Real aging reversal!
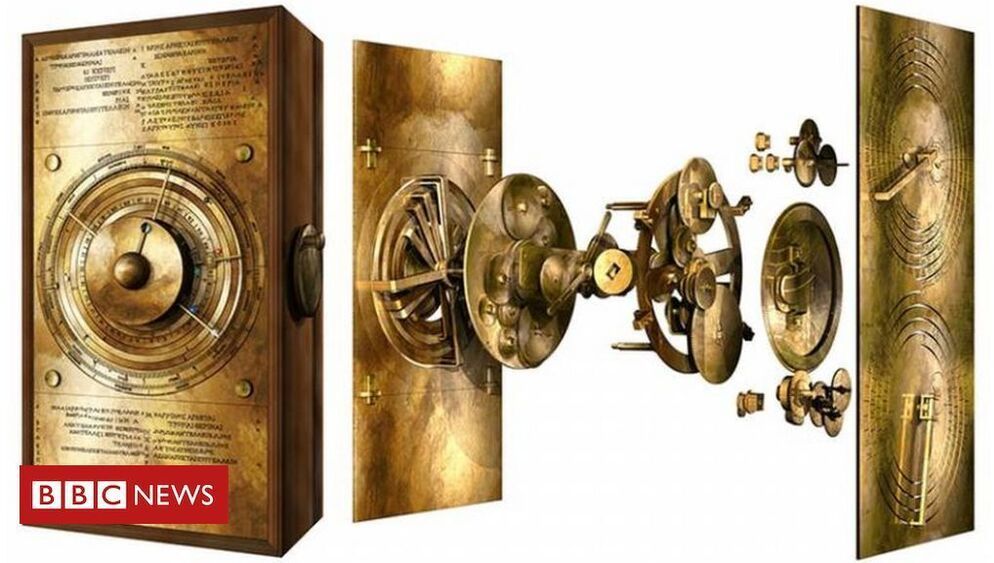



Most cancers are driven by continuous cell division, the cause of which is largely a mystery. Scientists at Vanderbilt University have discovered a genetic switch that seems to touch off that abnormal proliferation of cells—and they did it with the gene editing system CRISPR.
Using a genomewide CRISPR screen, the Vanderbilt team discovered that deleting a protein made by the gene TRAF3 causes cells to proliferate without stopping, even after they reach a certain density that would normally signal them to stop dividing. Because TRAF3 has not been linked to cancer before, the finding could offer key insights into the development of some cancers, the researchers reported in the journal eLife.
The team started with 40 million epithelial cells, using CRISPR to select cells that kept dividing uncontrollably. They were surprised to discover that a loss of TRAF3 activates signaling that in turn drives cell proliferation. TRAF3 normally activates immunity and had not been linked to uncontrolled cell growth before, they said.
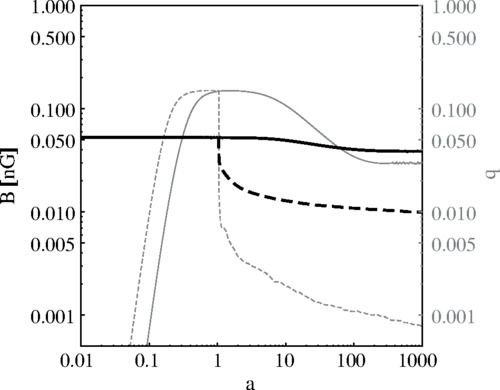
Primordial magnetic fields (PMFs), being present before the epoch of cosmic recombination, induce small-scale baryonic density fluctuations. These inhomogeneities lead to an inhomogeneous recombination process that alters the peaks and heights of the large-scale anisotropies of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation. Utilizing numerical compressible MHD calculations and a Monte Carlo Markov chain analysis, which compares calculated CMB anisotropies with those observed by the WMAP and Planck satellites, we derive limits on the magnitude of putative PMFs. We find that the total remaining present day field, integrated over all scales, cannot exceed 47 pG for scale-invariant PMFs and 8.9 pG for PMFs with a violet Batchelor spectrum at 95% confidence level.
