Some people have claimed that a “business case” for profitable interplanetary trade with a Mars settlement, or at least the identification a saleable product for trade, is required before such a settlement can be established or supported by business or government. But there is no reasonable prospect for trade in any significant mass of physical material from a Mars settlement back to Earth in the near future due to the high transport costs. In his recent article in the National Review, “Elon Musk’s Plan to Settle Mars,” Robert Zubrin makes exactly the same point: a business case based on physical trade is not necessary and makes little sense. Later trade and commerce via non-physical goods such as software is probable once a settlement is fully operational. More significant and interesting economic situations will occur on Mars.
A good model for the expenditures needed to found colonies is the Greek and Phoenician expansion all across the Mediterranean and Black Sea areas in the period early in Greek history (before about 600 BC), leading to the founding of one of the greatest trading cities in history, Carthage. The cities who founded each colony did not expect immediate profit, but wanted good places for an expanding population and knew that, once the new cities were established, trade would also become established. Most of the cost was probably in building more ships. When European colonies were first established in the New World by Spain and Portugal, the emphasis was initially on a search for treasure, not production of products. English and Dutch colonies later led the way to commerce across the Atlantic, with tobacco, sugar, and cotton suddenly becoming a major part of world trade.
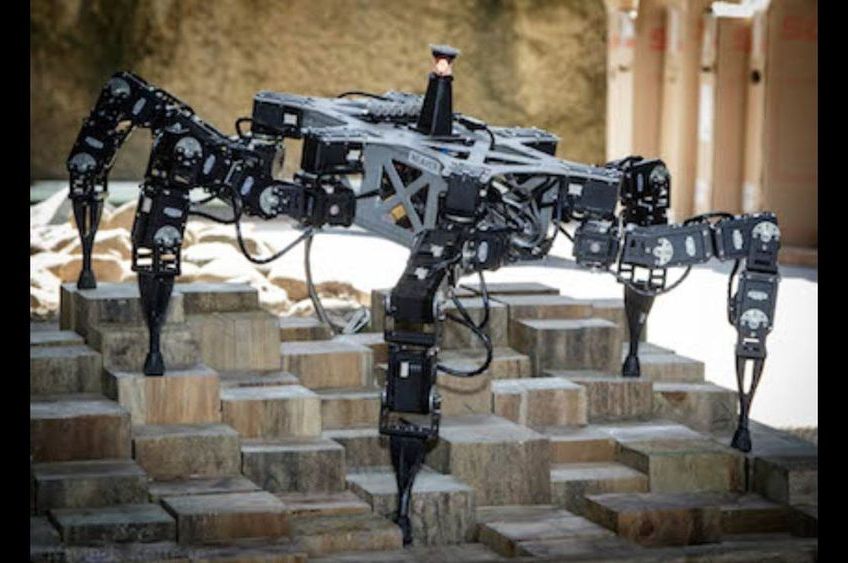
A look at some of the steps required to create a Mars settlement will help us understand at least a little about Mars settlement economics. For a Mars settlement, motivation and economics are interwoven. It is possible for at least a partial business case to be made for the transport of settlers and the materials they will need to initiate some phase of Mars settlement. This includes the current effort to create a large number of reliable, low cost, and reusable super-heavy boosters and spacecraft, able to take payloads of 100 tons or more of cargo and passengers to Mars and land them at the right location. Part of this development and construction cost will be defrayed by commercial and government uses of the same vehicles, such as placing very heavy payloads in LEO and taking equipment and passengers to and around the Moon.