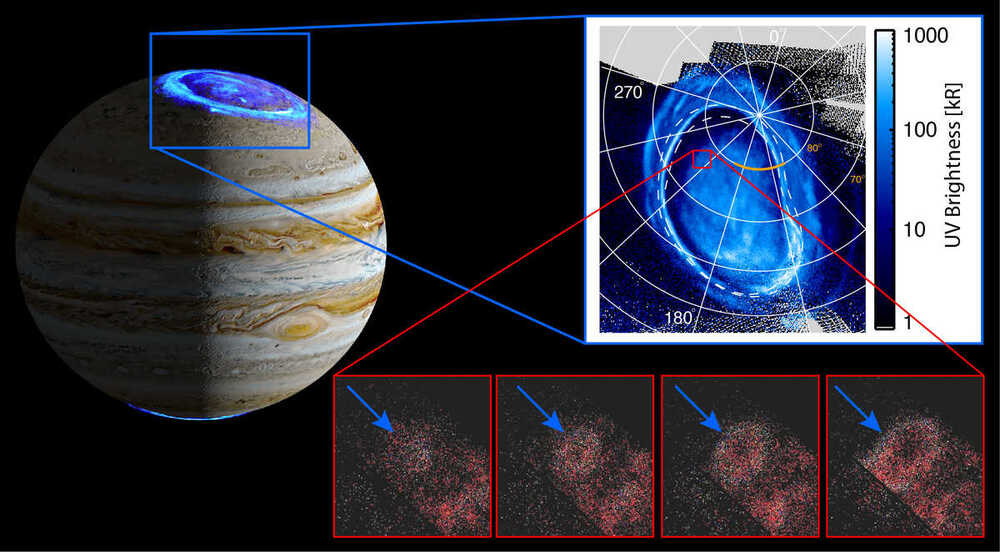
UVS images faint auroral rings that likely originate at edge of gas giant’s magnetosphere.


Researchers in Australia have discovered a gene responsible for a particularly aggressive type of hormone-sensitive breast cancer which has tragically low survival rates.
“Hopefully this will dramatically improve the poor outcomes these patients currently suffer,” said Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research epigeneticist Pilar Blancafort.
It’s hard to overstate just how different cancers can be from one another. Even under the umbrella of ‘breast cancer’ lie several types, such as hormone receptor sensitive, HER2 positive, or non-hormone sensitive breast cancer; within those groups, there are even more types that can respond to treatments differently from one another.

Sargramostim/GM-CSF is prescribed to boost white blood cells after cancer treatments or exposure to radiation. The protein stimulates the bone marrow to make more macrophages and granulocytes, specific types of white blood cells, and progenitor cells that repair blood vessels. These white blood cells circulate throughout the body and remove cells, bacteria and amyloid deposits and also repairing blood vessels.
The team carried out a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase II trial (NCT01409915) to test the safety and efficacy of Sargramostim treatment in participants with mild-moderate Alzheimer’s disease.
Study participants were either administered Sargramostim at the standard FDA dose of 250 μg/m2/day by subcutaneous injection, or saline for five days a week for three weeks. The study included 20 participants in the test and placebo group. Most participants in the study were recruited and treated at CU Anschutz with a few from the University of South Florida. The CU Anschutz researchers then conducted and studied multiple neurological, neuropsychological, cell, cytokine, Alzheimer’s pathology biomarkers and neuroimaging assessments.
The investigators found that short-term Sargramostim treatment increased innate and other immune cells, modulated cytokine measures, and was safe and well-tolerated by participants. They also found cognition memory improved by almost two points in the 30 point Mini-Mental State Exam. Brain amyloid, tangles, neurodegeneration, and measures of blood biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease, all improved toward normal.
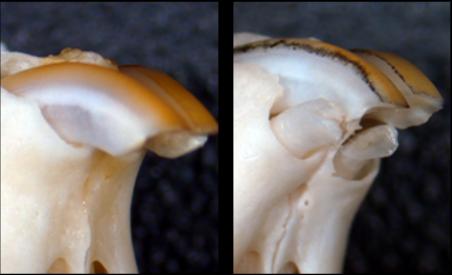
Experiments with this antibody revealed that BMP signaling is essential for determining the number of teeth in mice. Moreover, a single administration was enough to generate a whole tooth.
Japan — The tooth fairy is a welcome guest for any child who has lost a tooth. Not only will the fairy leave a small gift under the pillow, but the child can be assured of a new tooth in a few months. The same cannot be said of adults who have lost their teeth.
A new study by scientists at Kyoto University and the University of Fukui, however, may offer some hope. The team reports that an antibody for one gene — uterine sensitization associated gene-1 or USAG-1 — can stimulate tooth growth in mice suffering from tooth agenesis, a congenital condition. The paper was published in Science Advances.
Although the normal adult mouth has 32 teeth, about 1% of the population has more or fewer due to congenital conditions. Scientists have explored the genetic causes for cases having too many teeth as clues for regenerating teeth in adults.
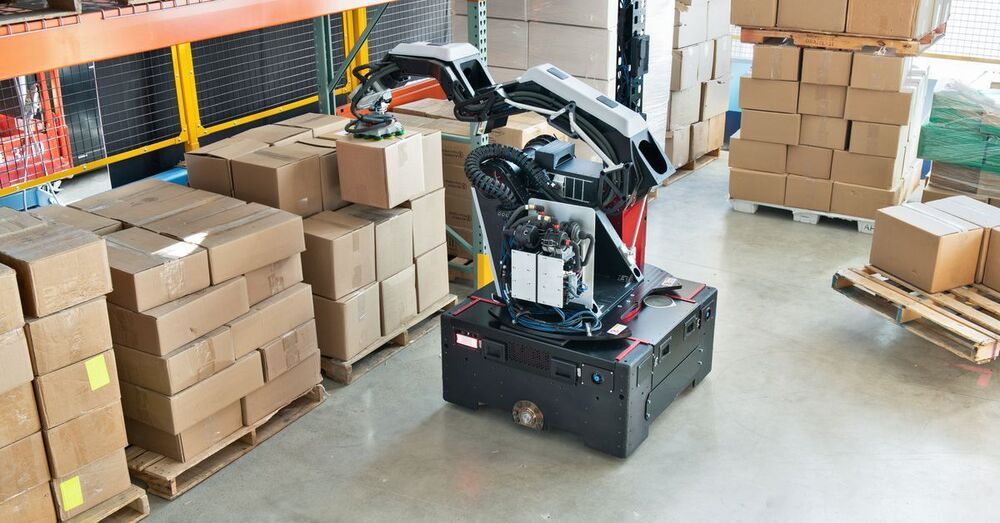