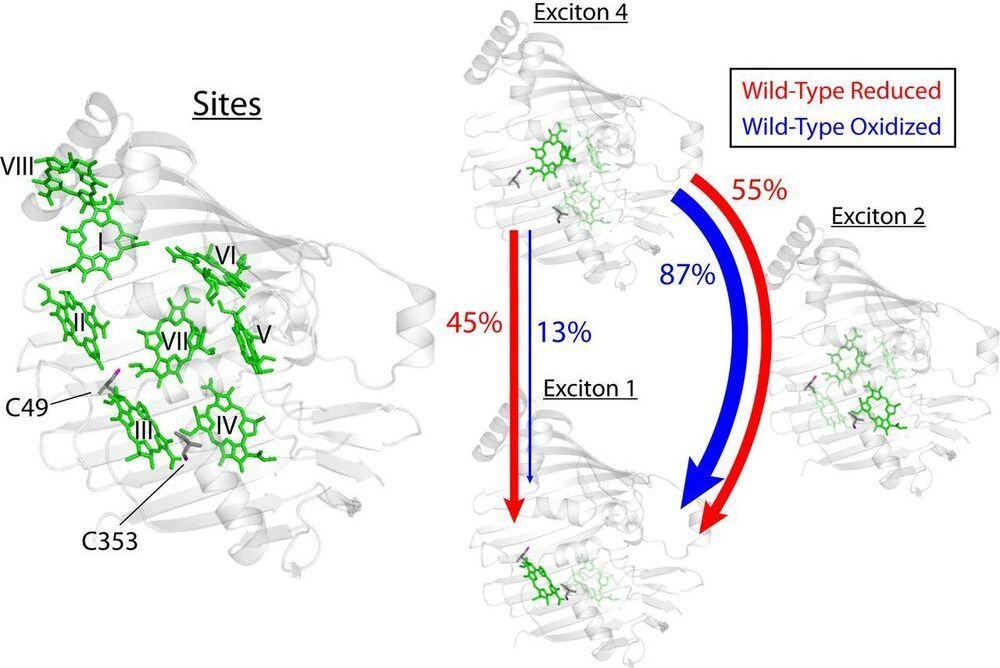
Photosynthetic light-harvesting antennae transfer energy toward reaction centers with high efficiency, but in high light or oxidative environments, the antennae divert energy to protect the photosynthetic apparatus. For a decade, quantum effects driven by vibronic coupling, where electronic and vibrational states couple, have been suggested to explain the energy transfer efficiency, but questions remain whether quantum effects are merely consequences of molecular systems. Here, we show evidence that biology tunes interpigment vibronic coupling, indicating that the quantum mechanism is operative in the efficient transfer regime and exploited by evolution for photoprotection. Specifically, the Fenna–Matthews–Olson complex uses redox-active cysteine residues to tune the resonance between its excitons and a pigment vibration to steer excess excitation toward a quenching site.
Photosynthetic species evolved to protect their light-harvesting apparatus from photoxidative damage driven by intracellular redox conditions or environmental conditions. The Fenna–Matthews–Olson (FMO) pigment–protein complex from green sulfur bacteria exhibits redox-dependent quenching behavior partially due to two internal cysteine residues. Here, we show evidence that a photosynthetic complex exploits the quantum mechanics of vibronic mixing to activate an oxidative photoprotective mechanism. We use two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy (2DES) to capture energy transfer dynamics in wild-type and cysteine-deficient FMO mutant proteins under both reducing and oxidizing conditions. Under reducing conditions, we find equal energy transfer through the exciton 4–1 and 4–2–1 pathways because the exciton 4–1 energy gap is vibronically coupled with a bacteriochlorophyll-a vibrational mode.
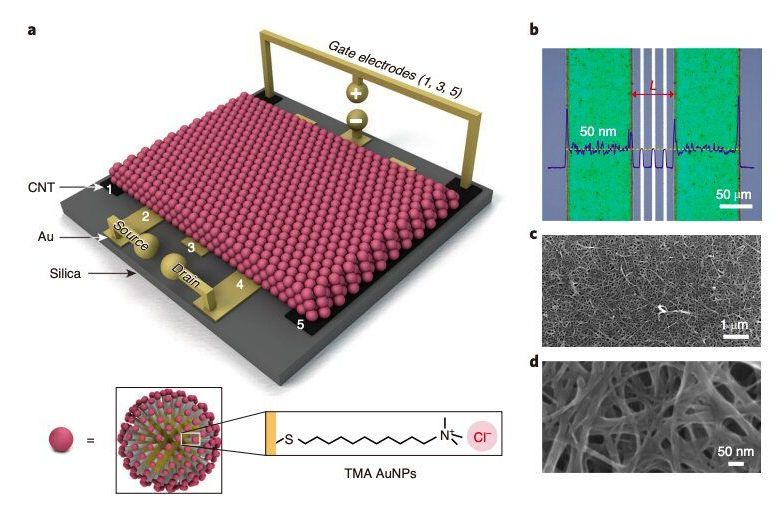
Transistors, devices that can amplify, conduct or switch electronic signals or electric current, are key components of many electronics on the market today. These devices can be fabricated using a variety of inorganic and organic semiconducting materials.
