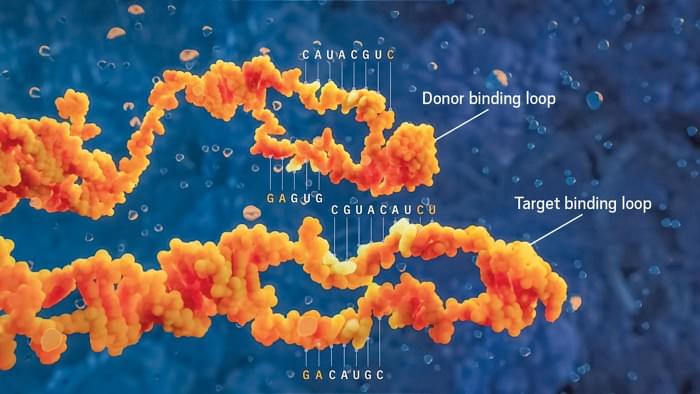
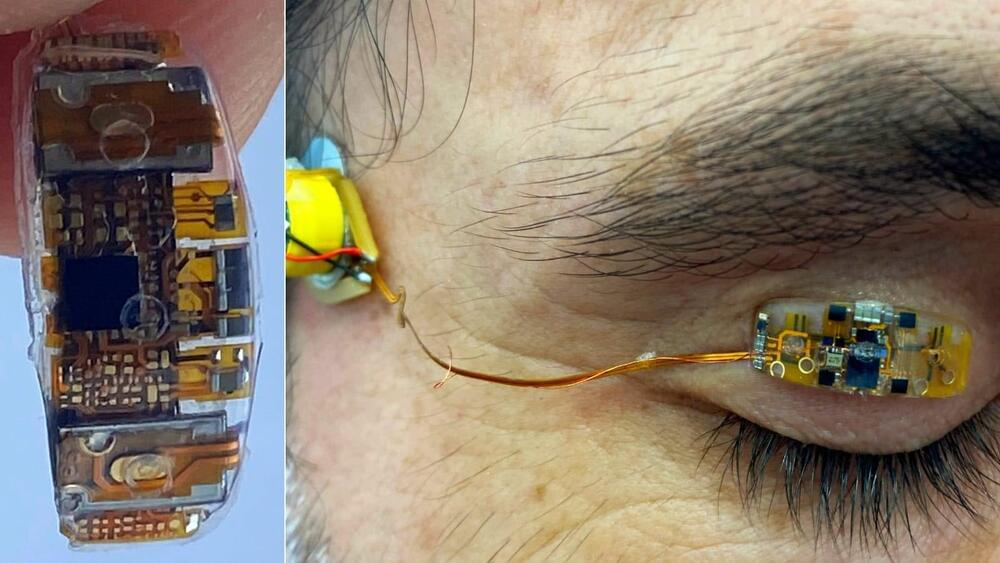
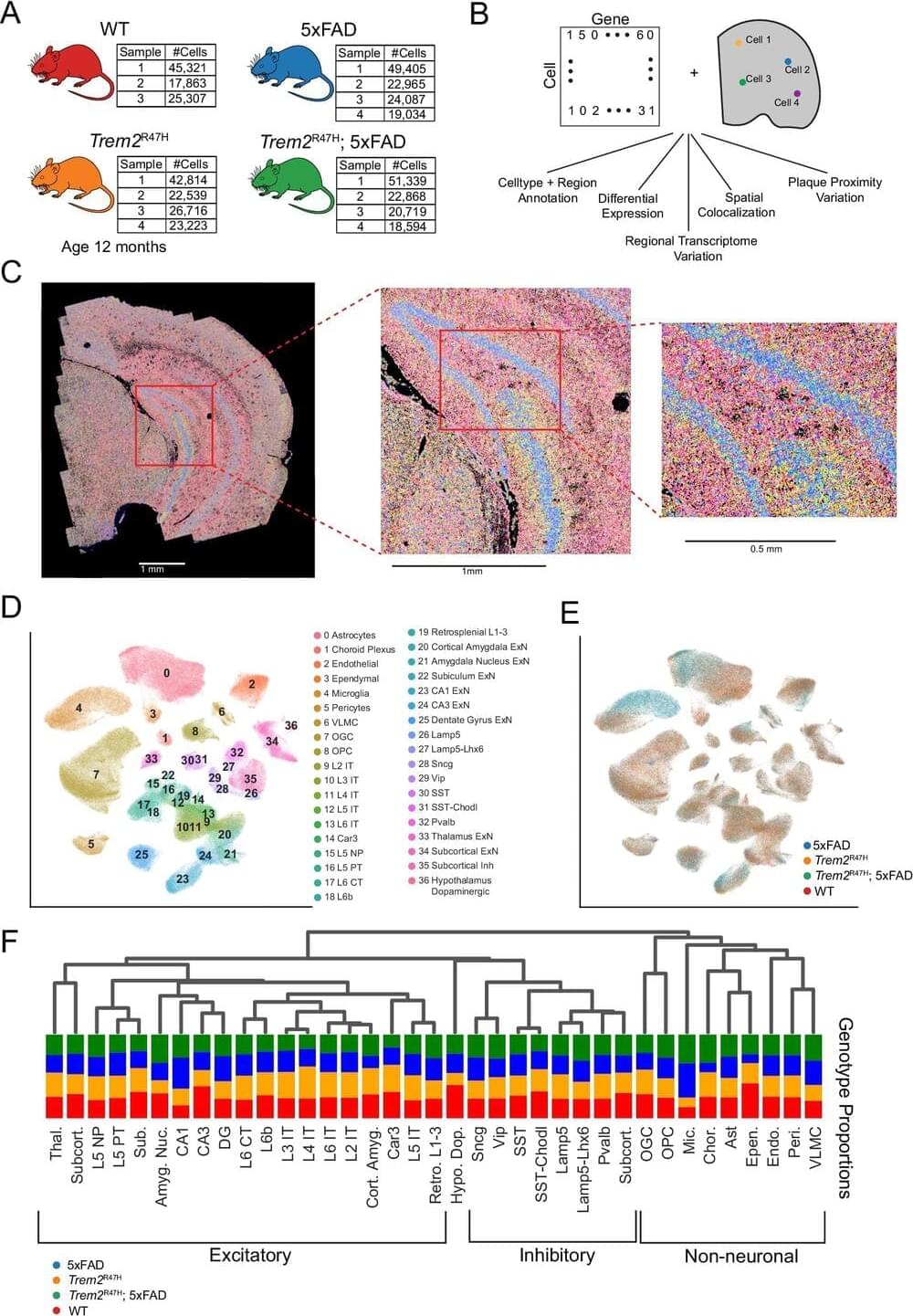
Nanoelectronics.
This new feature in Nano TV will present the best of science and technology in a short format, which is easy to understand and also appreciate the beauty of scientific knowledge. Catering to all, these shorts will be informative and educative. Explore science, explore Nanotechnology through our latest series called Nano Shorts.
Nanotechnology is the buzz of the world today. Here are some lesser-known facts about this emerging technology: