many unsupervised miles has Tesla’s FSD driven? A: Tesla’s FSD has driven over 50,000 unsupervised miles, demonstrating significant progress in autonomous driving capabilities.
🌐 Q: What indicates Tesla’s transition to software-defined earnings? A: FSD unsupervised miles and operating domain growth are key leading indicators of Tesla’s shift towards software-defined earnings.
🤖 Q: How does Tesla’s FSD showcase AI potential in driving? A: Tesla’s FSD unsupervised capabilities, demonstrated in complex driving scenarios, serve as a proof case for artificial intelligence’s potential in autonomous driving.
Post-Scarcity Civilizations: Infinite Resources & Our Future
In a future of limitless resources, what challenges remain when scarcity fades but human desires endure? Join us as we explore the path to post-scarcity civilizations, where technology solves material needs—but purpose, meaning, and new challenges await.
Watch my exclusive video Post-Consciousness Civilizations: https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–… Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa… Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30. Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Credits: Post-Scarcity Civilizations: Infinite Resources & Our Future Episode 495; April 17, 2025 Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Edited by: Donagh Broderick Graphics: Jeremy Jozwik, Ken York YD Visual Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator Markus Junnikkala, “A Fleet Behind the Moon” Phase Shift, “Forest Night” Kai Engel, “Endless Story About Sun and Moon” Chris Zabriskie, “Unfoldment, Revealment”, “A New Day in a New Sector” Taras Harkavyi, “Alpha and…” Stellardrone, “Red Giant”, “Billions and Billions“
Get Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa…
Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Post-Scarcity Civilizations: Infinite Resources & Our Future.
Episode 495; April 17, 2025
Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Edited by: Donagh Broderick.
Graphics: Jeremy Jozwik, Ken York YD Visual.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Markus Junnikkala, \

Earth has just received a radio signal sent from a galaxy that is 9 billion light years away
This is the first time that scientists have discovered a signal coming from a galaxy 9 billion light years from Earth.
The radio signal was detected by Pune, India’s giant VHF radio telescope.
The huge radio telescope is equipped with thirty parabolic antennas, each pointed skyward and with a diameter of about 45 meters.

Risky surgery after a stroke due to carotid artery stenosis may no longer be necessary in most patients
European research led by University College London (UCL), together with Amsterdam UMC and the University of Basel, shows that a significant proportion of patients who suffer a stroke due to carotid artery narrowing can be treated with medication only.
A risky carotid artery operation, currently still the standard treatment for many patients, may then no longer be necessary for this group of patients. This research, published in The Lancet Neurology, may lead to the global guidelines for the treatment of these patients being adjusted.
In the Netherlands, about 2,000 people with carotid artery stenosis are operated on every year after they have had a stroke. Thirty years ago, large studies showed that an operation in which a narrowing in the carotid artery is removed reduced the risk of a new stroke.
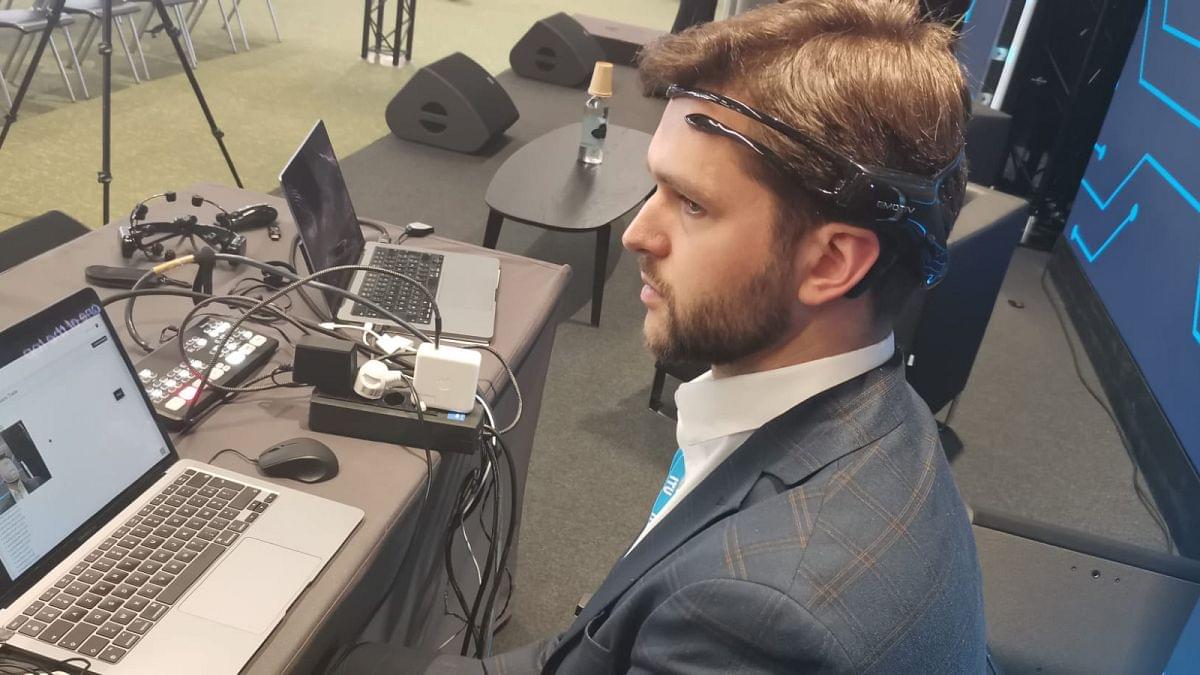