Metals are generally considered unsuitable for fabricating transistors, as they screen electric fields and thus make it difficult to realize devices with tunable electrical conductivity. A possible way to create electronic components based on metals is to use gradients of counterions in films of metal nanoparticles functionalized with charged organic ligands.
In the past, engineers have successfully used this strategy to create a variety of devices, ranging from resistors to diodes and sensors. Nonetheless, modulating the electrical conductivity of these devices has often proved to be very challenging.
These shifting dynamics in India’s digital marketplace are yet another warning sign of what’s been dubbed the splinternet, foreshadowing a possible world where each country sticks to its own apps and abandons the open and global nature of the internet. For now, however, these homegrown apps may find it difficult to compete at the same level unless the government decides to ban Facebook and Twitter, too.
While Twitter finds itself in a prolonged standoff with the Indian government over the company’s refusal to take down certain accounts, a senior executive of a very similar Indian social network says the sudden attention on his app has been “overwhelming.”
“It feels like … you’ve just been put in the finals of the World Cup suddenly and everyone’s watching you and the team,” Mayank Bidawatka, co-founder of Koo, told CNN Business.
Koo, touted by India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi and used enthusiastically by several officials and ministries in his government, has been downloaded 3.3 million times so far this year, per app analytics firm Sensor Tower. It’s a promising start for a company founded less than a year ago, but less than Twitter’s 4.2 million Indian downloads during the same period.
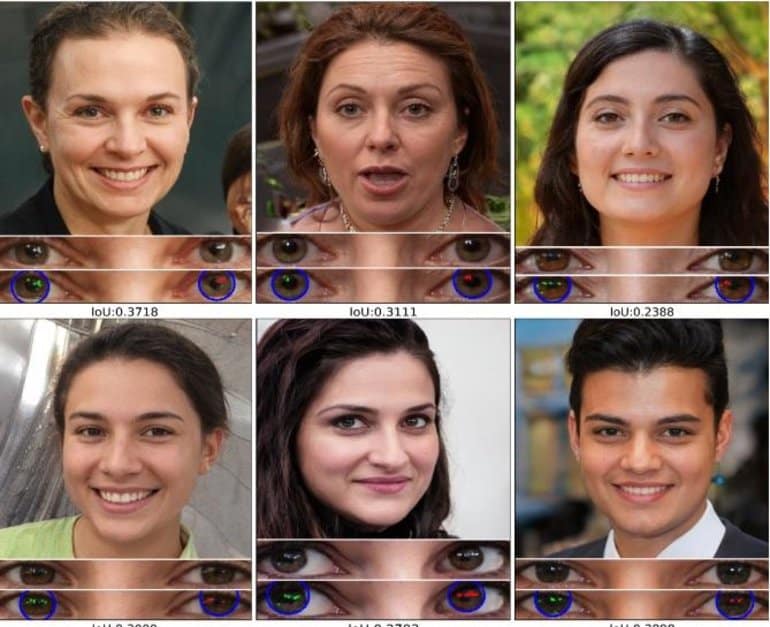

Summary: A newly developed AI tool can identify “deepfakes” of faces by examining the light reflection in the eyes of the images. The system is 94% accurate at detecting deepfakes.
Source: University ay Buffalo.
University at Buffalo computer scientists have developed a tool that automatically identifies deepfake photos by analyzing light reflections in the eyes.

The State of the Edge report is based on analysis of the potential growth of edge infrastructure from the bottom up across multiple sectors modeled by Tolaga Research. The forecast evaluates 43 use cases spanning 11 vertical industries.
The one thing these use cases have in common is a growing need to process and analyze data at the point where it is being created and consumed. Historically, IT organizations have deployed applications that process data in batch mode overnight. As organizations embrace digital business transformation initiatives, it’s becoming more apparent that data needs to be processed and analyzed at the edge in near real time.
Of course, there are multiple classes of edge computing platforms, ranging from smartphones and internet of things (IoT) gateways to complete hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) platforms that are being employed to process data at scale at the edge of a telecommunications network.