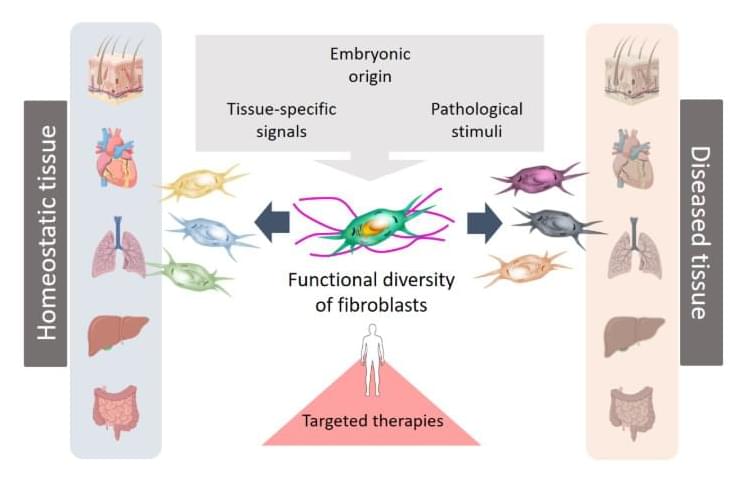
Fibroblasts are specialised connective tissue cells that play a key role in wound healing and tissue regeneration. The recent scientific publication from the University of Leipzig Medical Center shows that fibroblasts respond differently depending on the organ and disease context. Their functions are shaped by their embryonic origin, tissue-specific signals, and pathological stimuli. These specialised cells are not only involved in tissue repair and remodelling, but also influence the immune system and the development of diseases such as cancer, fibrosis and chronic inflammatory conditions.
“Until now, our understanding of fibroblast diversity has been based primarily on studies in animal models. This new review is the first to compare and integrate extensive human studies that have used modern single-cell technologies. This approach makes it possible to combine findings from different human studies, creating a comprehensive picture of the various origins and functions of human fibroblasts,” says Professor Sandra Franz, lead author of the study from the University of Leipzig Medical Center.
This deeper understanding of cellular heterogeneity opens up new avenues for the development of targeted therapies.