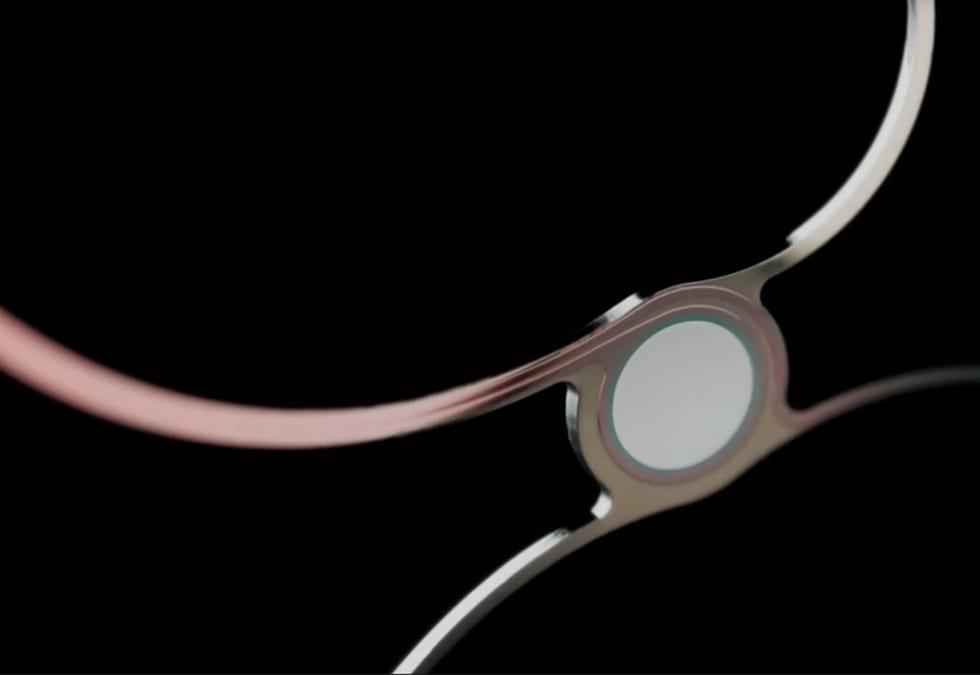
Non-invasive brain headset enables ALS patients to speak again
Patients with ALS often lose their ability to speak making it harder to communicate with their family. This AI-powered device wants to change that.