Distribution bots.
Boston Dynamics is best known for its robot dog Spot, a machine designed to work in a range of environments, from offshore oil rigs to deep underground mines. But in recent years, the company has increasingly focused attention on the logistics space, and today is unveiling a new robot with just one application in mind: moving boxes in warehouses.
The robot is called Stretch and looks relatively dull for a Boston Dynamics creation. It’s not modeled after humans or animals, and instead aims to be as practical as possible. It has a square mobile base containing a set of wheels, a “perception mast” with cameras and other sensors, and a huge robotic arm with seven degrees of freedom and a suction pad array on the end that can grab and move boxes up to 23 kilograms (50 lbs) in weight.
What connects Stretch to other Boston Dynamics machines is a focus on mobility. Usually, when automation equipment is installed in warehouses the system is bolted down in one place with a workflow modeled around it. Stretch, by comparison, is designed to slide into any existing workplace where it could be useful loading or unloading goods.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), which leads to a loss of central vision, is the most frequent cause of blindness in adults 50 years of age or older, affecting an estimated 196 million people worldwide. There is no cure, though treatment can slow the onset and preserve some vision.
Recently, however, researchers at the University of Rochester have made an important breakthrough in the quest for an AMD cure. Their first three-dimensional (3D) lab model mimics the part of the human retina affected in macular degeneration.
Their model combines stem cell-derived retinal tissue and vascular networks from human patients with bioengineered synthetic materials in a three-dimensional “matrix.” Notably, using patient-derived 3D retinal tissue allowed the researchers to investigate the underlying mechanisms involved in advanced neovascular macular degeneration, the wet form of macular degeneration, which is the more debilitating and blinding form of the disease.


The story of particle mass starts right after the big bang. During the very first moments of the universe, almost all particles were massless, traveling at the speed of light in a very hot “primordial soup.” At some point during this period, the Higgs field turned on, permeating the universe and giving mass to the elementary particles.
The Higgs field changed the environment when it was turned on, altering the way that particles behave. Some of the most common metaphors compare the Higgs field to a vat of molasses or thick syrup, which slows some particles as they travel through.
Others have envisioned the Higgs field as a crowd at a party or a horde of paparazzi. As famous scientists or A-list celebrities pass through, people surround them, slowing them down, but less-known faces travel through the crowds unnoticed. In these cases, popularity is synonymous with mass—the more popular you are, the more you will interact with the crowd, and the more “massive” you will be.

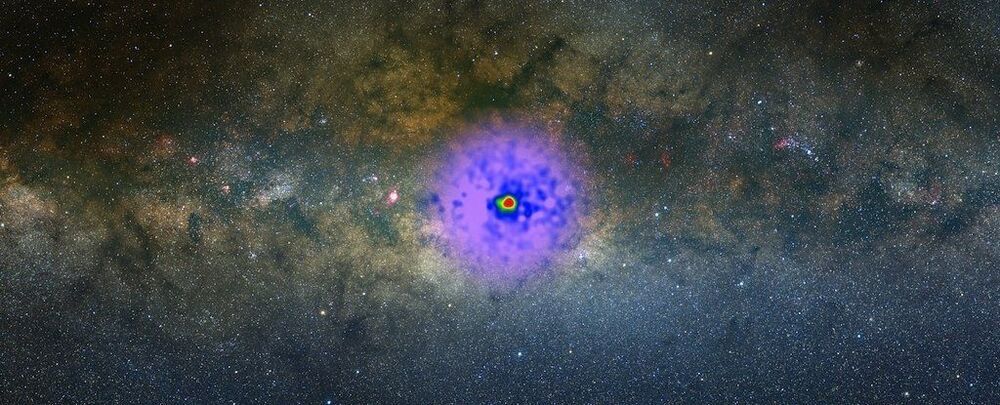
The center of the Milky Way is mysteriously glowing.
Sure, there’s a whole bunch of stars there, along with a black hole 4 million times the mass of the Sun — but subtract the light from all that, and we’re still left with this mysterious excess gamma radiation that suffuses the region.
It’s called the Galactic Center GeV Excess (GCE), and it’s puzzled scientists since its discovery by physicists Lisa Goodenough and Dan Hooper in 2009. In data from NASA’s Fermi telescope, they found excess gamma radiation — some of the most energetic light in the Universe — and we haven’t been able to directly detect whatever is causing it.