BlueOcean, a startup leveraging AI and machine learning to measure brand sentiment, has raised $15 million in capital.


The super app, synonymous with popular mobile apps like WeChat, Grab, GoTo and Paytm, has enjoyed noteworthy success in Asian countries, but is relatively absent in other markets. CNBC’s Nessa Anwar, joined by Arjun Kharpal, explains the strategies and evolution behind the world’s biggest super apps.
Like our Facebook page:
https://www.facebook.com/cnbcinternational.
Follow us on Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/cnbcinternational/
Follow us on Twitter:
Tweets by CNBCi

MIT physicists have observed signs of a rare type of superconductivity in a material called magic-angle twisted trilayer graphene. In a study appearing in Nature, the researchers report that the material exhibits superconductivity at surprisingly high magnetic fields of up to 10 Tesla, which is three times higher than what the material is predicted to endure if it were a conventional superconductor.
The results strongly imply that magic-angle trilayer graphene, which was initially discovered by the same group, is a very rare type of superconductor, known as a “spin-triplet,” that is impervious to high magnetic fields. Such exotic superconductors could vastly improve technologies such as magnetic resonance imaging, which uses superconducting wires under a magnetic field to resonate with and image biological tissue. MRI machines are currently limited to magnet fields of 1 to 3 Tesla. If they could be built with spin-triplet superconductors, MRI could operate under higher magnetic fields to produce sharper, deeper images of the human body.
The new evidence of spin-triplet superconductivity in trilayer graphene could also help scientists design stronger superconductors for practical quantum computing.

Amnesty International — part of the group that helped break the news of journalists and heads of state being targeted by NSO’s government-grade spyware, Pegasus — has released a tool to check if your phone has been affected. Alongside the tool is a great set of instructions, which should help you through the somewhat technical checking process. Using the tool involves backing up your phone to a separate computer and running a check on that backup. Read on if you’ve been side-eyeing your phone since the news broke and are looking for guidance on using Amnesty’s tool.
The process is straightforward, but it requires some patience.
As long as a white dwarf star is alive, life will likely not survive.
New research sheds light on the possibility of life emerging on planets orbiting white dwarf stars.

We probably at this point should make all animals immortal: 3.
The advance promises to unlock new insights into human biology and disease, aiding in the study of everything from the developing immune system to tissue regeneration to skin cancer.
“Studying biodiversity is not just about exploring the biology of a bunch of interesting organisms, but ultimately for a better understanding of human biology,” developmental biologist and lead study author Hiroshi Kiyonari said via email.
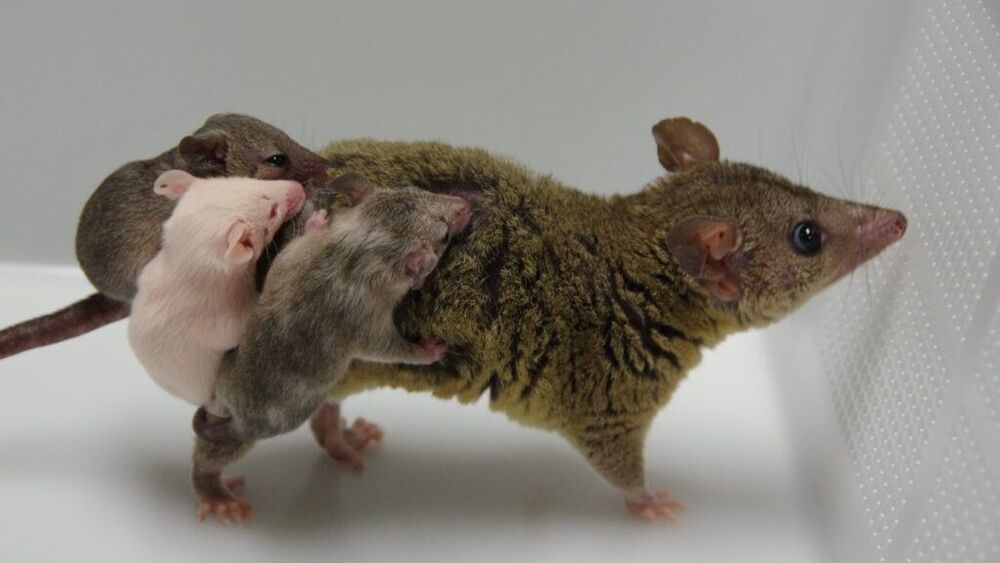
Five years ago, his team began to systematically work out the problem that had so long plagued the opossum field. The first barrier was to collect zygotes (fertilized eggs) at the right time. Ideally, that would be before they began dividing, when they are still a single cell. If you inject CRISPR at this stage, you can be sure all the resulting animals’ cells will carry whatever DNA changes you make. Doing it later can mean some cells but not others will be edited — a less ideal outcome known as mosaicism. Another benefit of collecting fertilized eggs as early as possible is that the shell coat hasn’t had time to thicken.
Part of a portable nuclear power plant arrives at Camp Century in 1960. Bettmann Archive/Getty ImagesIn a tunnel 40 feet beneath the surface of the Greenland ice sheet, a Geiger counter screamed. It was 1964, the height of the Cold War. U.S. soldiers in the tunnel, 800 miles from the North Pole, were dismantling the Army’s first portable nuclear reactor. Commanding Officer Joseph Franklin grabbed the radiation detector, ordered his men out and did a quick survey before retreating from the reactor.
The human trial of plasma dilution started in Russia last week. The lead researcher is checking how the biomarkers of aging will change in response to 110% plasma replacement during the therapy, and the difference between the group with albumin addition and without albumin. The trial is open to both Russian citizens and people from other countries. It is a hybrid model where part of the expenditures is paid by the volunteers, and part is provided by the patron of the research. This model allowed to get the trial started in record time — less than 9 months from conception to the start date.
The research group wants to test plasmapheresis in combination with other longevity therapies next to see if plasma dilution prior to the other therapy can enhance the results.
Are you interested in longevity news? Come over to https://youtube.com/x10show for more!
Does blood hold the secret to aging? That’s kind of what an ongoing clinical trial in Russia is trying to find out. Previous experiments carried out in aged mice suggest that plasma dilution has positive effects on cognition and neuroinflammation, and now scientists want to see if the procedure can positively impact humans too.
By the way, don’t forget our conference Ending Age-Related Diseases 2021 is coming soon! Follow this link to learn more and get your ticket:
