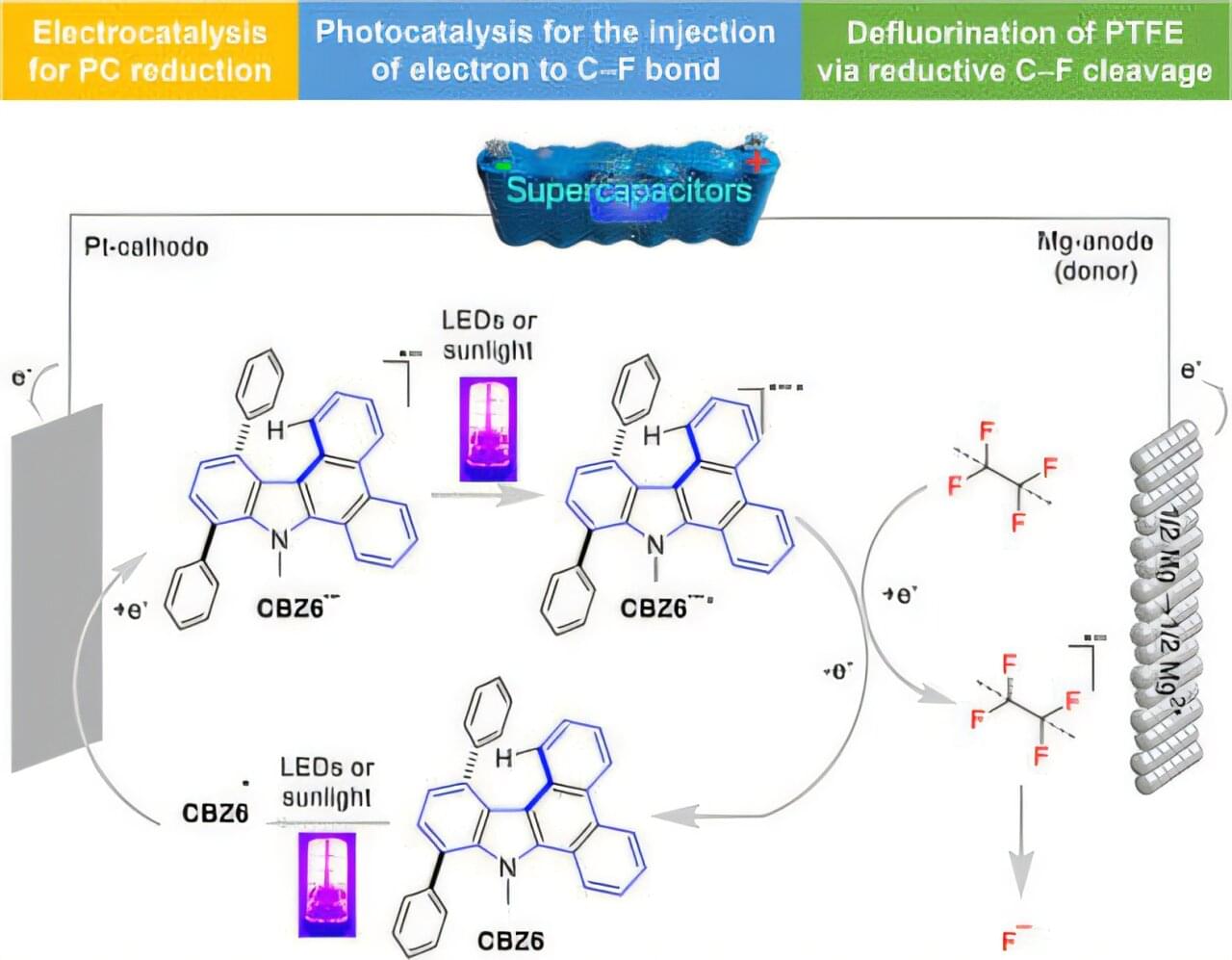
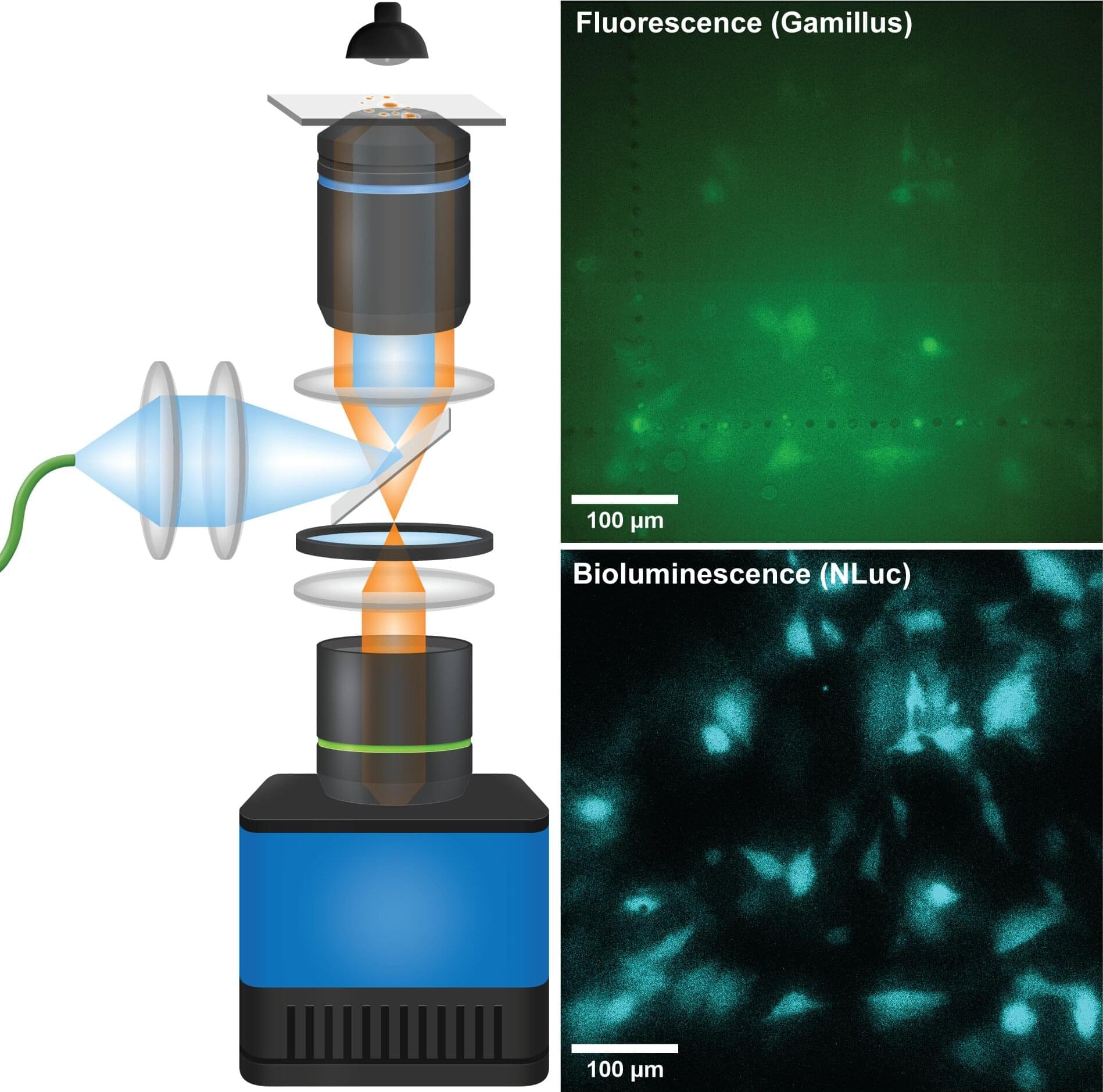
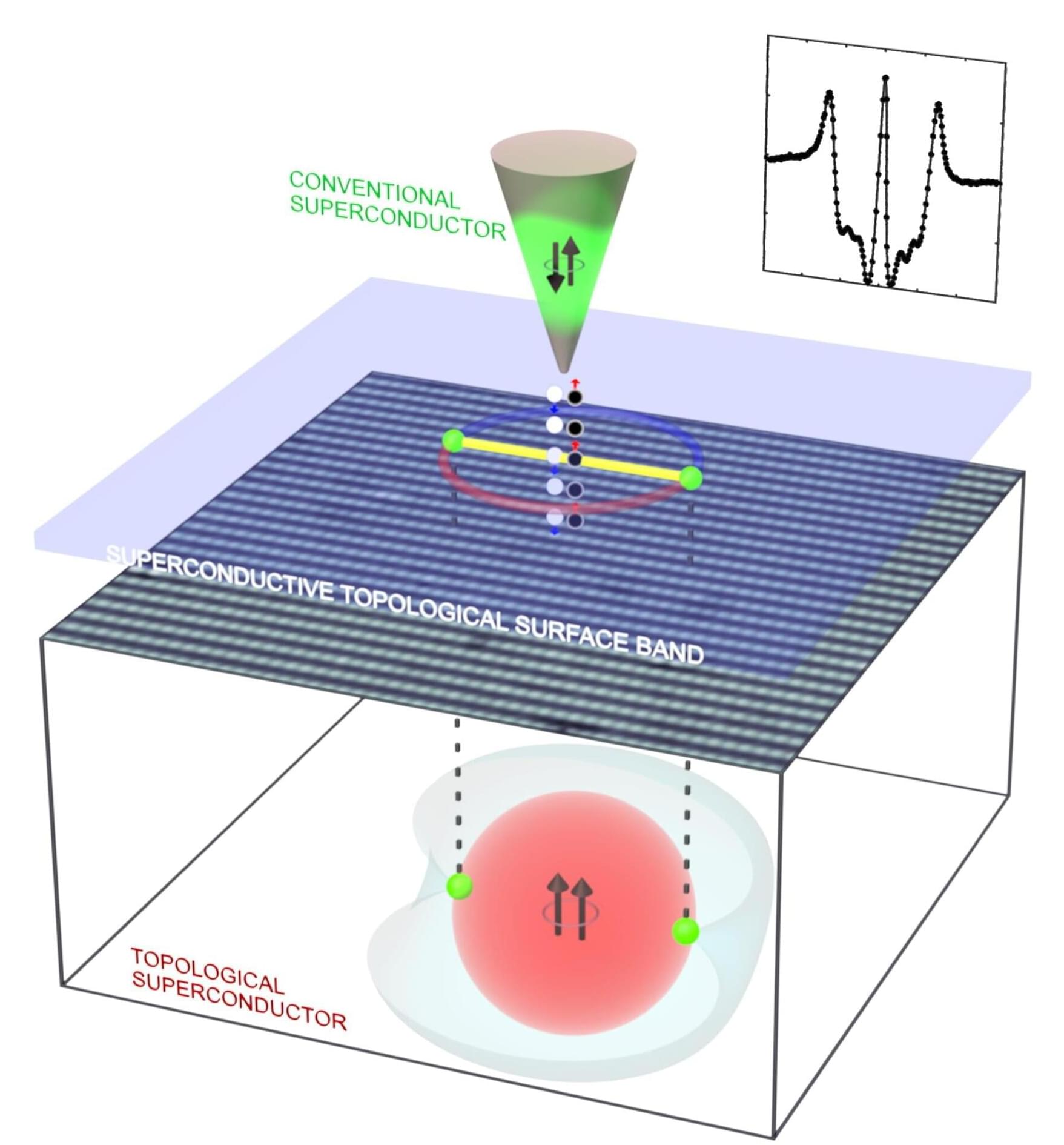
Several key moments in Earth’s history help us humans answer the question “How did we get here?” These moments also shed light on the question “Where are we going?” and offer scientists deeper insight into how organisms adapt to physical and chemical changes in their environment.
Among them is an extended evolutionary occurrence over 2 billion years ago, known as the Great Oxidation Event (GOE). This marked the first time that oxygen produced by photosynthesis—essential for the survival of humans and many other life forms—began to accumulate in significant amounts in the atmosphere.
If you traveled back in time to before the GOE (more than 2.4 billion years ago), you would encounter a largely anoxic (oxygen-free) environment. The organisms that thrived then were anaerobic, meaning they didn’t require oxygen and relied on processes like fermentation to generate energy. Some of these organisms still exist today in extreme environments such as acidic hot springs and hydrothermal vents.