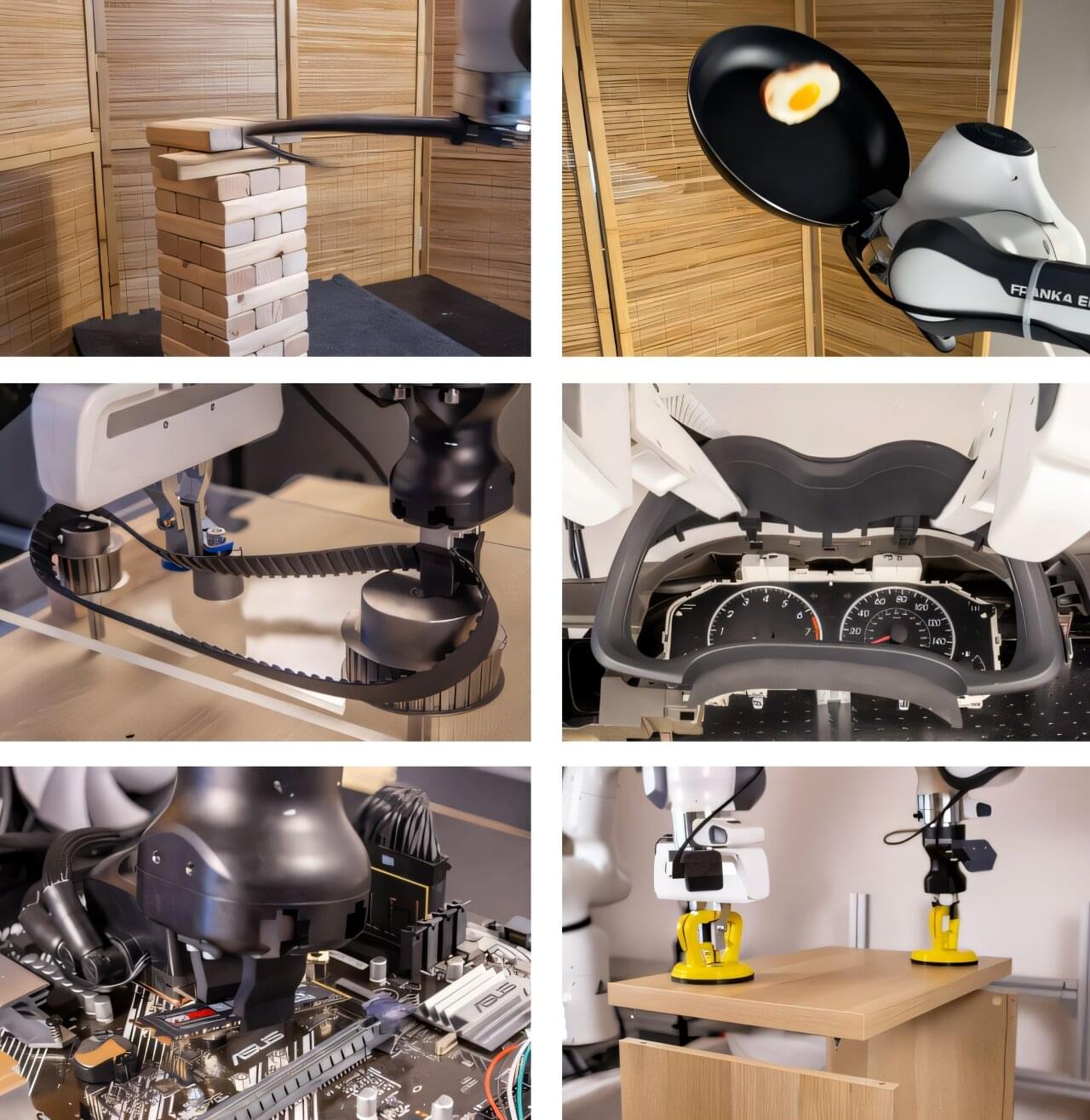
As robots increasingly handle everyday tasks, skilled engineers and effective strategies become indispensable when malfunctions occur.
At UC Berkeley, researchers in Sergey Levine’s Robotic AI and Learning Lab eyed a table where a tower of 39 Jenga blocks stood perfectly stacked. Then a white-and-black robot, its single limb doubled over like a hunched-over giraffe, zoomed toward the tower, brandishing a black leather whip.
Through what might have seemed to a casual viewer like a miracle of physics, the whip struck in precisely the right spot to send a single block flying out from the stack while the rest of the tower remained structurally sound.
