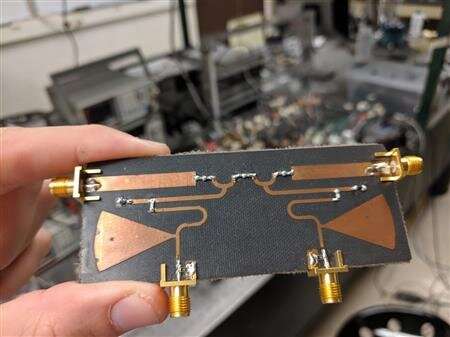
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have replicated one of the most well-known electromagnetic effects in physics, the Hall Effect, using radio waves (photons) instead of electric current (electrons). Their technique could be used to create advanced communication systems that boost signal transmission in one direction while simultaneously absorbing signals going in the opposite direction.
The Hall Effect, discovered in 1879 by Edwin Hall, occurs because of the interaction between charged particles and electromagnetic fields. In an electric field, negatively charged particles (electrons) experience a force opposite to the direction of the field. In a magnetic field, moving electrons experience a force in the direction perpendicular to both their motion and the magnetic field. These two forces combine in the Hall Effect, where perpendicular electric and magnetic fields combine to generate an electric current. Light isn’t charged, so regular electric and magnetic fields can’t be used to generate an analogous “current of light.” However, in a recent paper published in Physical Review Letters, researchers have done exactly this with the help of what they call “synthetic electric and magnetic fields.”
Principal investigator Gaurav Bahl’s research group has been working on several methods to improve radio and optical data transmission as well as fiber optic communication. Earlier this year, the group exploited an interaction between light and sound waves to suppress the scattering of light from material defects and published its results in Optica. In 2018, team member Christopher Peterson was the lead author in a Science Advances paper which explained a technology that promises to halve the bandwidth needed for communications by allowing an antenna to send and receive signals on the same frequency simultaneously through a process called nonreciprocal coupling.