This task, known as “Jenga whipping,” is a hobby pursued by people with the dexterity and reflexes to pull it off. Now, it’s been mastered by robots, thanks to a novel, AI-powered training method.
Bloomberg on the Economic Singularity:
“If AI is about to get much cheaper, the path to an answer on its economic impact is going to get shorter. For workers nervously wondering if large language models will make their skills redundant, a lot is riding on which camp is right.”
For investors in artificial intelligence, the last week delivered a painful shock. The sudden appearance of DeepSeek — a Chinese AI firm boasting a world-class model developed at bargain-basement costs — triggered a massive selloff in Nvidia and other US tech champions.
What matters for the economy, though, is not the ups and downs of stock prices for the Magnificent Seven, but whether AI drives gains in productivity, and how those gains are divided up. For all the excitement, and the trillion-dollar valuations for AI firms, evidence of a boost to productivity remains thin on the ground.
The creation of energy from nuclear fusion has been a goal for decades. And technology advances at companies like General Atomics in San Diego are bringing us closer to it. KPBS sci-tech reporter Thomas Fudge tells us about this quest to put the “sun in a bottle,” and use it to provide what would be abundant power.
#brain #brainhealth #discoveryourself #educationalyoutube #education #educationalvideo #health #healthtips.
#PhysicsOfTheImpossible.
#MichioKaku.
#TimeTravel.
#Teleportation.
#Invisibility.
#SciFiTech.
#ScientificImpossibilities.
#FutureTech.
#Physics Can the impossible be achieved scientifically? In this video, we explore the fascinating ideas from Physics of the Impossible by theoretical physicist Michio Kaku. We’ll discuss concepts like time travel, invisibility, and teleportation—could they become reality in the future?
If you’re a fan of science fiction and physics, this video is for you! Don’t forget to subscribe and turn on notifications for more exciting content.
📌 Topics Covered:
✔️ What is Physics of the Impossible?
✔️ The three categories of scientific impossibilities.
✔️ Is time travel possible?
✔️ Sci-fi technologies that may become real.
📚 Sources & References:
Can you make something invisible? Neil deGrasse Tyson and comedian Negin Farsad discover the science behind invisibility with professor of physics and optical science, Greg Gbur. What would real-life invisibility look like?
Can you be invisible in other parts of the magnetic spectrum? We discuss transparency versus invisibility and how metamaterials help us interact with different wavelengths. What does light have to do in order to make something invisible? We break down invisibility cloaks and other invisibility devices from fiction.
Could you make yourself invisible to all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum? We explore the main challenges in achieving invisibility and the difference between passive and active invisibility. How useful of a power would it be?
We discuss the interaction between waves and matter. What makes some waves reflect off matter and others pass through? Learn about x rays and how they work, plus, an at-home invisibility trick using prisms. Finally, could you make someone invisible to time?
A spy presses a button on their suit and blinks out of sight. A wizard wraps himself in a cloak and disappears. A star pilot flicks a switch, and their ship vanishes into space. Invisibility is one of the most tantalizing powers in fiction, spanning all kinds of stories. But could this fantasy ever become a reality? Max G. Levy digs into the technologies that could make invisibility possible.
Lesson by Max G. Levy, directed by Michalis Kalopaidis, Zedem Media.
Support Our Non-Profit Mission.
Support us on Patreon: http://bit.ly/TEDEdPatreon.
To try everything Brilliant has to offer—free—for a full 30 days, visit https://brilliant.org/ArtemKirsanov. You’ll also get 20% off an annual premium subscription.
Socials:
X/Twitter: https://twitter.com/ArtemKRSV
Patreon: / artemkirsanov.
My name is Artem, I’m a graduate student at NYU Center for Neural Science and researcher at Flatiron Institute.
In this video, we explore how the brain tags which memories to keep and the role of a special brain wave – a hippocampal sharp-wave ripple in this process.
Sam Harris and Roger Penrose discuss the mysteries of consciousness and selfhood.
Is the Self merely an illusion?
With a free trial, you can watch the full debate NOW at https://iai.tv/video/the-divided-self-sam-harris-roger-penro…escription.
Many have sought to divide the self into separate parts. From Aristotle’s distinction between the rational and irrational self to Freud’s separation of the conscious and unconscious mind, from Kahneman’s fast and slow self to McGilchrist’s selves of the left and right brain. But critics argue it makes no sense to see the self as divided. From Descartes to Sartre, many philosophers have concluded that to be conscious is to be conscious of something and there can be no further self hiding within consciousness. After all, if there are two aspects of the self does it not require a third to oversee or combine them? Meanwhile, neuroscience has been unable to identify a self at all let alone multiple selves.